Browse By Unit
3.6 Changes in the AD-AS Model in the Short Run
3 min read•june 18, 2024
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
GDP Determinants
In our initial discussion, we identified that there were determinants that would shift both aggregate demand and aggregate supply. The determinants of aggregate demand are the various types of spending that make up the formula for GDP:
- consumer spending 🛒
- investment spending 💵
- government spending 💰
- net exports (exports-imports) 💸 The determinants of aggregate supply include resource prices and availability, actions of the government, and productivity/technology. All of these determinants for both aggregate demand and aggregate supply can cause a shift of the corresponding curve either left (decrease) or right (increase).
Negative Supply Shock
In addition to these determinants of aggregate demand and aggregate supply, changes in the AD-AS Model can also occur from both negative supply shocks and positive supply shocks. A negative supply shock is an unexpected decrease in the availability of a key resource that temporarily decreases productivity. A negative supply shock will raise production costs and reduce the quantity that producers are willing to supply at any price level. This leads to a leftward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A real-life example of a negative supply shock is the disruptions to the world oil supplies that happen in 1973 and 1979. It was seen as a negative supply shock because it all happened at once when OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) placed an embargo on oil exports to the United States. This caused a decrease in the supply of oil and caused prices to rise. This also caused a fear that we would not be able to fill up at the gas tank, heat our homes, or run our factories.
Positive Supply Shock
A positive supply shock is an unexpected increase in the availability of a key resource that temporarily increases productivity. A positive supply shock will lower production costs and increase the quantity that producers are willing to supply at any price level. A good real-life example of a positive supply shock is the time period between 1995 and 2000 when there was an increasing use of the internet and other information technologies. This caused a huge growth in productivity.
AD⬆ leads to real GDP⬆, unemployment⬇ and price level⬆
AD⬇ leads to real GDP⬇, unemployment⬆ and price level⬇
SRAS⬆ leads to real GDP⬆, unemployment⬇ and price level⬇
SRAS⬇ leads to real GDP⬇ , unemployment⬆ and price level⬆
Let's look at some various scenarios that would cause short run changes in the AD-AS model.
Scenario # 1: Consumer Income Decreases as Taxes Increase
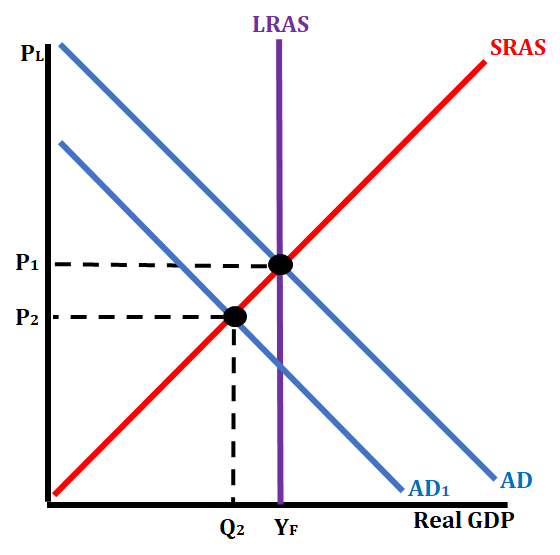
When taxes are increased, that allows for less consumer disposable income. This, in turn, will lead to consumers spending less money. The component of aggregate demand known as consumer spending will decrease, which leads to a decrease (leftward shift) of the aggregate demand curve. This causes a decrease in price level and a decrease in GDP.
Scenario # 2: The British government increases tariffs on imported inputs
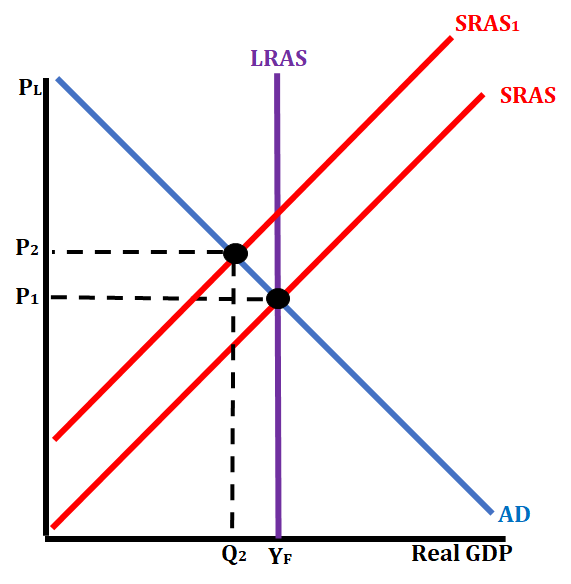
Tariffs are taxes on goods. In this particular scenario, the British government is placing tariffs on inputs (resources) that are coming into the country. That will raise the cost of these inputs (resources), making production costs greater for individual companies. With greater production costs, firms will produce less of their goods. This is shown by a decrease in the SRAS (shift to the left). This causes an increase in price level and a decrease in GDP.
Scenario # 3: Spanish exports become cheaper on the world market.
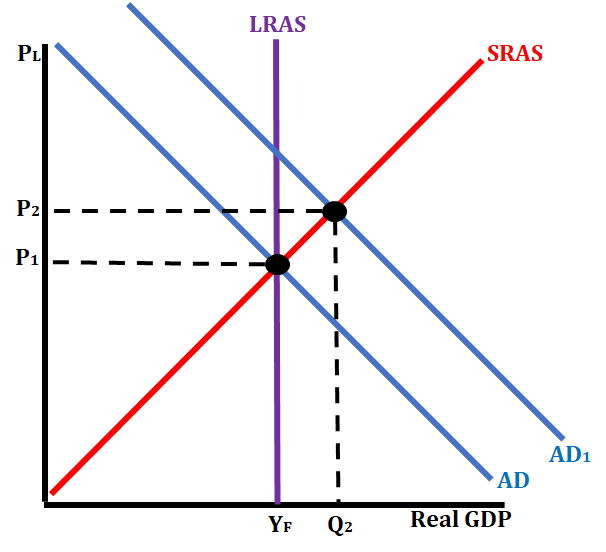
When the costs of exports become cheaper, other countries will be more willing to purchase goods from Spain. As they purchase more goods, this will affect the determinant known as net exports. When exports increase, net exports also increase. This causes an increase in aggregate demand (shift to the right) which causes an increase in price level and an increase in GDP.
Scenario #4: Corporate Taxes are reduced
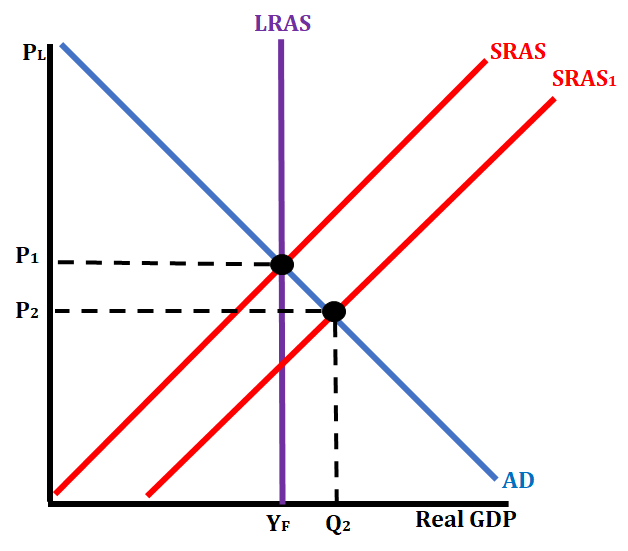
When corporate taxes are decreased, it lowers production costs for firms (businesses). With the lowering of production costs, the firms are able to increase their overall output. This is shown by shifting the SRAS to the right. This increase in the SRAS will cause the overall price level to drop and the real GDP to increase.
<< Hide Menu
3.6 Changes in the AD-AS Model in the Short Run
3 min read•june 18, 2024
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
Jeanne Stansak
Haseung Jun
GDP Determinants
In our initial discussion, we identified that there were determinants that would shift both aggregate demand and aggregate supply. The determinants of aggregate demand are the various types of spending that make up the formula for GDP:
- consumer spending 🛒
- investment spending 💵
- government spending 💰
- net exports (exports-imports) 💸 The determinants of aggregate supply include resource prices and availability, actions of the government, and productivity/technology. All of these determinants for both aggregate demand and aggregate supply can cause a shift of the corresponding curve either left (decrease) or right (increase).
Negative Supply Shock
In addition to these determinants of aggregate demand and aggregate supply, changes in the AD-AS Model can also occur from both negative supply shocks and positive supply shocks. A negative supply shock is an unexpected decrease in the availability of a key resource that temporarily decreases productivity. A negative supply shock will raise production costs and reduce the quantity that producers are willing to supply at any price level. This leads to a leftward shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve.
A real-life example of a negative supply shock is the disruptions to the world oil supplies that happen in 1973 and 1979. It was seen as a negative supply shock because it all happened at once when OPEC (Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries) placed an embargo on oil exports to the United States. This caused a decrease in the supply of oil and caused prices to rise. This also caused a fear that we would not be able to fill up at the gas tank, heat our homes, or run our factories.
Positive Supply Shock
A positive supply shock is an unexpected increase in the availability of a key resource that temporarily increases productivity. A positive supply shock will lower production costs and increase the quantity that producers are willing to supply at any price level. A good real-life example of a positive supply shock is the time period between 1995 and 2000 when there was an increasing use of the internet and other information technologies. This caused a huge growth in productivity.
AD⬆ leads to real GDP⬆, unemployment⬇ and price level⬆
AD⬇ leads to real GDP⬇, unemployment⬆ and price level⬇
SRAS⬆ leads to real GDP⬆, unemployment⬇ and price level⬇
SRAS⬇ leads to real GDP⬇ , unemployment⬆ and price level⬆
Let's look at some various scenarios that would cause short run changes in the AD-AS model.
Scenario # 1: Consumer Income Decreases as Taxes Increase

