Browse By Unit
3.6 Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
6 min read•june 18, 2024
Peter Apps
Kashvi Panjolia
Peter Apps
Kashvi Panjolia
Important Equations
The acceleration is equal to the rate of change of velocity with time, and velocity is equal to the rate of change of position with time.

Equation:
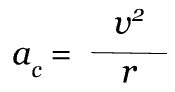
Surprisingly, in uniform circular motion, in which an object has constant speed, there is an acceleration due to a change in direction. Don’t forget, acceleration is a change in velocity, which is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction!
Centripetal Acceleration
Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration that an object experiences when it moves in a circular path. This acceleration is directed toward the center of the circle. It is also known as radial acceleration.
Imagine you are on a roller coaster and you experience the feeling of being pulled toward the center of the loop as you go through a loop-the-loop. This is an example of centripetal acceleration. The force that is pulling you toward the center of the loop is the centripetal force.
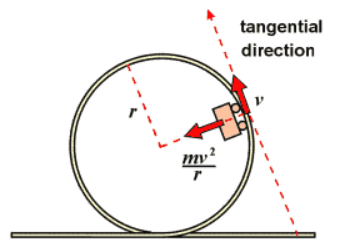
Image courtesy of Quora.
Force and acceleration are both quantities that have both magnitude and direction. The direction of the net force acting on an object is the same as the direction of its acceleration. This means that if you want to change the direction of an object's acceleration, you need to change the direction of the net force acting on it. For example, if you want to change the direction of a car's acceleration so it is accelerating and turning right, you need to give it a rightward net force.
The center of mass (COM) of a system is a point that represents the average position of all the mass in the system. Conceptually, it is the point where the entire mass of the system can be considered to be concentrated, which makes it the point at which the system would balance if it were suspended by a single point. The position of the center of mass depends on the distribution of mass within the system.
Consider a seesaw in a playground. The center of mass of a seesaw is located at the point where the board of the seesaw balances. This point is also known as the pivot point. If you place a heavier person on one side of the seesaw, the center of mass will shift closer to that side, and the seesaw will tilt in that direction.
Image courtesy of Albert.io.
The center of mass velocity is the velocity of the center of mass of the system, and it is equal to the rate of change of position of the center of mass with time. The acceleration of the center of mass is the rate of change of the center of mass velocity with time.
For example, if you want to know how fast a car is moving, you can measure its velocity. If you want to know how fast the car's velocity is changing, you can measure its acceleration. Similarly, if you want to know how fast the center of mass of a system is moving, you can measure its center of mass velocity, and if you want to know how fast the center of mass velocity is changing, you can measure the acceleration of the center of mass.
Velocity
While the centripetal acceleration points towards the center of the circle, the velocity vector does not. A key element of uniform circular motion is that the velocity is kept constant, so in order to have acceleration due to a change in direction only, the velocity vector must be tangent to the acceleration vector at all points along the circle. Tangent means that the velocity vector makes a 90-degree angle with the centripetal acceleration vector when the vectors are placed tail to tail.

Image courtesy of Study.com.
Since the velocity and acceleration vectors make a 90-degree angle, there is no component of the centripetal acceleration that is acting in the same direction as the velocity vector, so the acceleration will not affect the magnitude of the velocity. However, the acceleration vector does affect the direction of the velocity vector. If you add the acceleration and velocity vectors using vector addition, you will find that the direction of the resultant vector is always pointing along the circle, causing uniform circular motion.
We can relate the centripetal acceleration to the tangential velocity using this equation:
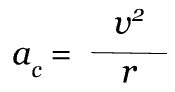
where a is the centripetal acceleration, v is the velocity, and r is the radius of the circle.
Centripetal Force
The centripetal force is defined as the force that is required to make an object move in a circular path. It is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the centripetal acceleration. The formula for centripetal force is: F = m * a_c, where F is the centripetal force, m is the mass of the object and a_c is the centripetal acceleration.
Recall that the centripetal force is not a new force; it is just another name for the net force directed toward the center of the circle. This net force could be caused by the normal force, tension, gravitational force, friction, or another type of force.
For example, when a car takes a turn, the tires exert friction on the road, and the friction force is what provides the centripetal force to keep the car moving in a circular path. Similarly, when a planet is orbiting the sun, it is the gravitational force of the sun that acts as the centripetal force.
The direction of the centripetal force vector is always pointed toward the center of the circle, like the acceleration vector. This occurs because the accleration vector always points in the same direction as the net force vector (in this case, the centripetal force) due to Newton's Second Law (F=ma).
It's also important to note that the greater the speed of an object, the greater the centripetal force required to keep it moving in a circular path. Similarly, the smaller the radius of a circular path, the greater the centripetal force required to keep an object moving in that path.

