Browse By Unit
Jeanne Stansak
Jeanne Stansak
The Demand For Money
There is an inverse relationship between nominal interest rates and the quantity of money demanded.
- Nominal interest rate = real interest rate + expected inflation rate. This inverse relationship is caused by a couple of reasons:
- People demand a certain amount of money or liquid asset. If a person chooses to hold 100 of bonds, which would pay a certain nominal interest rate. This nominal interest rate provides some additional purchasing power at the end of the loan period, as well as, compensation for inflation.
- Explanation: The opportunity cost of holding wealth in the form of money instead of in the form of other assets is the nominal interest rate. If interest rates are low, people demand more money because the opportunity cost is lower. If interest rates are high, people demand less money because the opportunity cost is higher.
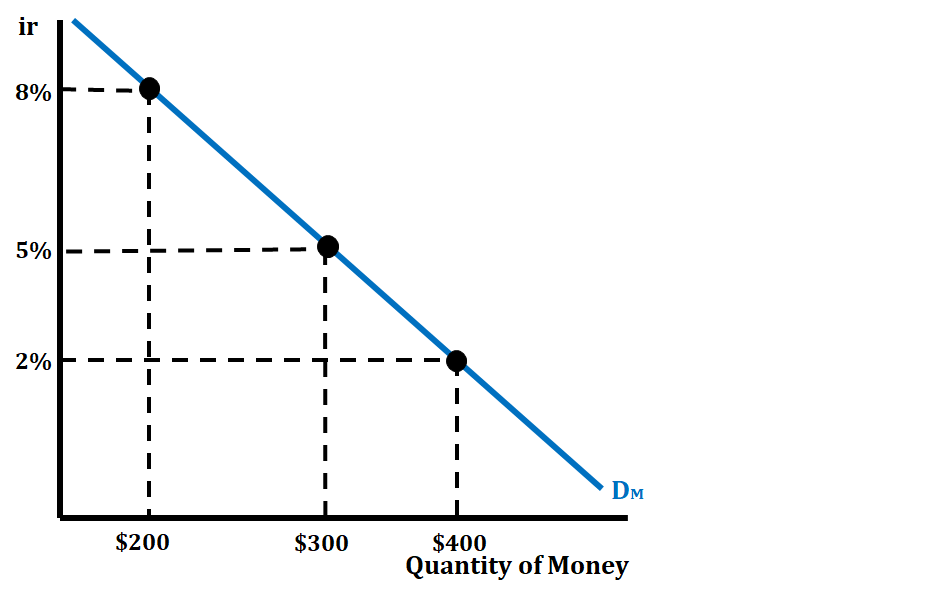