When taxes are increased, that allows for less consumer disposable income. This, in turn, will lead to consumers spending less money. The component of aggregate demand known as consumer spending will decrease, which leads to a decrease (leftward shift) of the aggregate demand curve. This causes a decrease in price level and a decrease in GDP.
Scenario # 2: The British government increases tariffs on imported inputs

Tariffs are taxes on goods. In this particular scenario, the British government is placing tariffs on inputs (resources) that are coming into the country. That will raise the cost of these inputs (resources), making production costs greater for individual companies. With greater production costs, firms will produce less of their goods. This is shown by a decrease in the SRAS (shift to the left). This causes an increase in price level and a decrease in GDP.
Scenario # 3: Spanish exports become cheaper on the world market.

When the costs of exports become cheaper, other countries will be more willing to purchase goods from Spain. As they purchase more goods, this will affect the determinant known as net exports. When exports increase, net exports also increase. This causes an increase in aggregate demand (shift to the right) which causes an increase in price level and an increase in GDP.
Scenario #4: Corporate Taxes are reduced

When corporate taxes are decreased, it lowers production costs for firms (businesses). With the lowering of production costs, the firms are able to increase their overall output. This is shown by shifting the SRAS to the right. This increase in the SRAS will cause the overall price level to drop and the real GDP to increase.

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.