Image courtesy of quickmeme.com.
Practice Questions
1. What is the direction of the centripetal acceleration of an object undergoing uniform circular motion? A) Radial B) Tangential C) Perpendicular D) Horizontal
Answer: A) Radial
2. An object of mass 5 kg is moving in a circular path of radius 3 m with a constant velocity of 4 m/s. What is the centripetal acceleration of the object? A) 12 m/s^2 B) 16 m/s^2 C) 20 m/s^2 D) 5.33 m/s^2
Answer: D) 5.33 m/s^2 Explanation: To find the centripetal acceleration, we use the formula a_c = v^2/r, where a_c is the centripetal acceleration, v is the velocity of the object and r is the radius of the circular path. Substituting the given values, we get a_c = (4 m/s)^2 / 3 m = 16 m/s^2 / 3 m = 5.33 m/s^2
3. A ball of mass 1 kg is tied to a string and is moving in a circular path of radius 0.5 m. If the ball is moving with a velocity of 3 m/s, what is the centripetal force acting on the ball? A) 2.25 N B) 4.5 N C) 9 N D) 1.5 N
Answer: D) 1.5 N Explanation: The centripetal force acting on an object in uniform circular motion is given by the formula F = m * a_c, where F is the centripetal force, m is the mass of the object and a_c is the centripetal acceleration. To find the centripetal acceleration, we use the formula a_c = v^2/r, where a_c is the centripetal acceleration, v is the velocity of the object and r is the radius of the circular path. By substituting the given values, we get a_c = (3 m/s)^2 / 0.5 m = 9 m^2/s^2 / 0.5 m = 18 m/s^2Then we can use the formula F = m * a_c to find the centripetal force acting on the ball, we know the mass of the ball is 1 kg, so we substitute the values into the formula: F = m * a_c = 1 kg * 18 m/s^2 = 18 N
<< Hide Menu
3.6 Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force
6 min read•june 18, 2024
Peter Apps
Kashvi Panjolia
Peter Apps
Kashvi Panjolia
Important Equations
The acceleration is equal to the rate of change of velocity with time, and velocity is equal to the rate of change of position with time.

Equation:
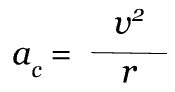
Surprisingly, in uniform circular motion, in which an object has constant speed, there is an acceleration due to a change in direction. Don’t forget, acceleration is a change in velocity, which is a vector quantity that has both magnitude and direction!
Centripetal Acceleration
Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration that an object experiences when it moves in a circular path. This acceleration is directed toward the center of the circle. It is also known as radial acceleration.
Imagine you are on a roller coaster and you experience the feeling of being pulled toward the center of the loop as you go through a loop-the-loop. This is an example of centripetal acceleration. The force that is pulling you toward the center of the loop is the centripetal force.

Image courtesy of Quora.
Force and acceleration are both quantities that have both magnitude and direction. The direction of the net force acting on an object is the same as the direction of its acceleration. This means that if you want to change the direction of an object's acceleration, you need to change the direction of the net force acting on it. For example, if you want to change the direction of a car's acceleration so it is accelerating and turning right, you need to give it a rightward net force.
The center of mass (COM) of a system is a point that represents the average position of all the mass in the system. Conceptually, it is the point where the entire mass of the system can be considered to be concentrated, which makes it the point at which the system would balance if it were suspended by a single point. The position of the center of mass depends on the distribution of mass within the system.
Consider a seesaw in a playground. The center of mass of a seesaw is located at the point where the board of the seesaw balances. This point is also known as the pivot point. If you place a heavier person on one side of the seesaw, the center of mass will shift closer to that side, and the seesaw will tilt in that direction.

