Browse By Unit
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Grow Grow Grow!
We always talk about economic growth. On the news, in books, it's everywhere! It's one of the top priorities when it comes to voting. So what exactly constitutes growth?
GDP per capita
Remember GDP? Growth is measured through real GDP per capita over time. Per capita is just real GDP divided by the number of people within that country. If this GDP per capita increases over time, then it's proof that economy grew.
GDP per capita = real GDP / population

Image Courtesy of Investopedia
Review
So far, we've learned about what economic growth can constitute. Do you remember??
Economic growth is seen by a rightward shift of the LRAS (Long-run aggregate supply) curve. This corresponds to a rightward shift of the Production Possibilities Frontier. It's like instead of operating at A, B, and C, the economy shifts its potential possibilities to Y, making it more efficient and productive to produce more of each product. Growth refers to an economy's ability to produce more than before, so expanding the production possibility frontier would prove to be an increase in ability to produce.
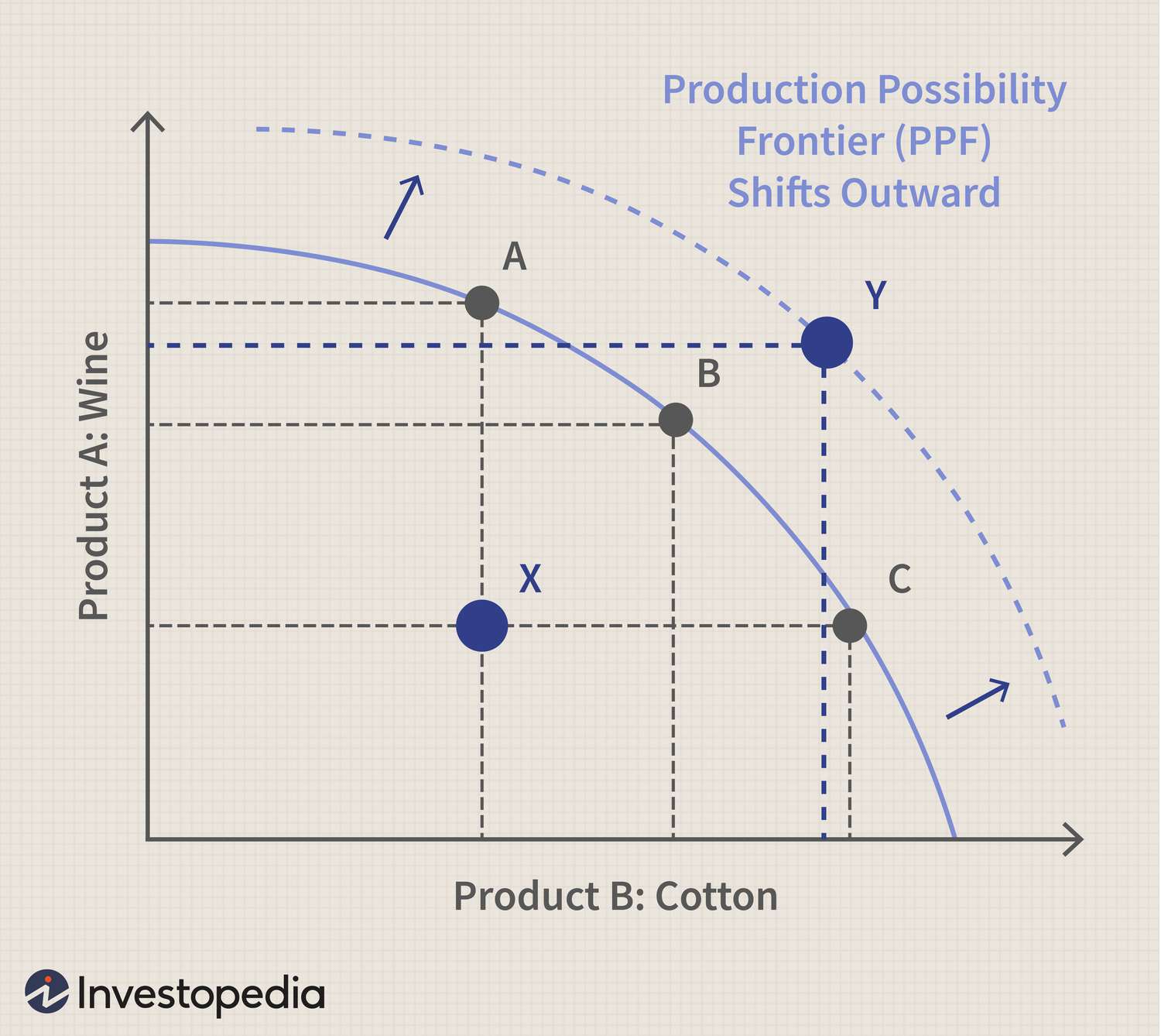
Image Courtesy of Investopedia
The long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) refers to the output that an economy can produce when using all its factors of production (human capital, physical capital, land, labor, entrepreneurship), and hence when operating at full employment. In the graph below, LRAS is shifted to LRAS1, which is a higher real GDP (or output). That's good news, because that's growth 🌱.
