Browse By Unit
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Exchange Rates
Exchange rates are the price at which one international currency can be exchanged for another. In other words, it's the price at which one currency can be bought with another.
**When the exchange rate increases, it is more expensive to purchase currency. This makes goods and services from this country more expensive. **
When the exchange rate decreases, it is less expensive to purchase currency. This makes goods and services from this country less expensive.
Appreciation occurs when the value of a country's currency increases relative to a foreign currency. Depreciation occurs when the value of a country's currency falls.
Exchange rates between countries are reciprocals of each other, meaning that when one currency appreciates, the other currency depreciates.
Gold Standard
A long time ago (meaning before the Great Depression) most economies were on the gold standard. This means that the exchange rates were always fixed no matter what, instead of fluctuating like it does today. This meant that if the value of franc appreciated, people could buy gold with their dollars, and then buy francs with the gold and then buy more dollars then they started out with by using the francs. Cool right?
However, this didn't work too well. If Americans loved French products, the exchange rate would still stay the same and result in the US with a balance of payment deficit. Most historians and economists also think the gold standard was one of the key causes for the economic collapse during the Great Depression. Now, we no longer use the gold standard, but it's worth noting that we once did.
Cost of a US Dollar
Let's look at various currencies and their exchange rates to the U.S. Dollar and whether they have appreciated or depreciated:
Cost of one U.S. Dollar
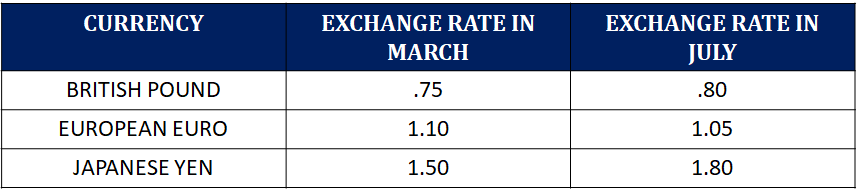
If we look at the British Pound, we see that the exchange rate increases from .75 to .80 from March to July. This means that the British Pound has become more expensive or has appreciated in value.
If we look at the European Euro, we see that the exchange rate decreases from 1.10 to 1.05 from March to July. This means that the European Euro has become less expensive, or has depreciated in value.
We can also use the information above to calculate the price of a U.S. good in the various currencies. We do this by simply multiplying the price of the U.S. good by the exchange rate for whichever country we are looking at. So for example, a $300 hotel room in the U.S. would cost 💷225 pounds in Britain.
Factors that Change Exchange Rates
Exchange rates include supply and demand. Almost think about the exchange rate as the price to "buy a pound" with dollars (USD). For example, if the dollar is stronger than a pound, it will be able to buy more pounds with $1. On the other hand, if a dollar is weak, it might not be even able to buy one pound.
Exchange rates are fluctuating every day. One day, a dollar could be strong, another day it could be weak. This is determined by (unsurprisingly) supply and demand. Like how the price of products in the market is determined by the equilibrium price, so is the price of a pound. But like regular good old supply and demand, we have factors that can shift the supply and demand curves to the right or to the left.
- Consumer tastes
- When Americans, for example, prefer European products and services, demand for euros increase (because you need euros to buy those European products). This causes the demand for euros shift to the right, increasing the quantity of euros and the price of the euros. Now, instead of being able to buy a euro with 2 in order to trade in for (or buy) a euro. In this case, the value of the dollar depreciates, because supply of the dollar has increased, or shifted to the right (more Europeans are trading in their euros for dollars, more dollars are now available in the markets.
- On the other hand, if Europeans have a strong preference of American products, demand for dollar (USD) will increase, since you can only buy American products with dollars. This causes the demand for dollars to shift to the right, increasing the quantity and price of dollars. Now you'll need 2 euros to trade in for one dollar, a change from 1 euro for 1 dollar. In this case, the value of the dollar appreciates.
