Browse By Unit
6.8 Confidence Intervals for the Difference of Two Proportions
5 min read•june 18, 2024
Josh Argo
Jed Quiaoit
Josh Argo
Jed Quiaoit
Two-Sample Z-Intervals
Have you ever seen two athletes and wondered how much better one was than the other? Maybe a basketball player who is really good at three pointers and another who seems to be just as good. How can you tell if one is actually better than the other? 🏀
One way to look at that is to determine what the difference in their shot percentage is by using a confidence interval. A confidence interval will give us a range of numbers that the difference in their percentages will be within.
The appropriate confidence interval procedure for a two-sample comparison of proportions for one categorical variable is a two-sample z-interval for a difference between population proportions.
In other words, a two-sample z-interval can be used to compare the proportions of a categorical variable between two independent populations. The procedure involves constructing a confidence interval for the difference between the two population proportions using the sample proportions, sample sizes, and standard errors.
To construct a two-sample z-interval, the following steps should be taken:
- Calculate the sample proportions for each population: p̂1 and p̂2
- Calculate the standard error for the difference between the two sample proportions: SE = √(p̂1(1-p̂1)/n1 + p̂2(1-p̂2)/n2) -- a clearer version of the formula is available in the image all the way down
- Calculate the z-score for the desired confidence level: zα/2
- Calculate the lower and upper limits of the confidence interval: p̂1 - p̂2 ± zα/2 * SE The resulting confidence interval will provide an estimate of the true difference between the population proportions, with a certain level of confidence (determined by the chosen confidence level). If the null hypothesis of no difference between the population proportions is true, the interval should contain 0. If the interval does not contain 0, then the null hypothesis can be rejected and we can conclude that there is a difference between the population proportions. We'll work or interpretations more in a future section, don't worry! 😉
Necessary Conditions
As with any forms of inference, we have some necessary conditions to check. These are essential anytime we are using a sample to make an inference about a population.
(1) Random
Probably the most important condition is that we need to be sure that both of our samples come from random samples. If we don't take a random sample from our population, then our findings suffer from sampling bias and we are stuck and we can't generalize our findings to our population. 😞
(2) Independence
To check that our sample is independent, we need to make sure that both of our populations are at least 10 times that of our samples. Also, if we are dealing with a randomized experiment, the random assignment of treatments classifies our samples as independently selected. 🔟
(3) Normal
When dealing with proportions, we always check our normal condition by using the Large Counts Condition, which states that our expected successes and failures is at least 10. Since we have two samples in this type of test, we have to check this condition for both samples. In other words, 🔔
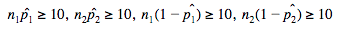
This verifies that our confidence interval is based off of a normal sampling distribution.
How Do I Calculate?
As I am sure you remember from Unit 6.2, a confidence interval is based on two aspects: a point estimate and a margin of error. A confidence interval for the difference of two population proportions is no different. 😲
(1) Point Estimate
In the case of a confidence interval for two proportions, the point estimate is the difference in our two sample proportions. We can find this by simply subtracting the two sample proportions, or p-hats.
(2) Margin of Error
As before, our margin of error is the "buffer zone" that we add and subtract to our point estimate to be sure that our interval encompasses our true population proportion difference. This is based off of two things: our critical value (z-score) and our standard error.
Formula
Our overall formula as found on the AP Statistics Course Exam Description looks like this:
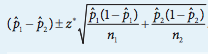
image courtesy of: apcentral.collegeboard.org
Using a Calculator
A much more efficient way of calculating a confidence interval for the difference of two population proportions is to use some form of technology such as a graphing calculator. On most common calculators, you will select "2 Prop Z Interval" from the Stats/Tests menu. 😌
Example
The-age old argument of Michael Jordan vs. Lebron James has risen again. In an effort to prove your point, you take their two career shots made percentages to see if they are REALLY different. To test this claim, you decide to construct a confidence interval for the difference in their proportion of shots. We take a sample of MJ shots and Lebron's shots from their first season in NBA. According to basketball-reference.com, MJ attempted 1623 field goals his first season, making 836 of them. Lebron attempted 1493 field goals, making 622 of his shots. Construct and interpret a 95% confidence interval to determine their difference in proportions of shots made. ☄️
Conditions
- Random: Since the problem looked at their first season, we will assume they were "randomly chosen." Sometimes, problems don't specify that it was randomly selected so we have to assume they were and proceed.
- Independent: Since it is reasonable to believe that MJ took at least 16,230 shots in his career and Lebron has taken at least 14,930 shots, we will say they are independent samples.
- Normal: Both MJ and Lebron had at least 10 makes and misses from their samples, so we can use a normal approximation for the sampling distribution of the difference in their proportion of shots made.
Do Calculations
Using a calculator for our calculations, we entered our data into "2 Prop Z Interval"
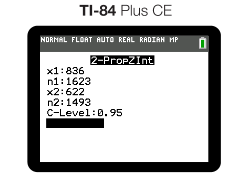
Which gives us the following interval:
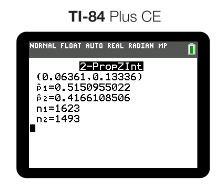
To find out more about how to interpret this interval, click ahead to Unit 6.9...
🎥 Watch: AP Stats - Inference: Confidence Intervals for Proportions