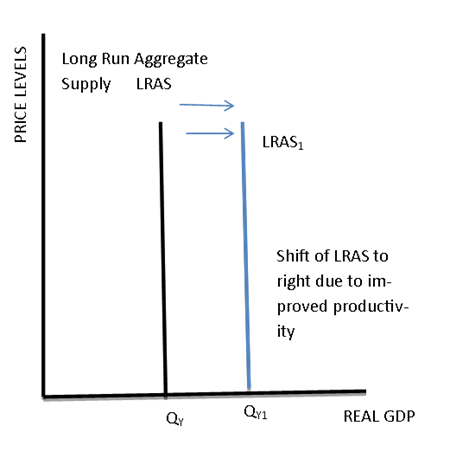
Image Courtesy of Albert.io
Aggregate Production Function
The aggregate production function is a function that shows the relationship between production and capital. It's another way to show long-run economic growth.
The aggregate production function shows that aggregate employment and aggregate output are directly related. Why? It's because more workers will produce more if all other factors are held constant. For example, if labor is insufficient, productivity will decline. The function basically calculates what inputs efficiently produce outputs.
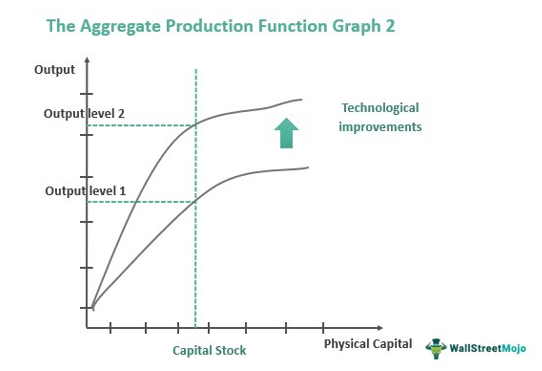
Image Courtesy of Wall Street Mojo
When the aggregate production function moves up, you know that it's an increase in productivity and economic growth!
Productivity
Productivity, according to the aggregate production function model, is determined by the amount of technology and physical and human capital per worker. It's the measuring of how much stuff can be produced by one worker during a given time. What does that mean? It means how much each worker has the skills and education for the work (human capital), how much of the physical environment is fit for working (physical capital) and how much technology there is to make tedious tasks faster and easier with the help of technology.
Factors
- Technology
- Advancement of technology could speed up production and influence productivity.
- For example, advances in agricultural technology could make farming more efficient and enable farmers grow more food. This would increase productivity and lead to economic growth.
- Even the invention of the wheel, Internet, and phones have changed the economy forever. Have you ever heard of the cotton gin? Invented by Eli Whitney, it increased the productivity of cotton exponentially. As a result, cotton became a very lucrative crop. Problem was, because many people went into the cotton industry, the demand for slaves soared in the South. Long story short, the invention of the cotton gin basically set the economic stage for the Civil War! A short tie to APUSH 😊
- Anywho, because technology is important, the government has created policies to fund research and provide incentives to invent new things. The government also funds professors and labs throughout our country in order to advance technology.
- Amount of physical capital
- Physical capital includes tangible, man-made objects that a company buys and uses to produce goods. The machinery, buildings, vehicles, and computers that a company owns are all considered part of its physical capital.
- For example, if a company invests in a new warehouse, then they can hire more workers, who will produce more goods. Thus, an increase in physical capital will lead to an increase in productivity.
- Supply-side policies are related to this because increased investment is also a type of increase in physical capital. More to come about supply-side stuff in the next section!