In the graph above, we are able to see the inverse relationship between the nominal interest rate and the quantity of money. As the nominal interest rate drops from 8% to 5%, we see the quantity of money increase from 300. The opposite is also true. If the nominal interest rate increases from 2% to 8%, we see the quantity of money decrease from 200.
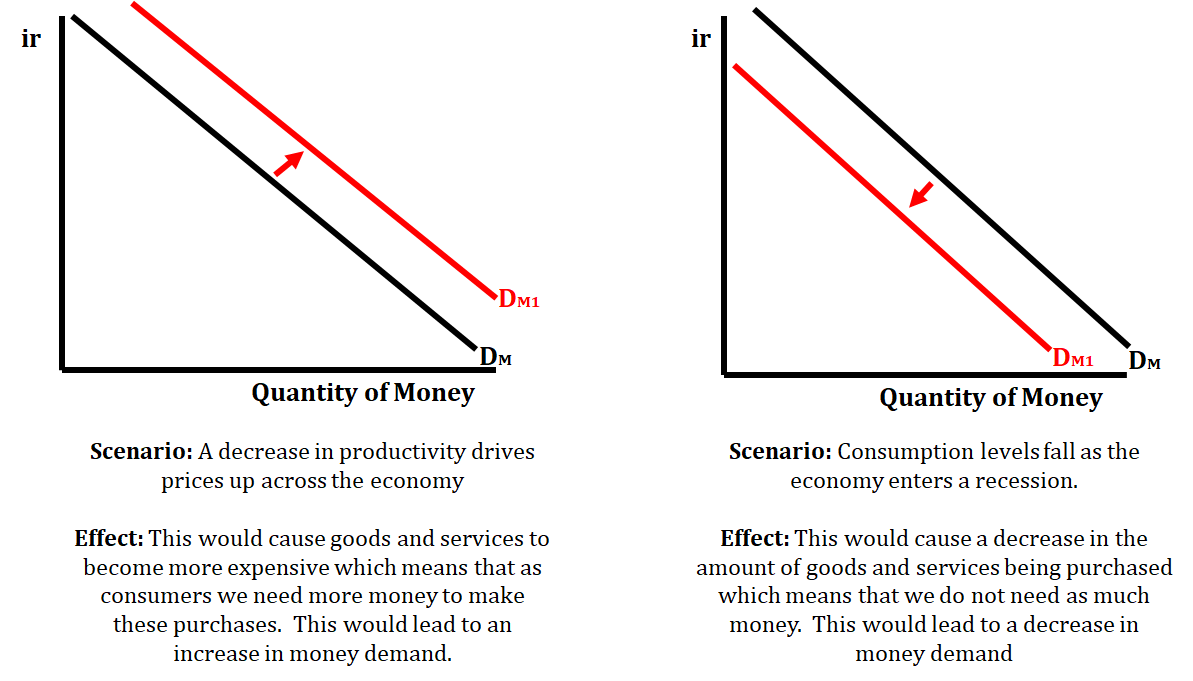
Shifters of the Demand for Money Curve
- Price Level
- Real GDP
- Transaction Costs Let's look at some examples:
The Supply of Money
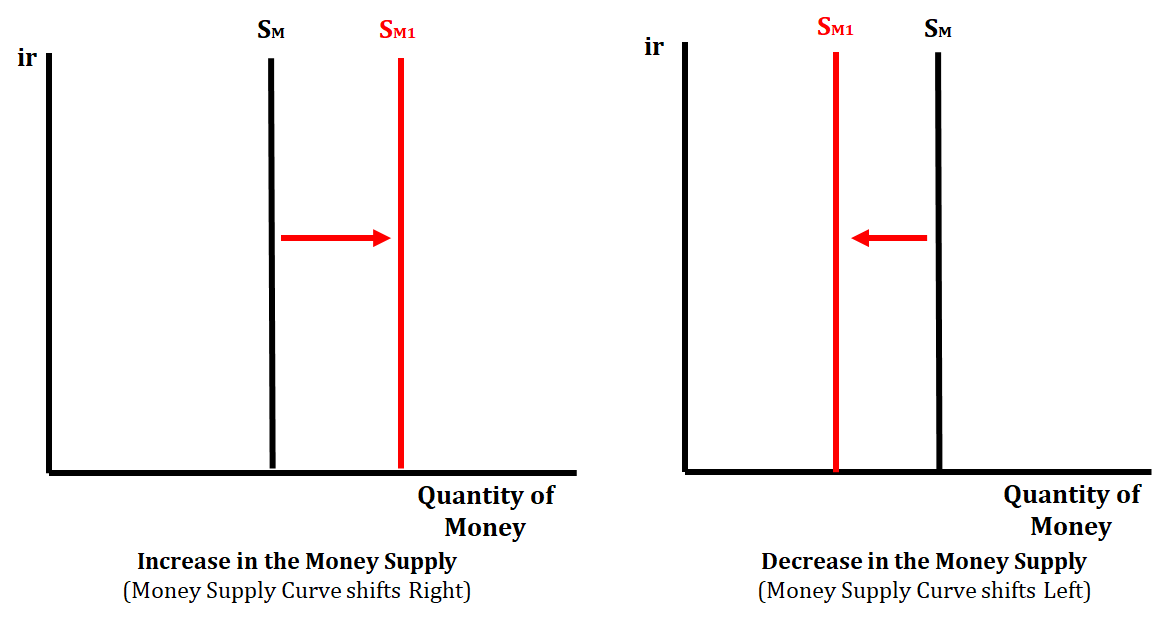
The monetary base of a nation is determined by the country’s central bank (FED). This means that the money supply is independent of the nominal interest rate. The supply of money will remain constant regardless of the nominal interest rate. The only way the money supply will change is as a result of monetary policy.
There are three tools that the FED uses to influence the money supply. These include the reserve requirement, the discount rate, open market operations (the buying and selling of bonds), and the federal funds rate.