Image courtesy of Albert.io.
The center of mass velocity is the velocity of the center of mass of the system, and it is equal to the rate of change of position of the center of mass with time. The acceleration of the center of mass is the rate of change of the center of mass velocity with time.
For example, if you want to know how fast a car is moving, you can measure its velocity. If you want to know how fast the car's velocity is changing, you can measure its acceleration. Similarly, if you want to know how fast the center of mass of a system is moving, you can measure its center of mass velocity, and if you want to know how fast the center of mass velocity is changing, you can measure the acceleration of the center of mass.
Velocity
While the centripetal acceleration points towards the center of the circle, the velocity vector does not. A key element of uniform circular motion is that the velocity is kept constant, so in order to have acceleration due to a change in direction only, the velocity vector must be tangent to the acceleration vector at all points along the circle. Tangent means that the velocity vector makes a 90-degree angle with the centripetal acceleration vector when the vectors are placed tail to tail.

Image courtesy of Study.com.
Since the velocity and acceleration vectors make a 90-degree angle, there is no component of the centripetal acceleration that is acting in the same direction as the velocity vector, so the acceleration will not affect the magnitude of the velocity. However, the acceleration vector does affect the direction of the velocity vector. If you add the acceleration and velocity vectors using vector addition, you will find that the direction of the resultant vector is always pointing along the circle, causing uniform circular motion.
We can relate the centripetal acceleration to the tangential velocity using this equation:
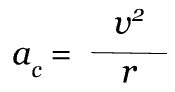
where a is the centripetal acceleration, v is the velocity, and r is the radius of the circle.
Centripetal Force
The centripetal force is defined as the force that is required to make an object move in a circular path. It is equal to the mass of the object multiplied by the centripetal acceleration. The formula for centripetal force is: F = m * a_c, where F is the centripetal force, m is the mass of the object and a_c is the centripetal acceleration.
Recall that the centripetal force is not a new force; it is just another name for the net force directed toward the center of the circle. This net force could be caused by the normal force, tension, gravitational force, friction, or another type of force.
For example, when a car takes a turn, the tires exert friction on the road, and the friction force is what provides the centripetal force to keep the car moving in a circular path. Similarly, when a planet is orbiting the sun, it is the gravitational force of the sun that acts as the centripetal force.
The direction of the centripetal force vector is always pointed toward the center of the circle, like the acceleration vector. This occurs because the accleration vector always points in the same direction as the net force vector (in this case, the centripetal force) due to Newton's Second Law (F=ma).
It's also important to note that the greater the speed of an object, the greater the centripetal force required to keep it moving in a circular path. Similarly, the smaller the radius of a circular path, the greater the centripetal force required to keep an object moving in that path.

Image courtesy of quickmeme.com.
Practice Questions
1. What is the direction of the centripetal acceleration of an object undergoing uniform circular motion? A) Radial B) Tangential C) Perpendicular D) Horizontal
Answer: A) Radial
2. An object of mass 5 kg is moving in a circular path of radius 3 m with a constant velocity of 4 m/s. What is the centripetal acceleration of the object? A) 12 m/s^2 B) 16 m/s^2 C) 20 m/s^2 D) 5.33 m/s^2
Answer: D) 5.33 m/s^2 Explanation: To find the centripetal acceleration, we use the formula a_c = v^2/r, where a_c is the centripetal acceleration, v is the velocity of the object and r is the radius of the circular path. Substituting the given values, we get a_c = (4 m/s)^2 / 3 m = 16 m/s^2 / 3 m = 5.33 m/s^2
3. A ball of mass 1 kg is tied to a string and is moving in a circular path of radius 0.5 m. If the ball is moving with a velocity of 3 m/s, what is the centripetal force acting on the ball? A) 2.25 N B) 4.5 N C) 9 N D) 1.5 N
Answer: D) 1.5 N Explanation: The centripetal force acting on an object in uniform circular motion is given by the formula F = m * a_c, where F is the centripetal force, m is the mass of the object and a_c is the centripetal acceleration. To find the centripetal acceleration, we use the formula a_c = v^2/r, where a_c is the centripetal acceleration, v is the velocity of the object and r is the radius of the circular path. By substituting the given values, we get a_c = (3 m/s)^2 / 0.5 m = 9 m^2/s^2 / 0.5 m = 18 m/s^2Then we can use the formula F = m * a_c to find the centripetal force acting on the ball, we know the mass of the ball is 1 kg, so we substitute the values into the formula: F = m * a_c = 1 kg * 18 m/s^2 = 18 N

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.