Browse By Unit
7.6 Psychoanalytic Theories of Personality
5 min read•june 18, 2024
Dalia Savy
John Mohl
Haseung Jun
Mary Valdez
Dalia Savy
John Mohl
Haseung Jun
Mary Valdez
Psychoanalytic Theories
Psychoanalytic theories look at the influence the unconscious has on personality. They are completely based on Freud's theory of personality.
Psychoanalysis used free association to explore an individual's unconscious 🧠 This is where the person relaxes and says whatever comes to their mind, no matter how crazy or unreasonable it is. Freud thought that eventually, something the person would say out loud would trigger thoughts in the unconscious ⛓️
The Unconscious
Freud believed that much of people's behavior is controlled by a region of the brain he called the unconscious. The unconscious stores all of the unacceptable thoughts and desires, which are sometimes repressed.
The preconscious is where our other thoughts live, and they can easily be accessed and brought to the conscious mind.
The conscious has all of the thoughts that we are aware of and express.
Freud also split personality based on three different parts:
- 🤫Id—The id is the storage of unconscious thoughts and these thoughts are all directed toward fulfilling sexual and aggressive drives. The id operates on the pleasure principle that wants automatic gratification. - 💡Built by our sexual and aggressive needs
- ⚖️Ego—The ego is between the id and the superego and it operates on the reality principle. It tries to satisfy what the id wants, but without the immediate gratification portion. Usually, because of the ego, needs are fulfilled in the long-run. - 💡Think of the ego as the decision maker and the balance between the id and superego.
- 💯Superego—The superego is basically our conscience. It tries to make us conform to and thrive in society. If the id pushed us to do something bad, the superego would, in turn, make us feel guilty because the behavior wasn't morally correct. - 💡Built by our parents and society.
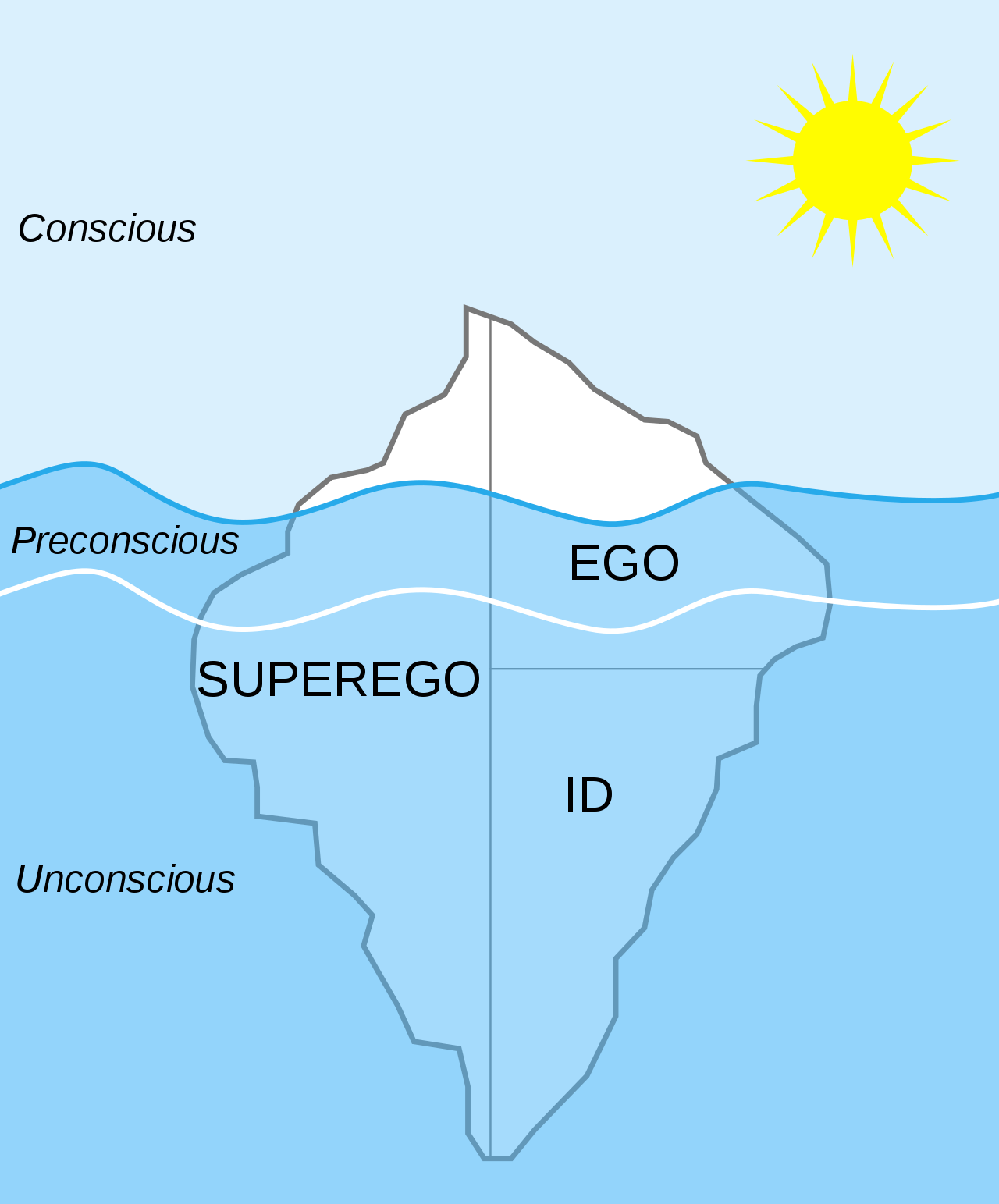
Image Courtesy of Simply Psychology.
Psychosexual Stages
Freud also believed that one’s personality was essentially set in early childhood and proposed that as we grow, we move from one psychosexual stage to another. These are childhood stages of developments that he created. Remember, Freud didn't have much research to back his theories up; he only really did case studies, which usually cannot be generalized to the whole population.
These childhood stages of development were all about how the id focused on specific pleasurable zones.
These include:
- Oral—pleasure focused on the mouth (sucking, biting, chewing) - Oral fixation—where the oral stage goes beyond the age of 1. Some examples are smoking, nail-biting, and gum-chewing.