When the FED uses these tools of monetary policy, they are able to either increase or decrease the money supply. The goal when the FED is using these tools is to either increase or decrease the nominal interest rate, which will cause the economy to expand or contract. We will look at this more closely when we review the money market equilibrium in the next section.
Money Market Equilibrium
Money market equilibrium is achieved when the interest rate at which the quantity of money demanded equals the quantity of money supplied. The nominal interest rate is the interest rate on the vertical axis and the quantity of money is on the horizontal axis.
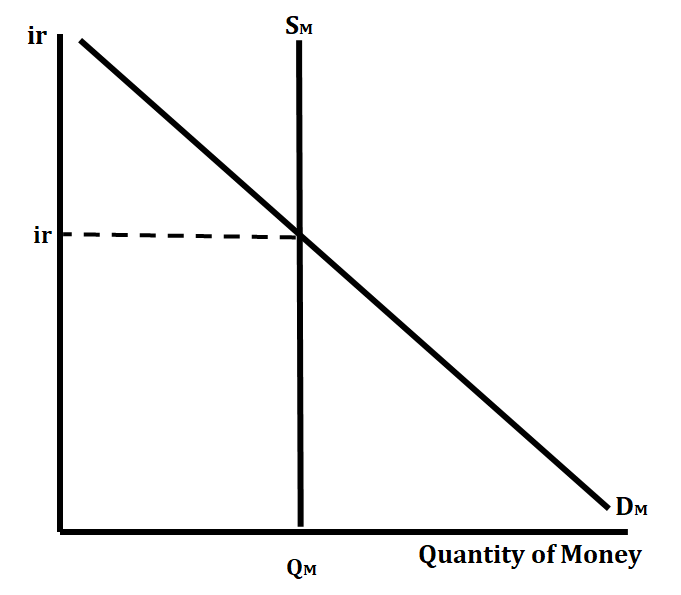