- It's important to note that the two cases actually have different axes when graphed with the supply and demand model. The first case, we're looking at the quantity and price of euros, so the x-axis would say "quantity of euros" while the y-axis would say "dollar price of a euro".
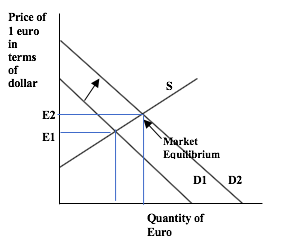
Image Courtesy of Study.com
- In the second case, we're looking at quantity and price of dollar, so the x-axis would say "quantity of dollars" while the y-axis would say "euro price of a dollar"
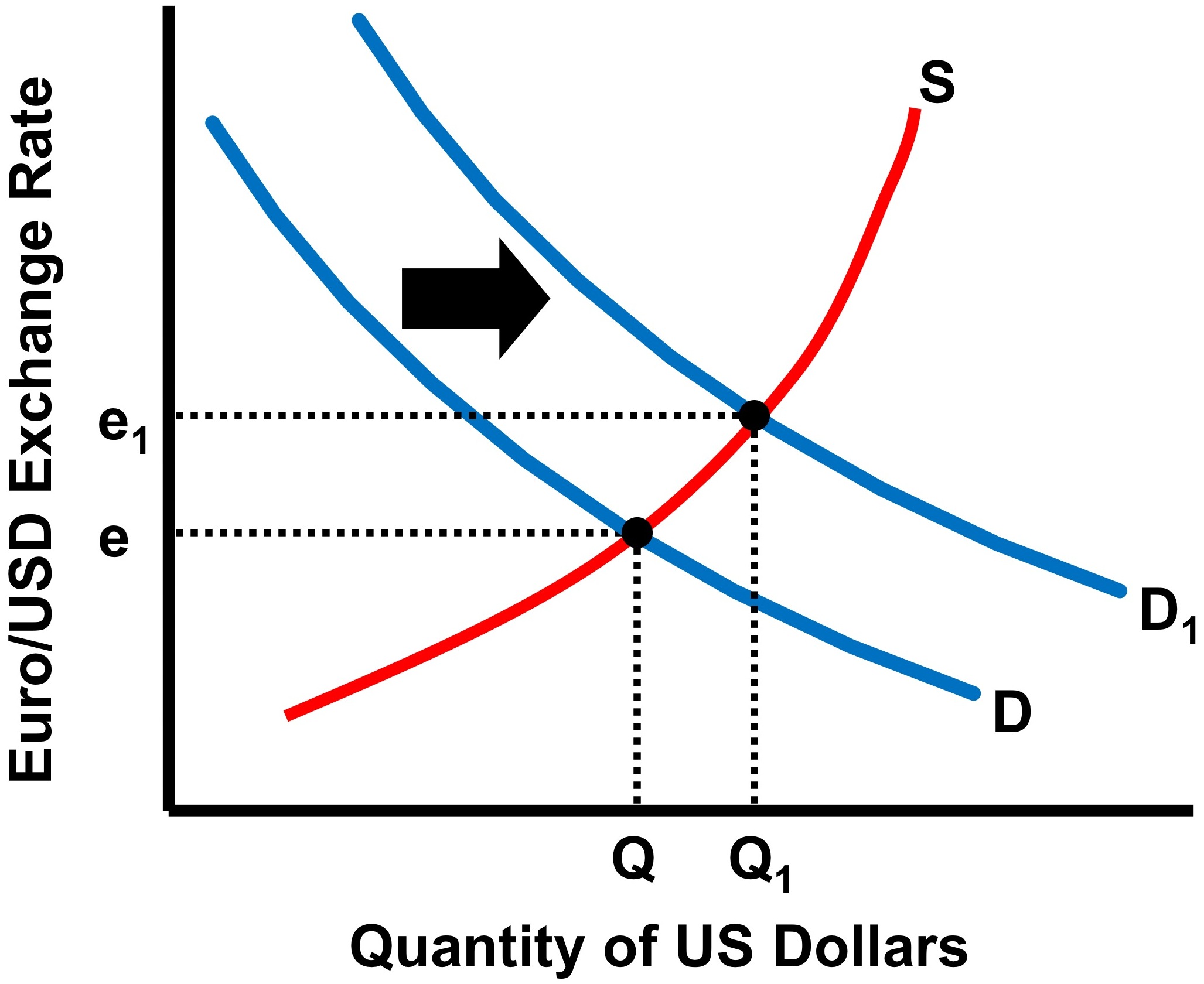
Image Courtesy of No Bull Economist Lesson
- If you wanted to see the dollar appreciate in the first case, you could simply shift demand for euros to the left (so that demand for euros goes down)
- Accordingly, if you wanted to see the dollar depreciate in the second case, you could simply shift demand for dollars to the left (so that the demand for dollar goes down)
- Relative income
- Income is a big issue. Remember how people spend more if they have more income? It's the same concept in macroeconomy too. If one nation's GDP is increasing and everyone's income is increasing, they will demand more of all goods and products, including international ones.