- Anal—pleasure focused on the bowel (potty training) 🚽- Anal Retentive—similar to oral fixation. Someone that is anal retentive focuses on being neat and organized. Extreme attention to detail.- Anal Expulsive—opposite of anal retentive. Person is usually disorganized, careless, and has some sort of artistic ability.
- Phallic—pleasure focused on the genitals - Includes the oedipus complex, which is where young boys feel attracted to their mother and feel jealousy toward their father. There is also the electra complex, where young girls feel attracted to their father and jealousy toward their mother.
- Latency—no sexual feelings
- Genital—relationships and mature sexual experiences
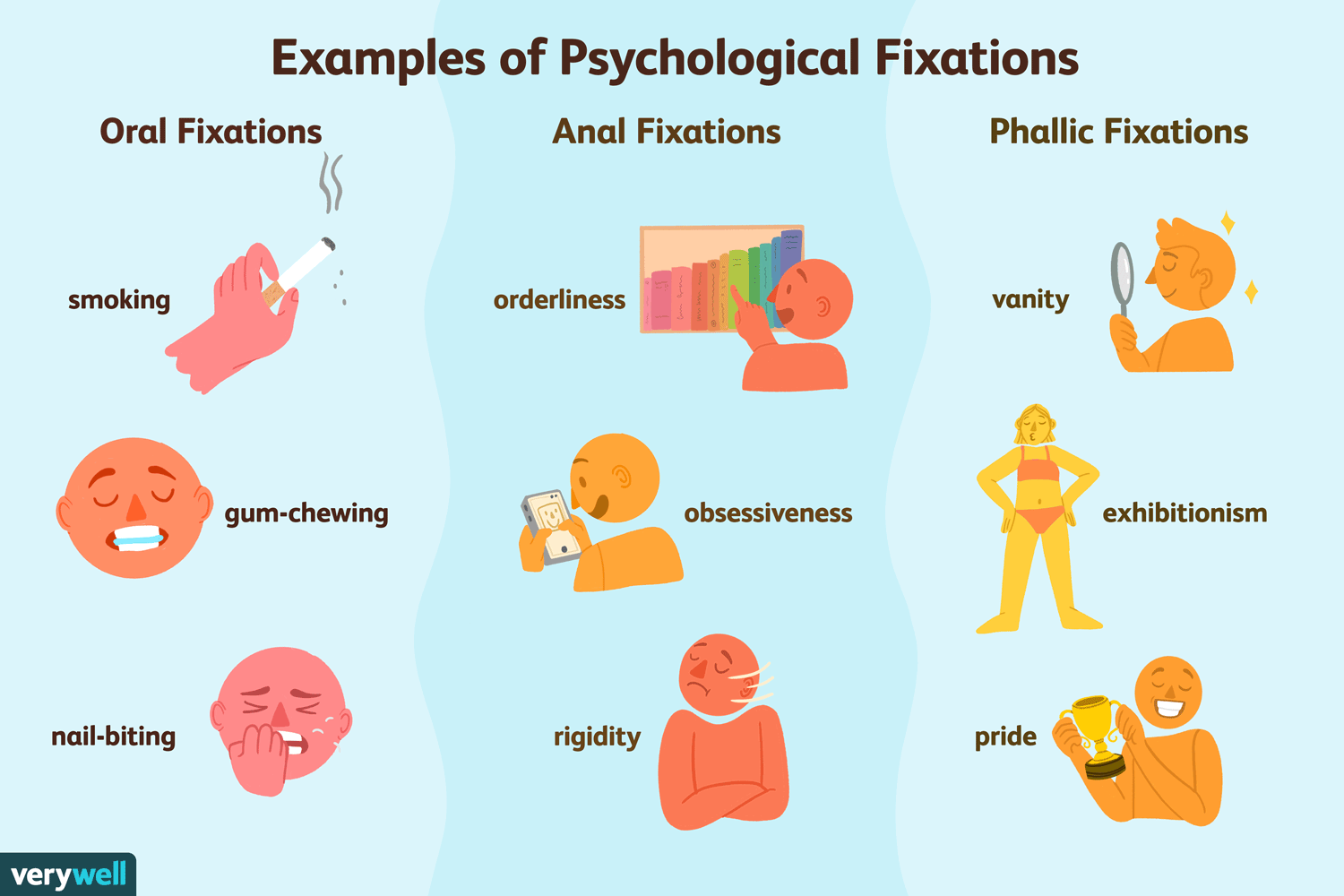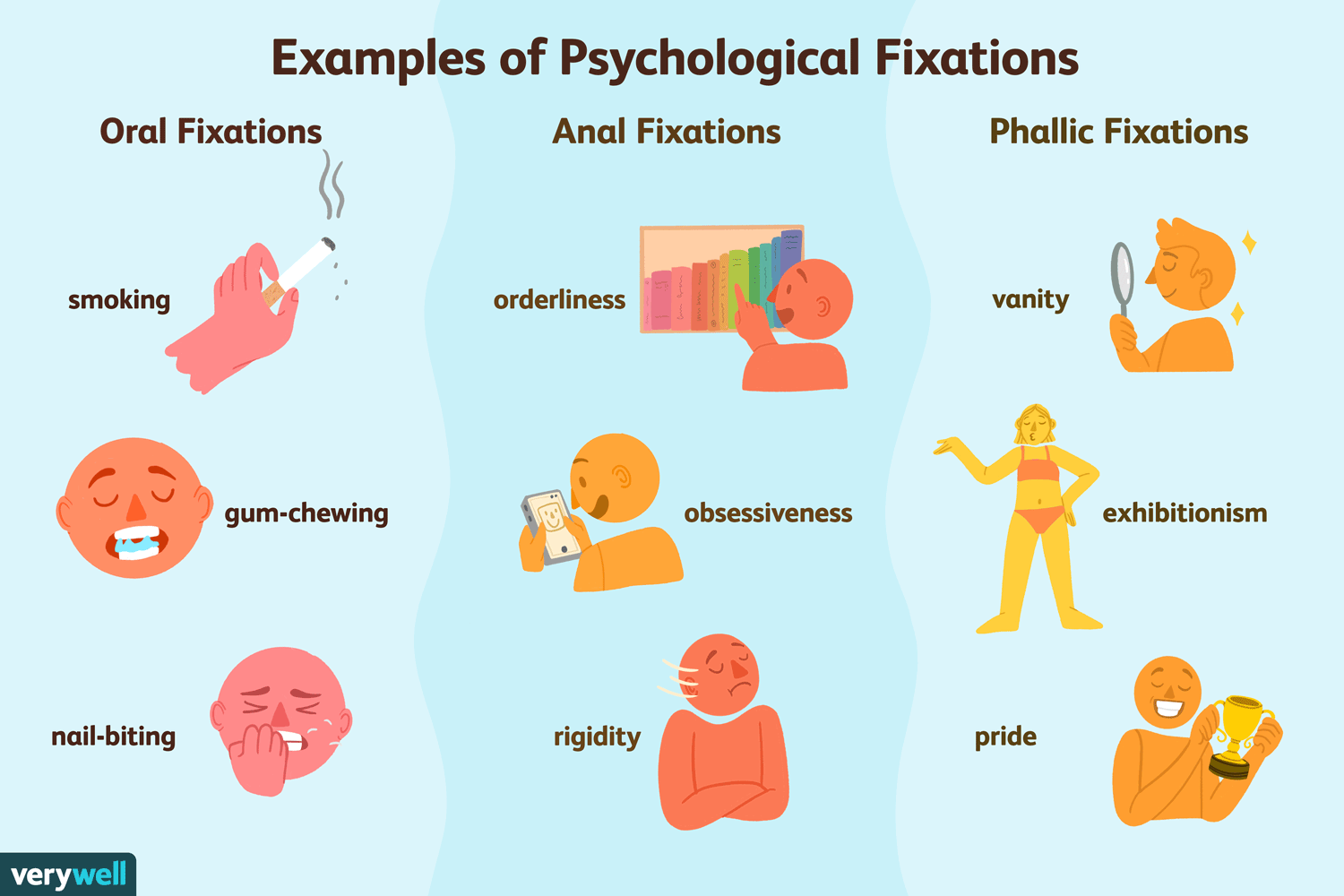
Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
After feeling threatened by the mother or father because of the oedipus complex/electra complex, usually identification occurs. This is where the child wants to be like that mother or father figure and adapt their traits. It only happens with the opposing sex parent and this is how, according to Freud, children coped with the feelings they felt during the phallic stage.
The parent becomes a role model.
Defense Mechanisms
Whenever the ego feels threatened by an action, it enlists a defense mechanism to rationalize behavior. There are several types you should know:
- 📌Repression—Gets rid of the cause of anxiety
- 👶Regression—Acting like a younger age when anxiety was not experienced. - An example is if a child sucked their thumb on the first day of school.
- 😡Reaction Formation—Expressing the exact opposite emotion of what one feels.- An example would be being angry but acting really kind in front of your friends.
- 🤦Projection—Taking how one feels and placing it on someone else - An example would be cheating on an exam and accusing your innocent classmate of cheating.
- 🍺Rationalization—Making excuses for one's situation or cause of anxiety - An example is that someone who drinks might put their drinking addiction on their friends saying they are just "socializing."
- ↔️Displacement—Changing the target of one's aggression- An example is if a child was mad at their parent, they might kick their dog 🐶
- Sublimation—Rechanneling emotions into a socially acceptable activity.- An example would be an aggressive person turning that aggression into passion and become a surgeon.
- ❌Denial—Refusing to believe an idea that causes anxiety - An example how smokers may refuse to admit that smoking is bad for their health.
- 🧠Intellectualization—Obtaining knowledge over something as a means of having a sense of control.- An example is if a person suffers a tragedy, they would try and seek counseling and identify with others going through the same thing.
