Browse By Unit
Peter Apps
Peter Apps
As of 2021, College Board only tests Units 1-7 on the AP Physics 1 exam. This page's content will not be tested on the exam, but we kept it online for you all as a resource.
Enduring Understanding 6.B 👨💻
A periodic wave is one that repeats as a function of both time and position and can be described by its amplitude, frequency, wavelength, speed, and energy.
Essential Knowledge 6.B.1 🏘
For a periodic wave, the period is the repeat time of the wave. The frequency is the number of repetitions of the wave per unit time.
Essential Knowledge 6.B.2 🏘
For a periodic wave, the wavelength is the repeat distance of the wave.
Essential Knowledge 6.B.4 🏘
For a periodic wave, wavelength is the ratio of speed over frequency.
Essential Knowledge 6.B.5 🏘
The observed frequency of a wave depends on the relative motion of source and observer.
Relationship between frequency and wavelength
As we saw above, the velocity of a wave is related to the wave’s frequency and the wavelength. As long as the velocity is constant, the frequency and wavelength have an inverse relationship (when one increases, the other decreases by the same factor).
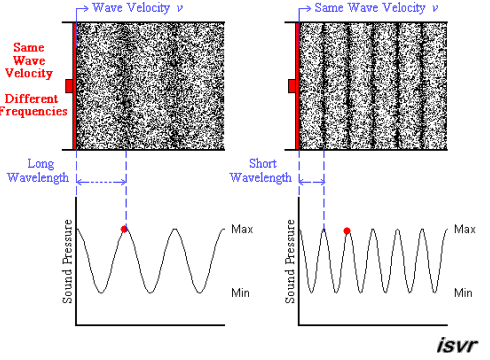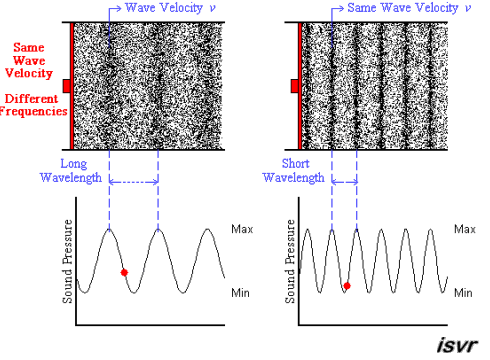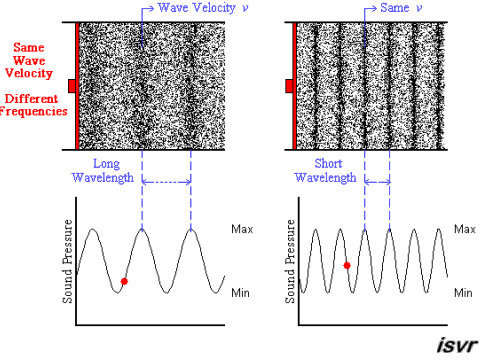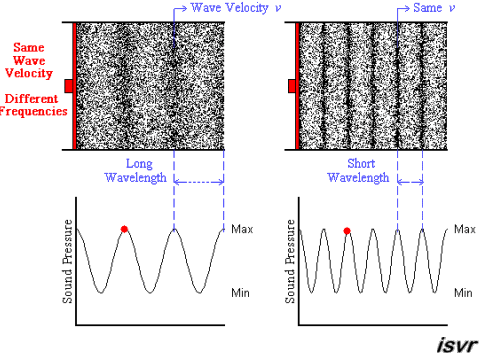
Image courtesy of Blog.Soton.
In this image we see that the longer wavelength corresponds to a smaller frequency (longer time between peaks) and the shorter wavelength causes the frequency to increase. In both cases, the velocity of the wave is the same.
Moving Sources of Waves
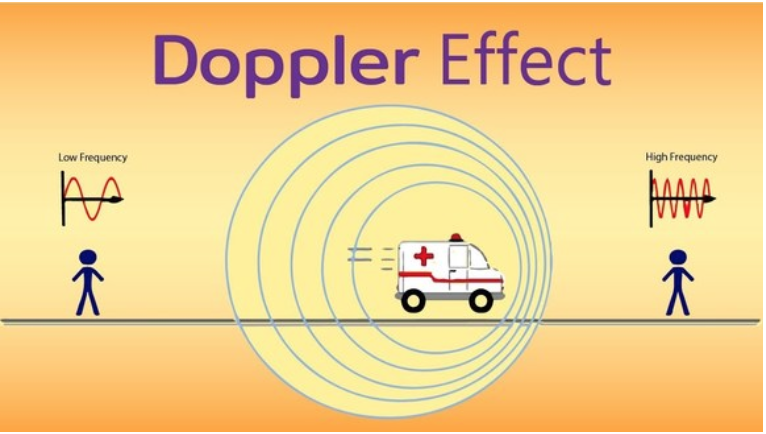
When a source of waves is in motion relative to an observer, the observed wavelength and frequency of the waves change. This effect is known as the Doppler Effect and basically results in the frequency appearing to be higher when the source is moving towards the observer and lower when the source is moving away. (The change in wavelengths is the opposite of this trend, since frequency and wavelengths are indirectly related.) The actual amount of shift in the frequency depends on the speed of the object and observer, but in general faster speeds lead to higher frequencies.
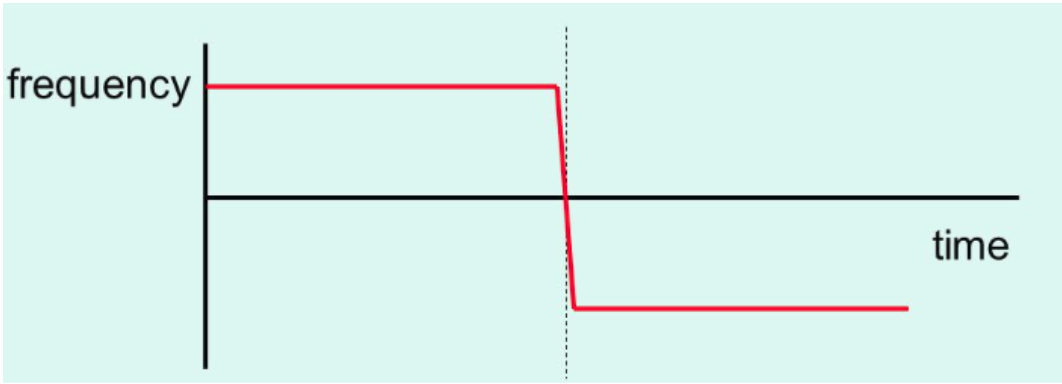
The graph above shows a wave-source moving towards and then passing an observer. Notice the sudden shift in frequency when the source switches from moving towards to moving away from the observer.
**** Note -** There are mathematical equations for modelling the Doppler Effect, and this effect also applies to light and other Electromagnetic waves too. However AP 1 will only test you on mechanical waves and qualitative relationships.
🎥Watch: AP Physics 1 - Unit 10 Streams
