Browse By Unit
Daniella Garcia-Loos
Daniella Garcia-Loos
Conservation of Energy
The Law of Conservation of Energy is as follows:
If only forces internal to the system are acting on an object in a physical system, then the total change in mechanical energy is zero.
The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental principle in physics that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant over time. The law applies to all types of energy, including kinetic energy (energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy due to position or configuration), thermal energy (energy associated with temperature), chemical energy (energy stored in chemical bonds), nuclear energy (energy stored in the nuclei of atoms), and more.
The law is based on the idea that energy is a conserved quantity, meaning that it cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted. This means that if energy is added to a system, it must also be removed in order for the total energy to remain constant. For example, if a ball is dropped and gains kinetic energy as it falls, the potential energy it had due to its height above the ground is converted into kinetic energy. Similarly, if a spring is compressed and potential energy is added to it, that energy can be released as kinetic energy when the spring is allowed to expand.
The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental principle in many branches of science, including thermodynamics, mechanics, and electromagnetism. It is used to understand and predict the behavior of natural systems, such as the motion of planets and stars, the behavior of fluids and gases, and the dynamics of electrical and magnetic fields. It is also used to design and improve man-made systems, such as engines, generators, and power plants.
This essentially means that energy in a system can change its form without energy leaving the system.
The equation version of this law is:
Which states that the total mechanical energy, ME, is the sum of the potential, U, and kinetic energy, K, in a system.
When a nonconservative force acts on a system, work is done, and this work does change the total mechanical energy of the system! This work can be found in a simple equation:
When you have a conservative system (total energy is a constant), you can use the Law of Conservation of Energy to calculate unknown quantities in many scenarios like rollercoasters, ramps, pendulums, and springs.
You can use this PhET simulation to see conservation of energy in practice!
Conservative Systems
Conservative forces are forces for which the work done on an object is independent of the path taken and is determined only by the initial and final positions of the object.
- Examples of conservative forces include gravitational force, elastic force (such as the force exerted by a spring), and electrostatic force.
- Conservative forces can be described by a scalar potential energy function, such as gravitational potential energy or elastic potential energy.
Nonconservative forces are forces for which the work done on an object depends on the path taken and is not determined solely by the initial and final positions of the object.
- Examples of nonconservative forces include friction, air resistance, and viscosity.
- Nonconservative forces can not be described by a scalar potential energy function.
- The total mechanical energy of a closed system is conserved for conservative forces but not for nonconservative forces.
- Conservative forces are related to the conservation of mechanical energy, nonconservative forces are not.
- In a conservative system, the total mechanical energy is constant, regardless of the path taken by the system, in a nonconservative system, the total mechanical energy is not conserved.
Practice Questions
1.
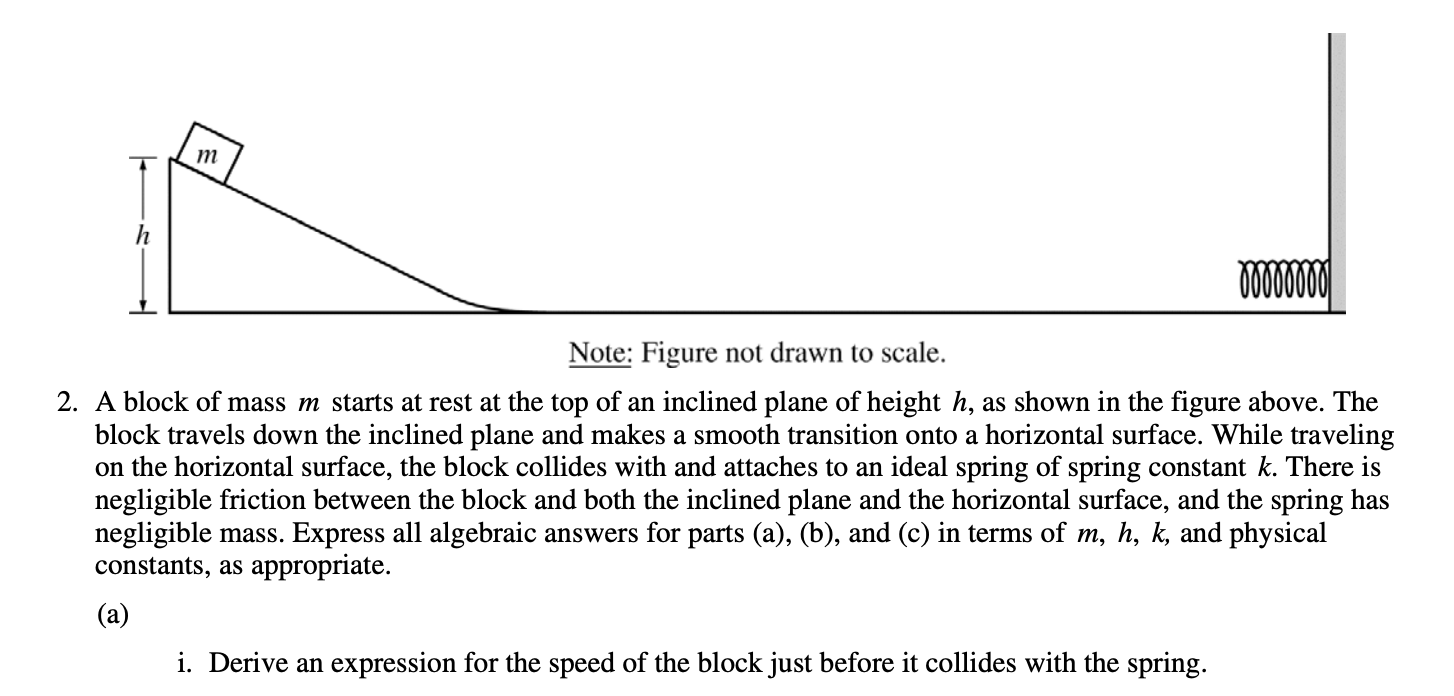
Taken from CollegeBoard
Always, always, always remember to state that you're using conservation of energy! You should begin all energy problems by stating whether or not energy is conserved as that typically earns you a point.
Then identify what is occurring at the beginning of the problem and what is occurring at the end in order to determine how energy is transferred.