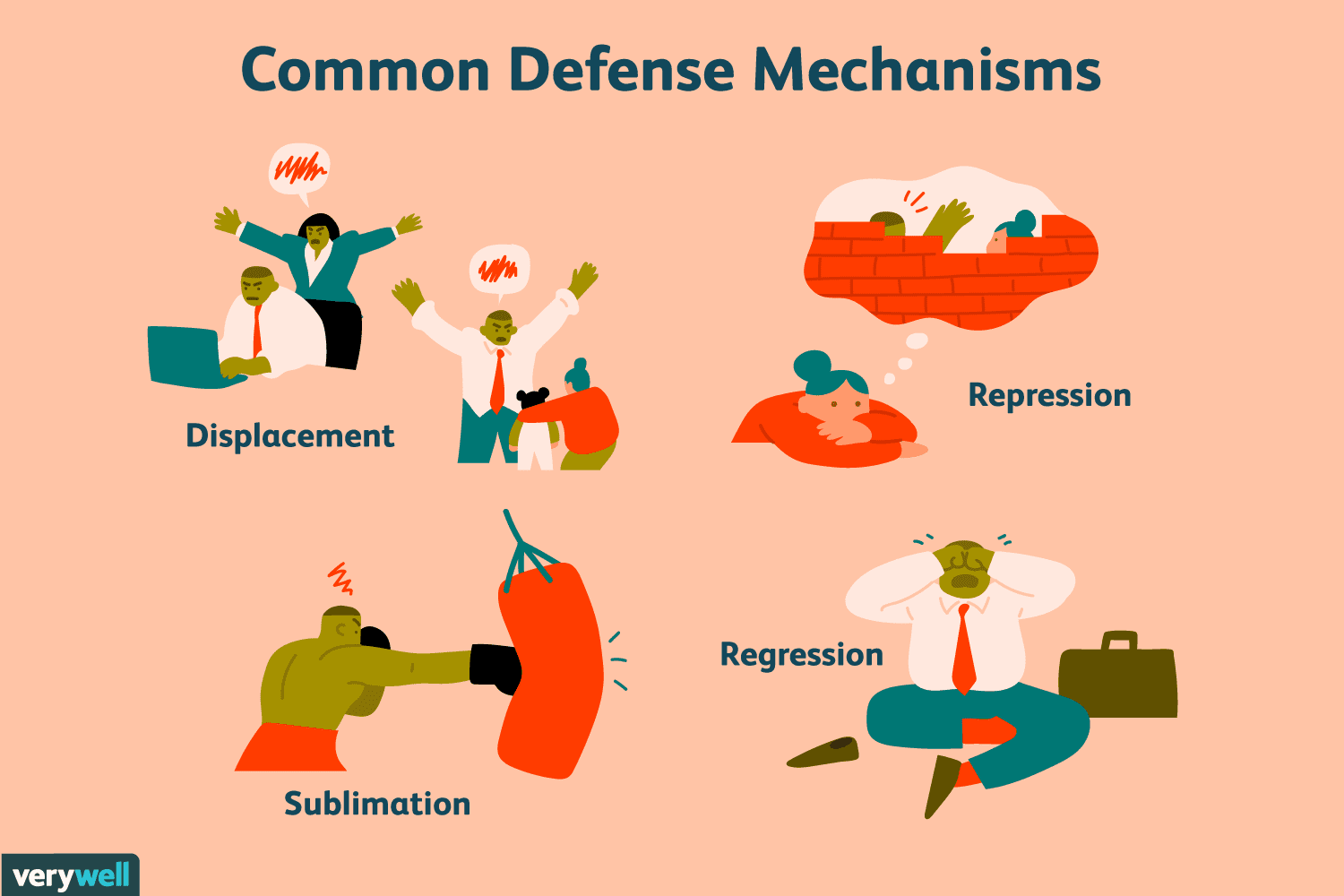
Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
Criticisms of Freud
- His findings are not really scientific; there is no empirical evidence. 🧪
- He overestimates the importance of early childhood and of sex. Psychologists today believe that we develop over a longer period of time, past our childhood.