<< Hide Menu
Peter Apps
Peter Apps
As of 2021, College Board only tests Units 1-7 on the AP Physics 1 exam. This page's content will not be tested on the exam, but we kept it online for you all as a resource.
Enduring Understanding 6.B 👨💻
A periodic wave is one that repeats as a function of both time and position and can be described by its amplitude, frequency, wavelength, speed, and energy.
Essential Knowledge 6.B.1 🏘
For a periodic wave, the period is the repeat time of the wave. The frequency is the number of repetitions of the wave per unit time.
Essential Knowledge 6.B.2 🏘
For a periodic wave, the wavelength is the repeat distance of the wave.
Essential Knowledge 6.B.4 🏘
For a periodic wave, wavelength is the ratio of speed over frequency.
Essential Knowledge 6.B.5 🏘
The observed frequency of a wave depends on the relative motion of source and observer.
Relationship between frequency and wavelength
As we saw above, the velocity of a wave is related to the wave’s frequency and the wavelength. As long as the velocity is constant, the frequency and wavelength have an inverse relationship (when one increases, the other decreases by the same factor).

Image courtesy of Blog.Soton.
In this image we see that the longer wavelength corresponds to a smaller frequency (longer time between peaks) and the shorter wavelength causes the frequency to increase. In both cases, the velocity of the wave is the same.
Moving Sources of Waves

When a source of waves is in motion relative to an observer, the observed wavelength and frequency of the waves change. This effect is known as the Doppler Effect and basically results in the frequency appearing to be higher when the source is moving towards the observer and lower when the source is moving away. (The change in wavelengths is the opposite of this trend, since frequency and wavelengths are indirectly related.) The actual amount of shift in the frequency depends on the speed of the object and observer, but in general faster speeds lead to higher frequencies.

The graph above shows a wave-source moving towards and then passing an observer. Notice the sudden shift in frequency when the source switches from moving towards to moving away from the observer.
**** Note -** There are mathematical equations for modelling the Doppler Effect, and this effect also applies to light and other Electromagnetic waves too. However AP 1 will only test you on mechanical waves and qualitative relationships.
🎥Watch: AP Physics 1 - Unit 10 Streams

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.