Browse By Unit
3.4 Gravitational Field/Acceleration Due to Gravity on Different Planets
4 min read•june 18, 2024
Peter Apps
Kashvi Panjolia
Peter Apps
Kashvi Panjolia
Overview
A gravitational field g at the location of an object with mass m causes a gravitational force of magnitude mg to be exerted on the object in the direction of the field.
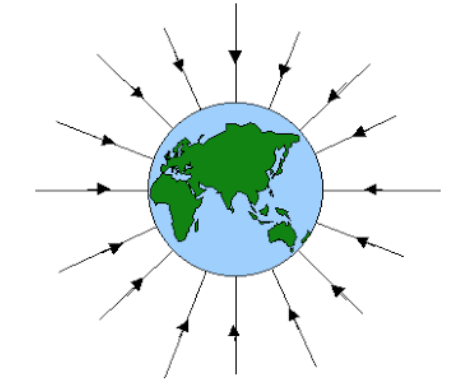
Image courtesy of mechanicaltopdc.
As pictured in the image above, the weight or gravitational force is always acting vertically downwards, towards the center of a planet. If this is the only force exerted on an object, the object is said to be in free fall. If you recall from kinematics, an object’s acceleration is equal to the acceleration due to gravity when in free fall. The variable g, or the gravitational field is subject to change based on the planet itself or the object’s location relative to the planet’s surface. On Earth, we know g as 9.8 m/s^2, but on other planets, the value is different.
Gravitational Field
A gravitational field is a region of space in which a physical body, such as a planet or a star, exerts a force on any other body within that region. The force that a body experiences in a gravitational field is caused by the presence of mass in the space around it. The strength of the gravitational field at a particular point is represented by the gravitational force per unit mass, also known as the gravitational acceleration (g). The gravitational field can be represented by a vector field, meaning that it has both magnitude and direction.
The gravitational field caused by a spherically symmetric object with mass is radial and, outside the object, varies as the inverse square of the radial distance from the center of that object. Sound familiar? The equation for a gravitational field can be derived from the equation for Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation and is used to find the gravitational field of a planet or other object based on its mass. Let's derive it using Newton's Second Law for a satellite orbiting a planet:

Image courtesy of Lumen Learning.
Based on this free-body diagram of a satellite orbiting a planet, we know that F, the force of the planet's gravity, is the only force acting in the direction of the net force of the satellite. Since the satellite is in circular motion, the velocity of the satellite is not included in the net force calculation since it is tangent to the circle. We can now use Newton's Second Law and Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation to relate the force between the satellite and the planet like this:
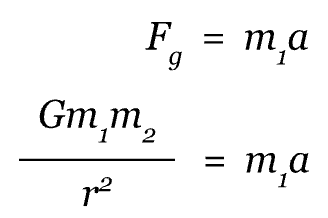
In this equation, m1 is the mass of the satellite and m2 is the mass of the planet. We use m1 on the right side of the expression because we are analyzing the forces acting on the satellite, not on the planet. From this equation, we can see that there is an m1 term on both sides of the equation so we can divide through by m1 to obtain:
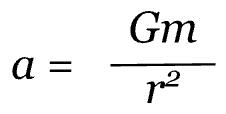
Since the acceleration is caused only by the gravitational force, we know that this is the equation for the acceleration of gravity, g.
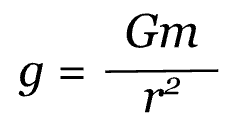
This equation can be used to determine the acceleration of gravity for any planet given its mass and radius. To recap, in this equation, g is the gravitational field in m/s/s, G is the universal gravitation constant 6.7 x 10^-11 N * m^2/kg^2, r is the radius in meters, and m is the mass in kilograms.
One more important idea we can glean from this equation is that the mass of the satellite or object in orbit doesn't matter, so the acceleration of gravity for all objects a certain distance away is the same, regardless of the mass of the object in orbit. Also, the r value in this equation represents the radius from the center of mass of the planet to the center of mass of the orbiting object, so you may have to add the distance an object is away from the planet to obtain the correct answer.