- If, for example, the US was in a recession while Europe was enjoying economic boom, Europeans would obviously want to buy more of American products with more money to spend. This will increase the demand for dollars and appreciate its value.
- Basically, if you have more money to spend then usual, you contribute to the change in exchange rates if you buy any foreign products.
- Relative inflation
- Ahhh, inflation. Where do we start? Inflation can have a big effect on exchange rate as well. I guess you can never escape inflation from economics 😅. Here, we have a situation where one nation's price level is increasing due to inflation at a way faster rate than another nation. Now, consumers from the inflation-high nation will demand more products from the other nation because it's cheaper. This will increase demand for products from the nation, appreciating its currency value.
- For example, suppose Europe is suffering from high inflation. Now, US goods will seem relatively cheap compared to European goods. Consequently, demand for American goods will increase and the dollar will appreciate.
- This is another reason why the Fed likely to keep inflationary pressures low.
- Speculation
- Humans cannot foresee the future, but we can always speculate! Because foreign currency acts kind of like assets, there will be investors trying to make some profit by buying currency at low rates and selling them at high rates. If many speculate interest rates will fall in the US relative to Europe, the euro will be a good investment, right? Most investors will start buy European assets, thus increasing the value of euro and depreciating the dollar.
<< Hide Menu
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Exchange Rates
Exchange rates are the price at which one international currency can be exchanged for another. In other words, it's the price at which one currency can be bought with another.
**When the exchange rate increases, it is more expensive to purchase currency. This makes goods and services from this country more expensive. **
When the exchange rate decreases, it is less expensive to purchase currency. This makes goods and services from this country less expensive.
Appreciation occurs when the value of a country's currency increases relative to a foreign currency. Depreciation occurs when the value of a country's currency falls.
Exchange rates between countries are reciprocals of each other, meaning that when one currency appreciates, the other currency depreciates.
Gold Standard
A long time ago (meaning before the Great Depression) most economies were on the gold standard. This means that the exchange rates were always fixed no matter what, instead of fluctuating like it does today. This meant that if the value of franc appreciated, people could buy gold with their dollars, and then buy francs with the gold and then buy more dollars then they started out with by using the francs. Cool right?
However, this didn't work too well. If Americans loved French products, the exchange rate would still stay the same and result in the US with a balance of payment deficit. Most historians and economists also think the gold standard was one of the key causes for the economic collapse during the Great Depression. Now, we no longer use the gold standard, but it's worth noting that we once did.

Cost of a US Dollar
Let's look at various currencies and their exchange rates to the U.S. Dollar and whether they have appreciated or depreciated:
Cost of one U.S. Dollar

If we look at the British Pound, we see that the exchange rate increases from .75 to .80 from March to July. This means that the British Pound has become more expensive or has appreciated in value.