Remember that the shifters of money demand include a change in the price level, a change in real GDP output, and a change in the transaction costs of spending money. The only shifter of the supply of money is the Federal Reserve.
Let's look at the various ways that the money market equilibrium change through four different examples.
Example 1:
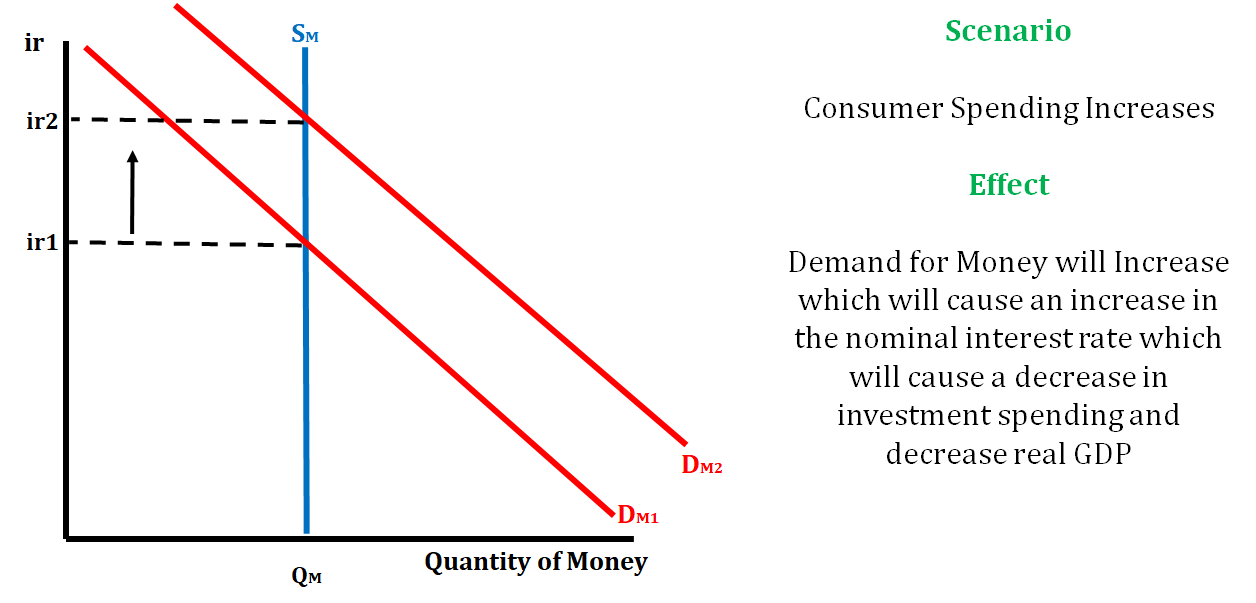
Example 2:
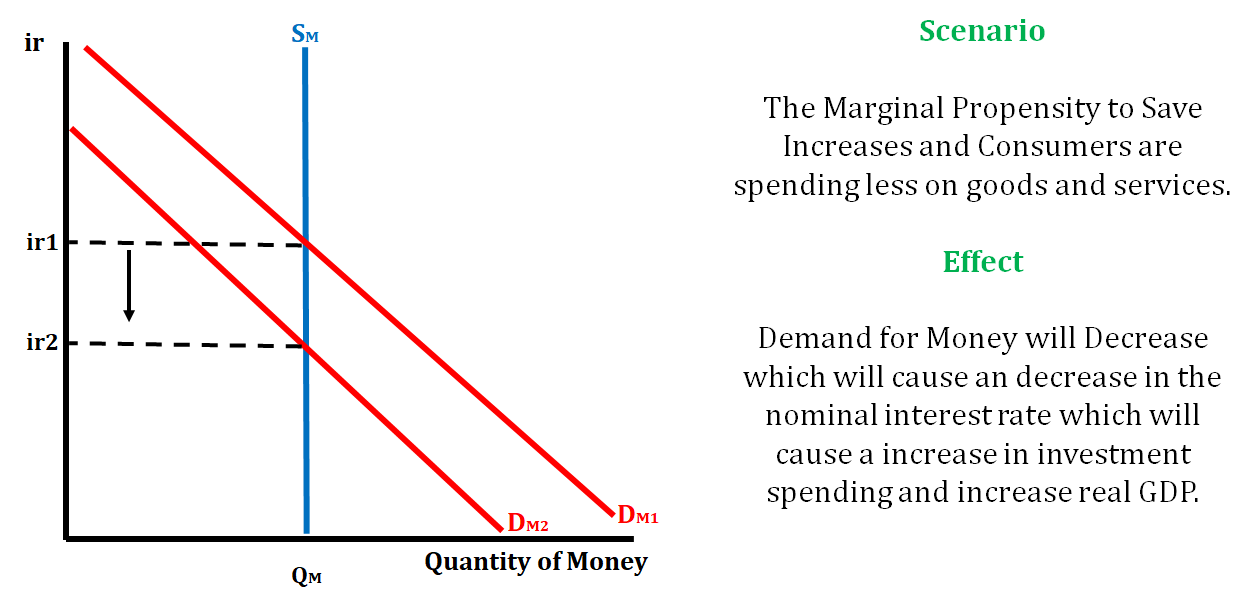
Example 3:
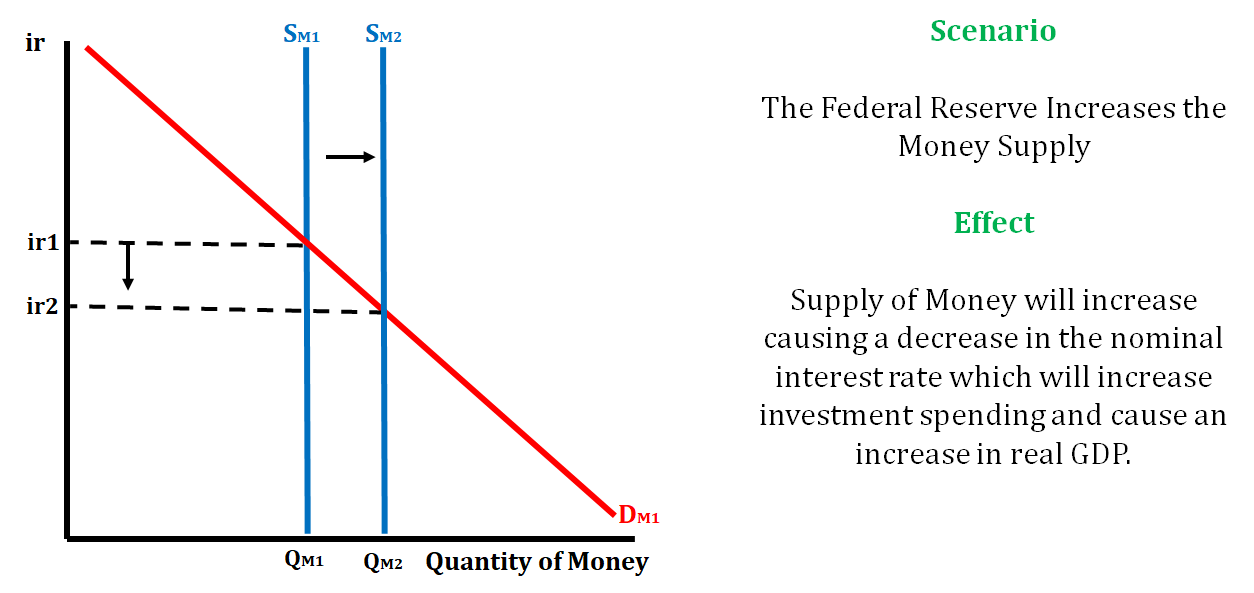
Example 4:
Investment Demand
Investment demand is the desired quantity of investment spending by firms across the economy on physical capital and other resources for the purpose of future productivity/profitability.