Practice Problems
1. How does the gravitational acceleration (g) on the surface of a planet change if the mass of the planet is doubled? a) It remains the same b) It is halved c) It is doubled d) It is quadrupled Answer: c) It is doubled
2. A planet has a mass of 6 x 10^24 kg and a radius of 6 x 10^6 m. Calculate the gravitational acceleration (g) on its surface.
a) 7.2 m/s^2
b) 9.8 m/s^2
c) 10.4 m/s^2
d) 18.6 m/s^2 Answer: d) 9.8 m/s^2
Explanation: g = Gm/r^2 = (6.67 x 10^-11 N*(m^2)/(kg^2))(6 x 10^24 kg) / (6 x 10^6 m)^2 = 9.8 m/s^2
3. How does the strength of the gravitational field change if the distance between two masses is doubled? a) It remains the same b) It is halved c) It is quartered d) It is doubled Answer: c) It is quartered
4. An object is located at a distance of 2 x 10^8 m from a star with a mass of 2 x 10^30 kg. Calculate the gravitational force (F) acting on the object.
a) -3.35 x 10^-6 N b) -4.92 x 10^-12 N c) -5.98 x 10^-9 N d) -6.67 x 10^-11 N Answer: d) -6.67 x 10^-11 N
Explanation: F = Gm1m2/r^2 = (6.67 x 10^-11 N*(m^2)/(kg^2))(2 x 10^30 kg)(1 kg) / (2 x 10^8 m)^2 = 6.67 x 10^-11 N
5. A planet has a mass of 6 x 10^24 kg and a radius of 6 x 10^6 m. What is the gravitational force (F) acting on an object with a mass of 50 kg located on the surface of the planet? a) 3 x 10^9 N b) 3 x 10^10 N c) 3 x 10^11 N d) 3 x 10^12 N Answer: b) 3 x 10^10 N (F = Gm1m2/r^2, where m1=mass of the planet, m2=mass of the object, r= radius of the planet, and G= gravitational constant)
🎥Watch: AP Physics 1 - Unit 3 Streams
<< Hide Menu
3.4 Gravitational Field/Acceleration Due to Gravity on Different Planets
4 min read•june 18, 2024
Peter Apps
Kashvi Panjolia
Peter Apps
Kashvi Panjolia
Overview
A gravitational field g at the location of an object with mass m causes a gravitational force of magnitude mg to be exerted on the object in the direction of the field.

Image courtesy of mechanicaltopdc.
As pictured in the image above, the weight or gravitational force is always acting vertically downwards, towards the center of a planet. If this is the only force exerted on an object, the object is said to be in free fall. If you recall from kinematics, an object’s acceleration is equal to the acceleration due to gravity when in free fall. The variable g, or the gravitational field is subject to change based on the planet itself or the object’s location relative to the planet’s surface. On Earth, we know g as 9.8 m/s^2, but on other planets, the value is different.
Gravitational Field
A gravitational field is a region of space in which a physical body, such as a planet or a star, exerts a force on any other body within that region. The force that a body experiences in a gravitational field is caused by the presence of mass in the space around it. The strength of the gravitational field at a particular point is represented by the gravitational force per unit mass, also known as the gravitational acceleration (g). The gravitational field can be represented by a vector field, meaning that it has both magnitude and direction.
The gravitational field caused by a spherically symmetric object with mass is radial and, outside the object, varies as the inverse square of the radial distance from the center of that object. Sound familiar? The equation for a gravitational field can be derived from the equation for Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation and is used to find the gravitational field of a planet or other object based on its mass. Let's derive it using Newton's Second Law for a satellite orbiting a planet:

Image courtesy of Lumen Learning.
Based on this free-body diagram of a satellite orbiting a planet, we know that F, the force of the planet's gravity, is the only force acting in the direction of the net force of the satellite. Since the satellite is in circular motion, the velocity of the satellite is not included in the net force calculation since it is tangent to the circle. We can now use Newton's Second Law and Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation to relate the force between the satellite and the planet like this:
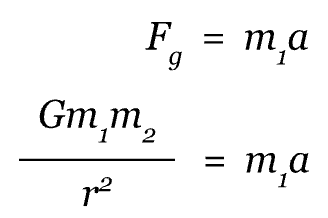
In this equation, m1 is the mass of the satellite and m2 is the mass of the planet. We use m1 on the right side of the expression because we are analyzing the forces acting on the satellite, not on the planet. From this equation, we can see that there is an m1 term on both sides of the equation so we can divide through by m1 to obtain:
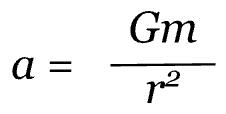
Since the acceleration is caused only by the gravitational force, we know that this is the equation for the acceleration of gravity, g.
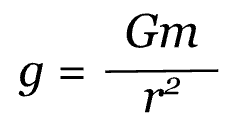
This equation can be used to determine the acceleration of gravity for any planet given its mass and radius. To recap, in this equation, g is the gravitational field in m/s/s, G is the universal gravitation constant 6.7 x 10^-11 N * m^2/kg^2, r is the radius in meters, and m is the mass in kilograms.
One more important idea we can glean from this equation is that the mass of the satellite or object in orbit doesn't matter, so the acceleration of gravity for all objects a certain distance away is the same, regardless of the mass of the object in orbit. Also, the r value in this equation represents the radius from the center of mass of the planet to the center of mass of the orbiting object, so you may have to add the distance an object is away from the planet to obtain the correct answer.


Practice Problems
1. How does the gravitational acceleration (g) on the surface of a planet change if the mass of the planet is doubled? a) It remains the same b) It is halved c) It is doubled d) It is quadrupled Answer: c) It is doubled
2. A planet has a mass of 6 x 10^24 kg and a radius of 6 x 10^6 m. Calculate the gravitational acceleration (g) on its surface.
a) 7.2 m/s^2
b) 9.8 m/s^2
c) 10.4 m/s^2
d) 18.6 m/s^2 Answer: d) 9.8 m/s^2
Explanation: g = Gm/r^2 = (6.67 x 10^-11 N*(m^2)/(kg^2))(6 x 10^24 kg) / (6 x 10^6 m)^2 = 9.8 m/s^2
3. How does the strength of the gravitational field change if the distance between two masses is doubled? a) It remains the same b) It is halved c) It is quartered d) It is doubled Answer: c) It is quartered
4. An object is located at a distance of 2 x 10^8 m from a star with a mass of 2 x 10^30 kg. Calculate the gravitational force (F) acting on the object.
a) -3.35 x 10^-6 N b) -4.92 x 10^-12 N c) -5.98 x 10^-9 N d) -6.67 x 10^-11 N Answer: d) -6.67 x 10^-11 N
Explanation: F = Gm1m2/r^2 = (6.67 x 10^-11 N*(m^2)/(kg^2))(2 x 10^30 kg)(1 kg) / (2 x 10^8 m)^2 = 6.67 x 10^-11 N
5. A planet has a mass of 6 x 10^24 kg and a radius of 6 x 10^6 m. What is the gravitational force (F) acting on an object with a mass of 50 kg located on the surface of the planet? a) 3 x 10^9 N b) 3 x 10^10 N c) 3 x 10^11 N d) 3 x 10^12 N Answer: b) 3 x 10^10 N (F = Gm1m2/r^2, where m1=mass of the planet, m2=mass of the object, r= radius of the planet, and G= gravitational constant)
🎥Watch: AP Physics 1 - Unit 3 Streams

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.