If we look at the European Euro, we see that the exchange rate decreases from 1.10 to 1.05 from March to July. This means that the European Euro has become less expensive, or has depreciated in value.
We can also use the information above to calculate the price of a U.S. good in the various currencies. We do this by simply multiplying the price of the U.S. good by the exchange rate for whichever country we are looking at. So for example, a $300 hotel room in the U.S. would cost 💷225 pounds in Britain.
Factors that Change Exchange Rates
Exchange rates include supply and demand. Almost think about the exchange rate as the price to "buy a pound" with dollars (USD). For example, if the dollar is stronger than a pound, it will be able to buy more pounds with $1. On the other hand, if a dollar is weak, it might not be even able to buy one pound.
Exchange rates are fluctuating every day. One day, a dollar could be strong, another day it could be weak. This is determined by (unsurprisingly) supply and demand. Like how the price of products in the market is determined by the equilibrium price, so is the price of a pound. But like regular good old supply and demand, we have factors that can shift the supply and demand curves to the right or to the left.
- Consumer tastes
- When Americans, for example, prefer European products and services, demand for euros increase (because you need euros to buy those European products). This causes the demand for euros shift to the right, increasing the quantity of euros and the price of the euros. Now, instead of being able to buy a euro with 2 in order to trade in for (or buy) a euro. In this case, the value of the dollar depreciates, because supply of the dollar has increased, or shifted to the right (more Europeans are trading in their euros for dollars, more dollars are now available in the markets.
- On the other hand, if Europeans have a strong preference of American products, demand for dollar (USD) will increase, since you can only buy American products with dollars. This causes the demand for dollars to shift to the right, increasing the quantity and price of dollars. Now you'll need 2 euros to trade in for one dollar, a change from 1 euro for 1 dollar. In this case, the value of the dollar appreciates.
- It's important to note that the two cases actually have different axes when graphed with the supply and demand model. The first case, we're looking at the quantity and price of euros, so the x-axis would say "quantity of euros" while the y-axis would say "dollar price of a euro".

Image Courtesy of Study.com
- In the second case, we're looking at quantity and price of dollar, so the x-axis would say "quantity of dollars" while the y-axis would say "euro price of a dollar"

Image Courtesy of No Bull Economist Lesson
- If you wanted to see the dollar appreciate in the first case, you could simply shift demand for euros to the left (so that demand for euros goes down)
- Accordingly, if you wanted to see the dollar depreciate in the second case, you could simply shift demand for dollars to the left (so that the demand for dollar goes down)
- Relative income
- Income is a big issue. Remember how people spend more if they have more income? It's the same concept in macroeconomy too. If one nation's GDP is increasing and everyone's income is increasing, they will demand more of all goods and products, including international ones.
- If, for example, the US was in a recession while Europe was enjoying economic boom, Europeans would obviously want to buy more of American products with more money to spend. This will increase the demand for dollars and appreciate its value.
- Basically, if you have more money to spend then usual, you contribute to the change in exchange rates if you buy any foreign products.
- Relative inflation
- Ahhh, inflation. Where do we start? Inflation can have a big effect on exchange rate as well. I guess you can never escape inflation from economics 😅. Here, we have a situation where one nation's price level is increasing due to inflation at a way faster rate than another nation. Now, consumers from the inflation-high nation will demand more products from the other nation because it's cheaper. This will increase demand for products from the nation, appreciating its currency value.
- For example, suppose Europe is suffering from high inflation. Now, US goods will seem relatively cheap compared to European goods. Consequently, demand for American goods will increase and the dollar will appreciate.
- This is another reason why the Fed likely to keep inflationary pressures low.
- Speculation
- Humans cannot foresee the future, but we can always speculate! Because foreign currency acts kind of like assets, there will be investors trying to make some profit by buying currency at low rates and selling them at high rates. If many speculate interest rates will fall in the US relative to Europe, the euro will be a good investment, right? Most investors will start buy European assets, thus increasing the value of euro and depreciating the dollar.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.