There is an inverse relationship between the nominal interest rate and the quantity of investment demanded. When the nominal interest rate falls, we see an increase in the quantity of investment demanded. The opposite is also true. When the nominal interest rate rises, we see a decrease in the quantity of investment demanded.
When interest rates increase, quantity of investment demanded decreases.
When interest rates decrease, quantity of investment demanded increases.
Investment demand changes due to monetary policy conducted by the Federal Reserve. When they practice an easy monetary policy and increase the money supply, they cause the nominal interest rate to fall, causing the quantity of investment demanded to increase. When they practice a tight monetary policy and decrease the money supply, they cause the nominal interest rate to increase, causing the quantity of investment demanded to decrease.
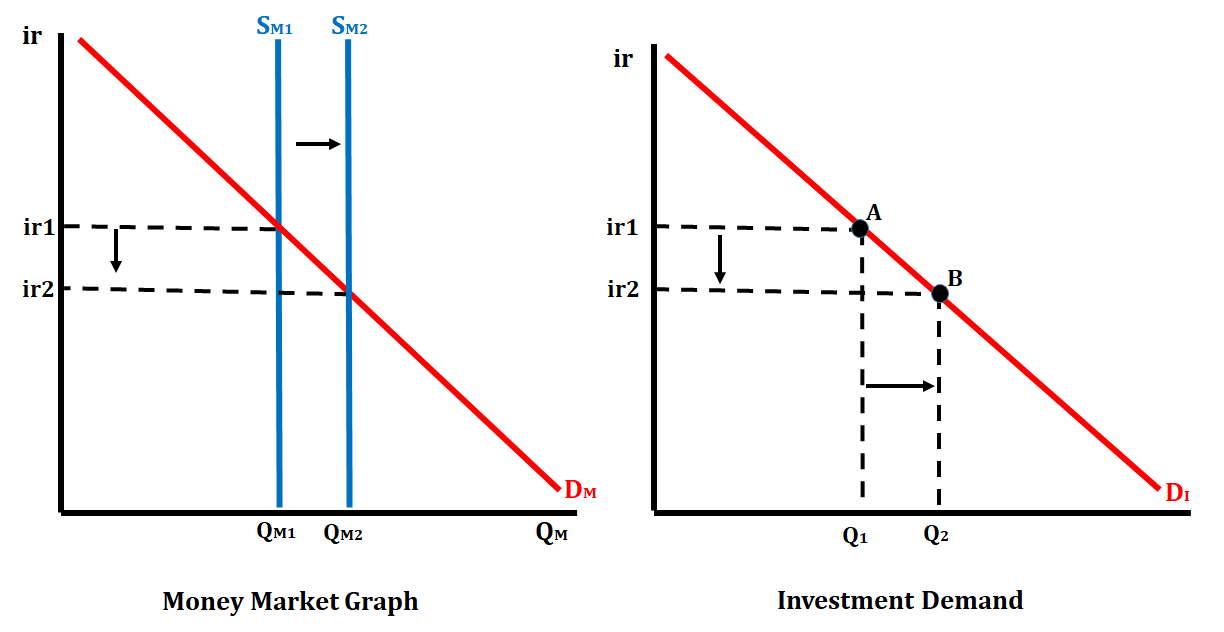
In the graph below, the Federal Reserve increases the money supply. This action will lower the nominal interest rate, and in turn, cause the quantity of investment demanded to increase.