- Little predictive power!
- Some psychologists, like Karen Horney and Nancy Chodorow, felt that Freud’s theories seemed chauvinistic.
- Today, psychologists agree with some of the defense mechanisms.
Impacts of Freud
Though it has its shortcomings, the Freudian theory has made tremendous impacts. Many people know that our unconscious thoughts shape our behavior. It has also made an impact on art (!!). Salvador Dali's paintings dept the Freudian unconscious, while Woody Allen's films feature a lot of characters going through psychoanalysis.
Psychodynamic Theory
Neo-Freudian psychologists were followers of Freud who took his ideas about the unconscious and expanded on them in a way that did not please Freud. They accepted the id, ego, and superego, the defense mechanisms, and the importance of the unconscious. Neo-Freudian psychologists emphasized social interactions more than sex.
Carl Jung
Jung agreed that the unconscious plays a large role in our development, but he thought it was more than just repressed thoughts. He proposed it consists of two different parts:
- Personal Unconscious—consists of painful memories and thoughts a person doesn't want to confront.
- Collective Unconscious—passed down through a species, inherited universal concepts that we all share as humans. These concepts are called archetypes.
Alfred Adler
He focused on the conscious role of the ego more than the unconscious. He believed that motivation comes from fear of failure, the inferiority complex, and the desire to achieve. He also thought about the superiority complex where people mask their fears of being inferior by acting superior.
He thought that we wanted to prove ourselves 🚀
🎥 Watch: AP Psychology—Personality Theories
🏆 Trivia—Personality, Motivation, and Emotion
<< Hide Menu
7.6 Psychoanalytic Theories of Personality
5 min read•june 18, 2024
Dalia Savy
John Mohl
Haseung Jun
Mary Valdez
Dalia Savy
John Mohl
Haseung Jun
Mary Valdez
Psychoanalytic Theories
Psychoanalytic theories look at the influence the unconscious has on personality. They are completely based on Freud's theory of personality.
Psychoanalysis used free association to explore an individual's unconscious 🧠 This is where the person relaxes and says whatever comes to their mind, no matter how crazy or unreasonable it is. Freud thought that eventually, something the person would say out loud would trigger thoughts in the unconscious ⛓️
The Unconscious
Freud believed that much of people's behavior is controlled by a region of the brain he called the unconscious. The unconscious stores all of the unacceptable thoughts and desires, which are sometimes repressed.
The preconscious is where our other thoughts live, and they can easily be accessed and brought to the conscious mind.
The conscious has all of the thoughts that we are aware of and express.
Freud also split personality based on three different parts:
- 🤫Id—The id is the storage of unconscious thoughts and these thoughts are all directed toward fulfilling sexual and aggressive drives. The id operates on the pleasure principle that wants automatic gratification. - 💡Built by our sexual and aggressive needs
- ⚖️Ego—The ego is between the id and the superego and it operates on the reality principle. It tries to satisfy what the id wants, but without the immediate gratification portion. Usually, because of the ego, needs are fulfilled in the long-run. - 💡Think of the ego as the decision maker and the balance between the id and superego.
- 💯Superego—The superego is basically our conscience. It tries to make us conform to and thrive in society. If the id pushed us to do something bad, the superego would, in turn, make us feel guilty because the behavior wasn't morally correct. - 💡Built by our parents and society.

Image Courtesy of Simply Psychology.
Psychosexual Stages
Freud also believed that one’s personality was essentially set in early childhood and proposed that as we grow, we move from one psychosexual stage to another. These are childhood stages of developments that he created. Remember, Freud didn't have much research to back his theories up; he only really did case studies, which usually cannot be generalized to the whole population.
These childhood stages of development were all about how the id focused on specific pleasurable zones.
These include:
- Oral—pleasure focused on the mouth (sucking, biting, chewing) - Oral fixation—where the oral stage goes beyond the age of 1. Some examples are smoking, nail-biting, and gum-chewing.