<< Hide Menu
6.8 Confidence Intervals for the Difference of Two Proportions
5 min read•june 18, 2024
Josh Argo
Jed Quiaoit
Josh Argo
Jed Quiaoit
Two-Sample Z-Intervals
Have you ever seen two athletes and wondered how much better one was than the other? Maybe a basketball player who is really good at three pointers and another who seems to be just as good. How can you tell if one is actually better than the other? 🏀
One way to look at that is to determine what the difference in their shot percentage is by using a confidence interval. A confidence interval will give us a range of numbers that the difference in their percentages will be within.
The appropriate confidence interval procedure for a two-sample comparison of proportions for one categorical variable is a two-sample z-interval for a difference between population proportions.
In other words, a two-sample z-interval can be used to compare the proportions of a categorical variable between two independent populations. The procedure involves constructing a confidence interval for the difference between the two population proportions using the sample proportions, sample sizes, and standard errors.
To construct a two-sample z-interval, the following steps should be taken:
- Calculate the sample proportions for each population: p̂1 and p̂2
- Calculate the standard error for the difference between the two sample proportions: SE = √(p̂1(1-p̂1)/n1 + p̂2(1-p̂2)/n2) -- a clearer version of the formula is available in the image all the way down
- Calculate the z-score for the desired confidence level: zα/2
- Calculate the lower and upper limits of the confidence interval: p̂1 - p̂2 ± zα/2 * SE The resulting confidence interval will provide an estimate of the true difference between the population proportions, with a certain level of confidence (determined by the chosen confidence level). If the null hypothesis of no difference between the population proportions is true, the interval should contain 0. If the interval does not contain 0, then the null hypothesis can be rejected and we can conclude that there is a difference between the population proportions. We'll work or interpretations more in a future section, don't worry! 😉
Necessary Conditions
As with any forms of inference, we have some necessary conditions to check. These are essential anytime we are using a sample to make an inference about a population.
(1) Random
Probably the most important condition is that we need to be sure that both of our samples come from random samples. If we don't take a random sample from our population, then our findings suffer from sampling bias and we are stuck and we can't generalize our findings to our population. 😞
(2) Independence
To check that our sample is independent, we need to make sure that both of our populations are at least 10 times that of our samples. Also, if we are dealing with a randomized experiment, the random assignment of treatments classifies our samples as independently selected. 🔟
(3) Normal
When dealing with proportions, we always check our normal condition by using the Large Counts Condition, which states that our expected successes and failures is at least 10. Since we have two samples in this type of test, we have to check this condition for both samples. In other words, 🔔
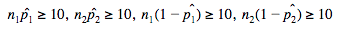
This verifies that our confidence interval is based off of a normal sampling distribution.
How Do I Calculate?
As I am sure you remember from Unit 6.2, a confidence interval is based on two aspects: a point estimate and a margin of error. A confidence interval for the difference of two population proportions is no different. 😲
(1) Point Estimate
In the case of a confidence interval for two proportions, the point estimate is the difference in our two sample proportions. We can find this by simply subtracting the two sample proportions, or p-hats.
(2) Margin of Error
As before, our margin of error is the "buffer zone" that we add and subtract to our point estimate to be sure that our interval encompasses our true population proportion difference. This is based off of two things: our critical value (z-score) and our standard error.
Formula
Our overall formula as found on the AP Statistics Course Exam Description looks like this:
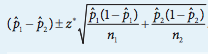
image courtesy of: apcentral.collegeboard.org
Using a Calculator
A much more efficient way of calculating a confidence interval for the difference of two population proportions is to use some form of technology such as a graphing calculator. On most common calculators, you will select "2 Prop Z Interval" from the Stats/Tests menu. 😌
Example
The-age old argument of Michael Jordan vs. Lebron James has risen again. In an effort to prove your point, you take their two career shots made percentages to see if they are REALLY different. To test this claim, you decide to construct a confidence interval for the difference in their proportion of shots. We take a sample of MJ shots and Lebron's shots from their first season in NBA. According to basketball-reference.com, MJ attempted 1623 field goals his first season, making 836 of them. Lebron attempted 1493 field goals, making 622 of his shots. Construct and interpret a 95% confidence interval to determine their difference in proportions of shots made. ☄️
Conditions
- Random: Since the problem looked at their first season, we will assume they were "randomly chosen." Sometimes, problems don't specify that it was randomly selected so we have to assume they were and proceed.
- Independent: Since it is reasonable to believe that MJ took at least 16,230 shots in his career and Lebron has taken at least 14,930 shots, we will say they are independent samples.
- Normal: Both MJ and Lebron had at least 10 makes and misses from their samples, so we can use a normal approximation for the sampling distribution of the difference in their proportion of shots made.
Do Calculations
Using a calculator for our calculations, we entered our data into "2 Prop Z Interval"

Which gives us the following interval:

To find out more about how to interpret this interval, click ahead to Unit 6.9...
🎥 Watch: AP Stats - Inference: Confidence Intervals for Proportions

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.