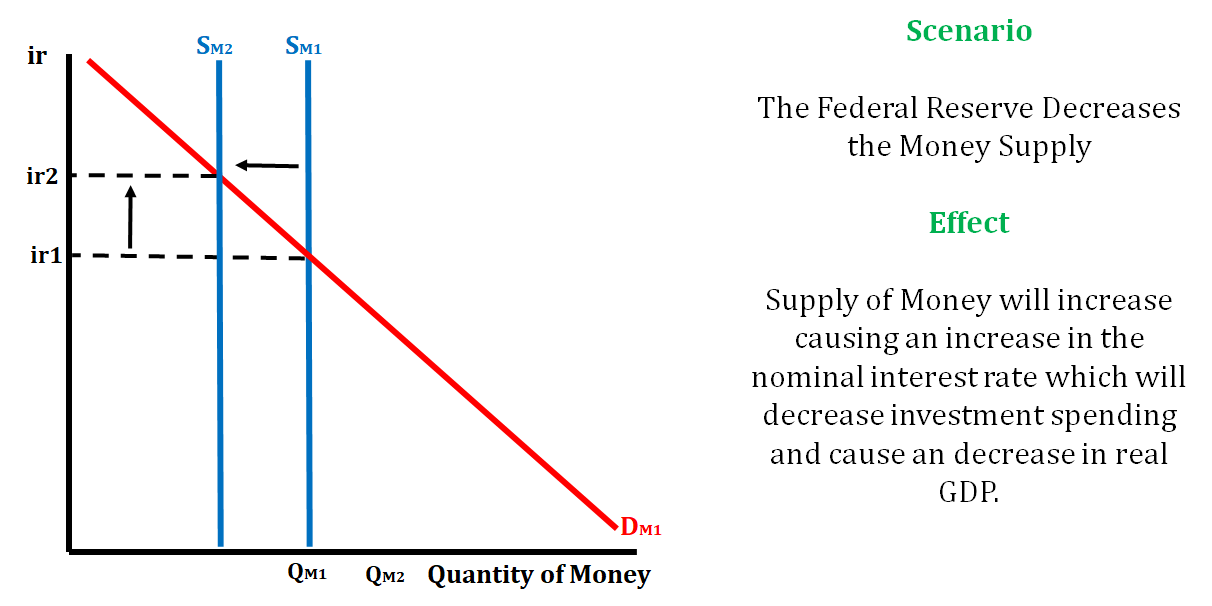
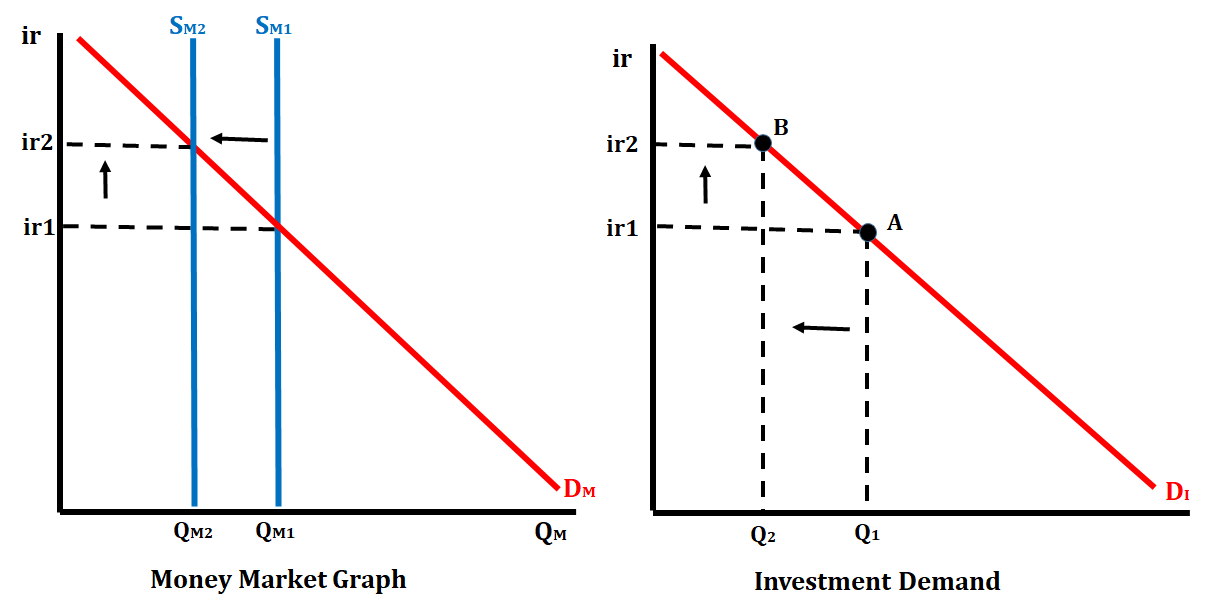
In the graph below, the Federal Reserve decreases the money supply. This action will raise the nominal interest rate, and in turn, cause the quantity of investment demanded to decrease.