- Anal—pleasure focused on the bowel (potty training) 🚽- Anal Retentive—similar to oral fixation. Someone that is anal retentive focuses on being neat and organized. Extreme attention to detail.- Anal Expulsive—opposite of anal retentive. Person is usually disorganized, careless, and has some sort of artistic ability.
- Phallic—pleasure focused on the genitals - Includes the oedipus complex, which is where young boys feel attracted to their mother and feel jealousy toward their father. There is also the electra complex, where young girls feel attracted to their father and jealousy toward their mother.
- Latency—no sexual feelings
- Genital—relationships and mature sexual experiences

Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
After feeling threatened by the mother or father because of the oedipus complex/electra complex, usually identification occurs. This is where the child wants to be like that mother or father figure and adapt their traits. It only happens with the opposing sex parent and this is how, according to Freud, children coped with the feelings they felt during the phallic stage.
The parent becomes a role model.
Defense Mechanisms
Whenever the ego feels threatened by an action, it enlists a defense mechanism to rationalize behavior. There are several types you should know:
- 📌Repression—Gets rid of the cause of anxiety
- 👶Regression—Acting like a younger age when anxiety was not experienced. - An example is if a child sucked their thumb on the first day of school.
- 😡Reaction Formation—Expressing the exact opposite emotion of what one feels.- An example would be being angry but acting really kind in front of your friends.
- 🤦Projection—Taking how one feels and placing it on someone else - An example would be cheating on an exam and accusing your innocent classmate of cheating.
- 🍺Rationalization—Making excuses for one's situation or cause of anxiety - An example is that someone who drinks might put their drinking addiction on their friends saying they are just "socializing."
- ↔️Displacement—Changing the target of one's aggression- An example is if a child was mad at their parent, they might kick their dog 🐶
- Sublimation—Rechanneling emotions into a socially acceptable activity.- An example would be an aggressive person turning that aggression into passion and become a surgeon.
- ❌Denial—Refusing to believe an idea that causes anxiety - An example how smokers may refuse to admit that smoking is bad for their health.
- 🧠Intellectualization—Obtaining knowledge over something as a means of having a sense of control.- An example is if a person suffers a tragedy, they would try and seek counseling and identify with others going through the same thing.

Image Courtesy of Verywell Mind.
Criticisms of Freud
- His findings are not really scientific; there is no empirical evidence. 🧪
- He overestimates the importance of early childhood and of sex. Psychologists today believe that we develop over a longer period of time, past our childhood.
- Little predictive power!
- Some psychologists, like Karen Horney and Nancy Chodorow, felt that Freud’s theories seemed chauvinistic.
- Today, psychologists agree with some of the defense mechanisms.
Impacts of Freud
Though it has its shortcomings, the Freudian theory has made tremendous impacts. Many people know that our unconscious thoughts shape our behavior. It has also made an impact on art (!!). Salvador Dali's paintings dept the Freudian unconscious, while Woody Allen's films feature a lot of characters going through psychoanalysis.
Psychodynamic Theory
Neo-Freudian psychologists were followers of Freud who took his ideas about the unconscious and expanded on them in a way that did not please Freud. They accepted the id, ego, and superego, the defense mechanisms, and the importance of the unconscious. Neo-Freudian psychologists emphasized social interactions more than sex.
Carl Jung
Jung agreed that the unconscious plays a large role in our development, but he thought it was more than just repressed thoughts. He proposed it consists of two different parts:
- Personal Unconscious—consists of painful memories and thoughts a person doesn't want to confront.
- Collective Unconscious—passed down through a species, inherited universal concepts that we all share as humans. These concepts are called archetypes.
Alfred Adler
He focused on the conscious role of the ego more than the unconscious. He believed that motivation comes from fear of failure, the inferiority complex, and the desire to achieve. He also thought about the superiority complex where people mask their fears of being inferior by acting superior.
He thought that we wanted to prove ourselves 🚀
🎥 Watch: AP Psychology—Personality Theories
🏆 Trivia—Personality, Motivation, and Emotion

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.