- Amount of human capital
- Human capital includes resources that people can provide such as education, experience, or unique skills. If the workers are more skilled and have obtained higher education then productivity will increase.
- If a hotel workers knew how to speak different languages in order to help its guests, that would be a plus right?
- If an accountant earned a stockbroker's license, that would increase the accountant's productivity.
- If the hospital is vaccinated against a disease, they'll be more productive even during disease outbreaks.
- Because human capital is super valuable in productivity, many nations create policies to increase human capital. These include more subsidies for public education, lower prices of interest of student loans and promote research through governmental agencies.
- Remember, even you studying this right now is increasing human capital because it might help sometime in your life and increase your productivity. So keep up the good work and you got this!! 🦾
- Natural resources
- Natural resources are crucial to success in an economy. If a nation lacks minerals, fertile soil, timber or is landlocked, the economy will struggle to grow. Though some countries have found other ways to grow, natural resources are definitely great if you have them.
- An example is Canada. Canada is blessed with a bunch of natural resources, so even with a smaller population than the US, it has been able to grow its economy pretty quickly.
- Nonrenewable resources, as you probably know, are resources that cannot be replenished. Meaning, once you use them, they're gone and we'll only keep running out of them. Examples include oil and coal.
- Renewable resources, on the other hand, are resources that can be replenished. These include things like timer and salmon.
- Environmental policies strive to protect these natural resources, but it can decrease productivity a little since these resources are used through regulations (used at smaller amounts) in the short run.
- However, in the long run, environmental policies increase productivity 😉
Common Factor
What do these four factors have in common? It's all about money 💵. All these factors require some sort of investment from saving. Firms invest in physical capital and individuals invest in human capital. Physical capital (obviously) needs money because you have to build things, and higher education costs money for human capital. This is why saving is as important as investing. If you haven't saved enough money, you'll likely have to take out a loan in college. If you have money, it'll be easier for you to invest in human capital.
Quick MCQ
Which of the following would likely slow a nation's long-term economic growth?
A. Guaranteed low-interest loans for college students
B. Removal of a tax on income earned on saving
C. Removal of the investment tax credit
D. More research grants given to medical schools
E. Conservation policies to manage the renewable harvest of timber
✨
✨
✨
✨
✨
✨
✨
✨
Answer: C. Removal of the investment tax credit
If you don't know what tax credits are, it's ok! You can solve this problem through process of elimination without even knowing what tax credits are. A, B, D, and E are all policies that increase productivity. A and B increases productivity in the human capital realm, D for technology and E for natural resources. That only leaves you with C, which is the correct answer.
If you're curious, tax credits provide incentives to those who invest in assets. If these tax credits are removed, investment would slow down, meaning no money 💰 and less productivity.
<< Hide Menu
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Grow Grow Grow!
We always talk about economic growth. On the news, in books, it's everywhere! It's one of the top priorities when it comes to voting. So what exactly constitutes growth?
GDP per capita
Remember GDP? Growth is measured through real GDP per capita over time. Per capita is just real GDP divided by the number of people within that country. If this GDP per capita increases over time, then it's proof that economy grew.
GDP per capita = real GDP / population

Image Courtesy of Investopedia
Review
So far, we've learned about what economic growth can constitute. Do you remember??
Economic growth is seen by a rightward shift of the LRAS (Long-run aggregate supply) curve. This corresponds to a rightward shift of the Production Possibilities Frontier. It's like instead of operating at A, B, and C, the economy shifts its potential possibilities to Y, making it more efficient and productive to produce more of each product. Growth refers to an economy's ability to produce more than before, so expanding the production possibility frontier would prove to be an increase in ability to produce.

Image Courtesy of Investopedia
The long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) refers to the output that an economy can produce when using all its factors of production (human capital, physical capital, land, labor, entrepreneurship), and hence when operating at full employment. In the graph below, LRAS is shifted to LRAS1, which is a higher real GDP (or output). That's good news, because that's growth 🌱.

Image Courtesy of Albert.io
Aggregate Production Function
The aggregate production function is a function that shows the relationship between production and capital. It's another way to show long-run economic growth.
The aggregate production function shows that aggregate employment and aggregate output are directly related. Why? It's because more workers will produce more if all other factors are held constant. For example, if labor is insufficient, productivity will decline. The function basically calculates what inputs efficiently produce outputs.