<< Hide Menu
Jeanne Stansak
Jeanne Stansak
The Demand For Money
There is an inverse relationship between nominal interest rates and the quantity of money demanded.
- Nominal interest rate = real interest rate + expected inflation rate. This inverse relationship is caused by a couple of reasons:
- People demand a certain amount of money or liquid asset. If a person chooses to hold 100 of bonds, which would pay a certain nominal interest rate. This nominal interest rate provides some additional purchasing power at the end of the loan period, as well as, compensation for inflation.
- Explanation: The opportunity cost of holding wealth in the form of money instead of in the form of other assets is the nominal interest rate. If interest rates are low, people demand more money because the opportunity cost is lower. If interest rates are high, people demand less money because the opportunity cost is higher.


In the graph above, we are able to see the inverse relationship between the nominal interest rate and the quantity of money. As the nominal interest rate drops from 8% to 5%, we see the quantity of money increase from 300. The opposite is also true. If the nominal interest rate increases from 2% to 8%, we see the quantity of money decrease from 200.
Shifters of the Demand for Money Curve
- Price Level
- Real GDP
- Transaction Costs Let's look at some examples:

The Supply of Money
The monetary base of a nation is determined by the country’s central bank (FED). This means that the money supply is independent of the nominal interest rate. The supply of money will remain constant regardless of the nominal interest rate. The only way the money supply will change is as a result of monetary policy.
There are three tools that the FED uses to influence the money supply. These include the reserve requirement, the discount rate, open market operations (the buying and selling of bonds), and the federal funds rate.

When the FED uses these tools of monetary policy, they are able to either increase or decrease the money supply. The goal when the FED is using these tools is to either increase or decrease the nominal interest rate, which will cause the economy to expand or contract. We will look at this more closely when we review the money market equilibrium in the next section.

Money Market Equilibrium
Money market equilibrium is achieved when the interest rate at which the quantity of money demanded equals the quantity of money supplied. The nominal interest rate is the interest rate on the vertical axis and the quantity of money is on the horizontal axis.

Remember that the shifters of money demand include a change in the price level, a change in real GDP output, and a change in the transaction costs of spending money. The only shifter of the supply of money is the Federal Reserve.
Let's look at the various ways that the money market equilibrium change through four different examples.
Example 1:

Example 2:

Example 3:

Example 4:

Investment Demand
Investment demand is the desired quantity of investment spending by firms across the economy on physical capital and other resources for the purpose of future productivity/profitability.
There is an inverse relationship between the nominal interest rate and the quantity of investment demanded. When the nominal interest rate falls, we see an increase in the quantity of investment demanded. The opposite is also true. When the nominal interest rate rises, we see a decrease in the quantity of investment demanded.
When interest rates increase, quantity of investment demanded decreases.
When interest rates decrease, quantity of investment demanded increases.
Investment demand changes due to monetary policy conducted by the Federal Reserve. When they practice an easy monetary policy and increase the money supply, they cause the nominal interest rate to fall, causing the quantity of investment demanded to increase. When they practice a tight monetary policy and decrease the money supply, they cause the nominal interest rate to increase, causing the quantity of investment demanded to decrease.
In the graph below, the Federal Reserve increases the money supply. This action will lower the nominal interest rate, and in turn, cause the quantity of investment demanded to increase.

In the graph below, the Federal Reserve decreases the money supply. This action will raise the nominal interest rate, and in turn, cause the quantity of investment demanded to decrease.


© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.