2.
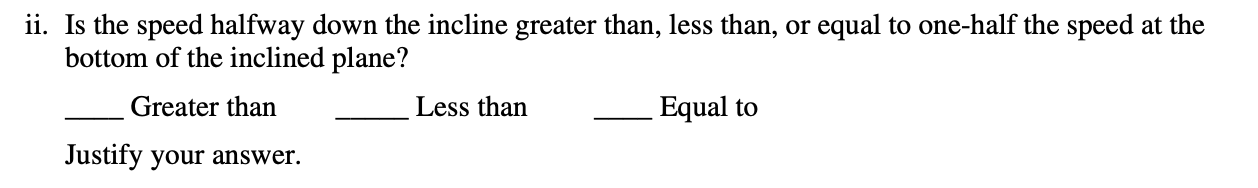
Answer:
AP loves to make students think about proportions, so whenever asked about comparing the same variable, try to find an equation you can use! Don't try to plug in anything to the equation, just look at what coefficients are different at the two moments in time you are examining.
Additionally, you should notice that they wanted you to look at the relationship you discovered in a previous part of the question.

3.
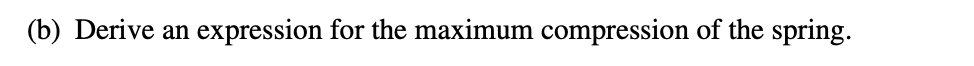
Answer:
Same process as the previous part!

4.

Answer:
If you haven't learned about differential equations in calculus that's okay! But once you do, you should notice that AP will never ask you to solve them due to the time crunch you are in unless they are incredibly simple. Additionally, take note that you did not have to use all the variables they listed in the question. Most FRQs will focus on more than one unit of physics and you will have to be aware of the intersections between things like forces and energy.

5.
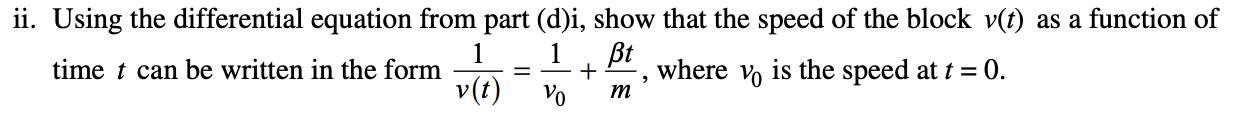
Answer:
Separating variables is always the first step in resolving a differential equation, then integration. Notice that if it is a definite integral they want you to place the bounds/ use the correct limits and if it is an indefinite integral(which is not common in the realm of physics) they will give you a freebie point for just stating +C!