Image Courtesy of Wall Street Mojo
When the aggregate production function moves up, you know that it's an increase in productivity and economic growth!
Productivity
Productivity, according to the aggregate production function model, is determined by the amount of technology and physical and human capital per worker. It's the measuring of how much stuff can be produced by one worker during a given time. What does that mean? It means how much each worker has the skills and education for the work (human capital), how much of the physical environment is fit for working (physical capital) and how much technology there is to make tedious tasks faster and easier with the help of technology.
Factors
- Technology
- Advancement of technology could speed up production and influence productivity.
- For example, advances in agricultural technology could make farming more efficient and enable farmers grow more food. This would increase productivity and lead to economic growth.
- Even the invention of the wheel, Internet, and phones have changed the economy forever. Have you ever heard of the cotton gin? Invented by Eli Whitney, it increased the productivity of cotton exponentially. As a result, cotton became a very lucrative crop. Problem was, because many people went into the cotton industry, the demand for slaves soared in the South. Long story short, the invention of the cotton gin basically set the economic stage for the Civil War! A short tie to APUSH 😊
- Anywho, because technology is important, the government has created policies to fund research and provide incentives to invent new things. The government also funds professors and labs throughout our country in order to advance technology.
- Amount of physical capital
- Physical capital includes tangible, man-made objects that a company buys and uses to produce goods. The machinery, buildings, vehicles, and computers that a company owns are all considered part of its physical capital.
- For example, if a company invests in a new warehouse, then they can hire more workers, who will produce more goods. Thus, an increase in physical capital will lead to an increase in productivity.
- Supply-side policies are related to this because increased investment is also a type of increase in physical capital. More to come about supply-side stuff in the next section!
- Amount of human capital
- Human capital includes resources that people can provide such as education, experience, or unique skills. If the workers are more skilled and have obtained higher education then productivity will increase.
- If a hotel workers knew how to speak different languages in order to help its guests, that would be a plus right?
- If an accountant earned a stockbroker's license, that would increase the accountant's productivity.
- If the hospital is vaccinated against a disease, they'll be more productive even during disease outbreaks.
- Because human capital is super valuable in productivity, many nations create policies to increase human capital. These include more subsidies for public education, lower prices of interest of student loans and promote research through governmental agencies.
- Remember, even you studying this right now is increasing human capital because it might help sometime in your life and increase your productivity. So keep up the good work and you got this!! 🦾
- Natural resources
- Natural resources are crucial to success in an economy. If a nation lacks minerals, fertile soil, timber or is landlocked, the economy will struggle to grow. Though some countries have found other ways to grow, natural resources are definitely great if you have them.
- An example is Canada. Canada is blessed with a bunch of natural resources, so even with a smaller population than the US, it has been able to grow its economy pretty quickly.
- Nonrenewable resources, as you probably know, are resources that cannot be replenished. Meaning, once you use them, they're gone and we'll only keep running out of them. Examples include oil and coal.
- Renewable resources, on the other hand, are resources that can be replenished. These include things like timer and salmon.
- Environmental policies strive to protect these natural resources, but it can decrease productivity a little since these resources are used through regulations (used at smaller amounts) in the short run.
- However, in the long run, environmental policies increase productivity 😉
Common Factor
What do these four factors have in common? It's all about money 💵. All these factors require some sort of investment from saving. Firms invest in physical capital and individuals invest in human capital. Physical capital (obviously) needs money because you have to build things, and higher education costs money for human capital. This is why saving is as important as investing. If you haven't saved enough money, you'll likely have to take out a loan in college. If you have money, it'll be easier for you to invest in human capital.
Quick MCQ
Which of the following would likely slow a nation's long-term economic growth?
A. Guaranteed low-interest loans for college students
B. Removal of a tax on income earned on saving
C. Removal of the investment tax credit
D. More research grants given to medical schools
E. Conservation policies to manage the renewable harvest of timber
✨
✨
✨
✨
✨
✨
✨
✨
Answer: C. Removal of the investment tax credit
If you don't know what tax credits are, it's ok! You can solve this problem through process of elimination without even knowing what tax credits are. A, B, D, and E are all policies that increase productivity. A and B increases productivity in the human capital realm, D for technology and E for natural resources. That only leaves you with C, which is the correct answer.
If you're curious, tax credits provide incentives to those who invest in assets. If these tax credits are removed, investment would slow down, meaning no money 💰 and less productivity.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.