<< Hide Menu
Daniella Garcia-Loos
Daniella Garcia-Loos
Conservation of Energy
The Law of Conservation of Energy is as follows:
If only forces internal to the system are acting on an object in a physical system, then the total change in mechanical energy is zero.
The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental principle in physics that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted from one form to another. This means that the total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant over time. The law applies to all types of energy, including kinetic energy (energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy due to position or configuration), thermal energy (energy associated with temperature), chemical energy (energy stored in chemical bonds), nuclear energy (energy stored in the nuclei of atoms), and more.
The law is based on the idea that energy is a conserved quantity, meaning that it cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or converted. This means that if energy is added to a system, it must also be removed in order for the total energy to remain constant. For example, if a ball is dropped and gains kinetic energy as it falls, the potential energy it had due to its height above the ground is converted into kinetic energy. Similarly, if a spring is compressed and potential energy is added to it, that energy can be released as kinetic energy when the spring is allowed to expand.
The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental principle in many branches of science, including thermodynamics, mechanics, and electromagnetism. It is used to understand and predict the behavior of natural systems, such as the motion of planets and stars, the behavior of fluids and gases, and the dynamics of electrical and magnetic fields. It is also used to design and improve man-made systems, such as engines, generators, and power plants.
This essentially means that energy in a system can change its form without energy leaving the system.
The equation version of this law is:
Which states that the total mechanical energy, ME, is the sum of the potential, U, and kinetic energy, K, in a system.
When a nonconservative force acts on a system, work is done, and this work does change the total mechanical energy of the system! This work can be found in a simple equation:
When you have a conservative system (total energy is a constant), you can use the Law of Conservation of Energy to calculate unknown quantities in many scenarios like rollercoasters, ramps, pendulums, and springs.
You can use this PhET simulation to see conservation of energy in practice!
Conservative Systems
Conservative forces are forces for which the work done on an object is independent of the path taken and is determined only by the initial and final positions of the object.
- Examples of conservative forces include gravitational force, elastic force (such as the force exerted by a spring), and electrostatic force.
- Conservative forces can be described by a scalar potential energy function, such as gravitational potential energy or elastic potential energy.
Nonconservative forces are forces for which the work done on an object depends on the path taken and is not determined solely by the initial and final positions of the object.
- Examples of nonconservative forces include friction, air resistance, and viscosity.
- Nonconservative forces can not be described by a scalar potential energy function.
- The total mechanical energy of a closed system is conserved for conservative forces but not for nonconservative forces.
- Conservative forces are related to the conservation of mechanical energy, nonconservative forces are not.
- In a conservative system, the total mechanical energy is constant, regardless of the path taken by the system, in a nonconservative system, the total mechanical energy is not conserved.
Practice Questions
1.

Taken from CollegeBoard
Always, always, always remember to state that you're using conservation of energy! You should begin all energy problems by stating whether or not energy is conserved as that typically earns you a point.
Then identify what is occurring at the beginning of the problem and what is occurring at the end in order to determine how energy is transferred.

2.
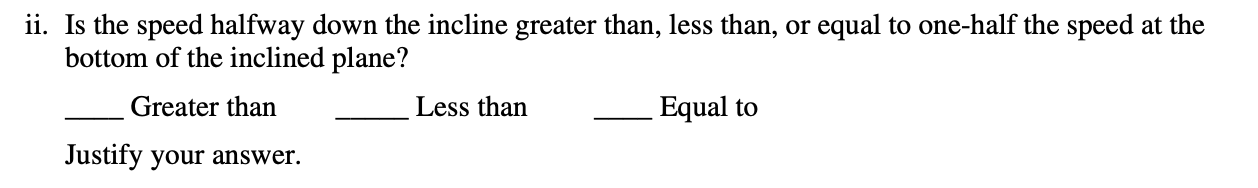
Answer:
AP loves to make students think about proportions, so whenever asked about comparing the same variable, try to find an equation you can use! Don't try to plug in anything to the equation, just look at what coefficients are different at the two moments in time you are examining.
Additionally, you should notice that they wanted you to look at the relationship you discovered in a previous part of the question.

3.
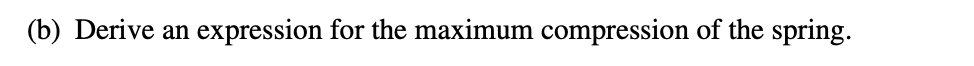
Answer:
Same process as the previous part!

4.

Answer:
If you haven't learned about differential equations in calculus that's okay! But once you do, you should notice that AP will never ask you to solve them due to the time crunch you are in unless they are incredibly simple. Additionally, take note that you did not have to use all the variables they listed in the question. Most FRQs will focus on more than one unit of physics and you will have to be aware of the intersections between things like forces and energy.

5.
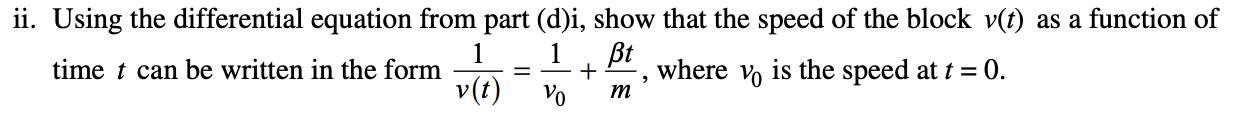
Answer:
Separating variables is always the first step in resolving a differential equation, then integration. Notice that if it is a definite integral they want you to place the bounds/ use the correct limits and if it is an indefinite integral(which is not common in the realm of physics) they will give you a freebie point for just stating +C!


© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.