Browse By Unit
3.7 Diffusion of Religion and Language
10 min read•june 18, 2024
Danna Esther Gelfand
Danna Esther Gelfand
Language
Languages can unify, diffuse, change, divide, and more. A language family is a group of languages originating from an earlier language (protolanguage-reconstructed ancestral language). The Indo-European language family is the largest language family. It includes European, some Asian, and newly adopted American languages.

Language Sub-families
Subfamilies are Divisions within a language family where the commonalities are more definite and the origin is more recent. Indo-European languages have spread through expansion and relocation diffusion. (There are 2.5 to 3.5 billion speakers. There are two theories of the origin of the Indo-European language family:
-
Anatolian dispersion (sedentary farmer) - language diffused through agriculture.
-
Kurgan Hypothesis (Nomadic warrior) - language diffused through conquest. The branches of the Indo-European language family include but are not limited to germanic, Baltic-Slavic, Roman, Celtic, and Indo-Iranian. Languages can diverge (scatter and develop variations)
-
Germanic languages reflect the expansion of peoples out of Northern Europe to the west and south ex: German, English, and Swedish.
-
Romance languages are located in areas that were once controlled by the Roman Empire. Ex: French, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese. Language divergence occurs when a language breaks down into two such as Spanish and Portuguese. Language convergence occurs when two languages form into one such as Malta forming from Maltese and English. The Sino-Tibetan language family is the second largest, originating and diffusing throughout Asian regions and territories.
Common and Mixed Languages
Lingua Francas are adopted common languages due to trade and business, such as English, Spanish, and Chinese. Creole languages (a mixture of two languages that is a native language of a group of people). It is used to describe languages in the Caribbean when slavery and colonization merged cultures. Ex: Haitian Creole.
A pidgin language is a language that develops when two or more different languages meet in one geographic region, usually a result of trading among people who speak different languages such as Swahili which combines some Bantu dialects with Arabic. When it evolves into a primary language of a region, it becomes a creole language.
Dialects
Dialects are variations of speech. Different regions throughout the United States have dialects of the English language. Someone in the southern regions may pronounce English words differently compared to someone in the northern regions of the US due to variations in vocabulary and accent.
An isogloss is a geographic “barrier” that exists between the use of one word over another.
Bilingualism
Bilingualism is the speaking of two or more languages. This proves more beneficial than monolingualism (one official language) in that it establishes cultural diversity, alliances among political figures, improved communication, tourism which is also beneficial economically, syncretism, and a sense of belonging (sense of place) among cultural landscapes of minority language speakers.
It can also have negative consequences of cultural tensions such as discrimination, increased costs for educating multiple languages as opposed to one, and making certain news resources and documents are in multiple languages. Many countries have one sole official language by law that all must speak. Ex: Argentina-Spanish, Brazil-Portuguese, France-French, Germany-German.
The United States does NOT have an official language. Africa has the most languages out of any continent. Many Africans are bilingual.
Referring back to Hierarchical Diffusion, The English language diffused through India under British colonial rule through hierarchical diffusion. The British Raj brought a new administrative system to India and the language of the ruling authority was English therefore those in office had to learn English. English spread from the ruler to the population.
Religions
Common Terms
Universalizing Religion - anyone can be a member of it. Their beliefs attract the universal population. Missionaries were sent throughout the world seeking converts. Diversity in its worshipers from various ethnic backgrounds. They spread through three main ones, Christianity, Buddhism, and Islam.
Ethnic Religion - part of a particular ethnic or political group. In order to practice the religion you must be born into it and/or through marriage. Ex: Judaism, Hinduism. Ethnic religions are found near the hearth(origin) but spread through relocation diffusion. Judaism diffused by the scattering of Jews around the world after the Roman destruction of Jerusalem in 70 AD. Ethnic religions haven’t spread primarily because in some cases, universalizing religions, replace ethnic religions.
Tribal religions are practiced in small, cultural groups. They usually combine the ethnic beliefs of tribes and local areas with animism and/or diffused religions. Ex: Shamanism.
Syncretism is the combination of multiple religious beliefs and ideals.
Animism is the belief that spirits live within objects. Ex: Shinto, the traditional religion of Japan, is highly animistic.
The Branch is a large fundamental division within a religion followed by Denomination which is a division of a branch that unites a number of local congregations in a single legal and administrative body followed by a sect which is a relatively small group that has broken away from an established denomination.
Monotheism and Polytheism are the two classifications of religion.
Monotheistic when they believe in one supreme being or god.
Polytheistic religions believe in more than one supreme deity. Polytheistic religions practiced today include Hinduism and Shintoism.
Pagans are followers of a polytheistic religion in ancient times.
Proselytic religion is a universalizing religion that tries to convert others to practice.
Fundamentalism is the literal/strict interpretation of the fundamental(basic) principles of religion.
Theocracies are governments ruled by religious laws. During the Enlightenment era, the vast majority of theocracies ended in the western hemisphere. Today, it is still practiced in countries such as Iran and Saudi Arabia.
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic universalizing religion spread throughout Europe mostly by Hierarchical and expansion diffusion. Through Relocation Diffusion it was brought to the new world. It is the largest Universalizing religion.
It is founded on the teachings of Jesus, believing that God is a Trinity and Jesus Christ is the Son of God. The three main branches of Christianity are Catholics, Orthodox, and Protestants. Roman Catholics have deep roots in Latin American culture and are present as well in Southwest Europe, Protestants present in Northwest Europe and North America, and Orthodox in Eastern Europe.
Eastern Orthodoxy is the largest single religious faith in Greece, Cyprus, and Russia.
Protestantism
Protestantism is the theological system of any of the churches of western Christendom that separated from the Roman Catholic Church during the Reformation. A Lutheran is a member of one of the Protestant churches that follow the teachings of Martin Luther. A Baptist is a member of a Christian denomination that baptizes believers by immersion and that is usually Calvinistic in doctrine. Mormonism is a term used to describe religious, ideological, and cultural aspects of the various denominations of the Latter Day Saint movement.
Protestant missionaries spread their religious beliefs throughout Sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America. The spread of the British empire diffused Protestantism into South Asia, East Asia, and the Pacific Islands with citizens residing in China, India, and Japan maintaining their strong ethnic beliefs and resisting the spread of Protestantism.
A sacred space in Christianity is a church.
Islam
Islam is based on the teachings of Mohammed, a prophet following Abraham, Moses, and David. It is the second largest universalizing religion. Those who practice Islam are Muslims, which means in Arabic “one who surrenders to God” while Islam translates to “submitting to the will of god”.
The Koran (Quran) is a sacred book. Muslims follow the tenets of their religion strictly.
The five pillars of Islam are a repetition of the Muslim creed, prayer five times daily, observance of the one month of fasting called Ramadan, almsgiving (giving to others as an act of virtue), and lastly a pilgrimage to Mecca before death.

The two branches of Islam are Sunni and Shiite. The division between the Sunni and Shia originated in a disagreement over leadership after Muhammad’s death in 632 CE. Sunnis have much more followers than Shiites.
Through expansion diffusion, it spread throughout Southwest Asia and into India after Muhammad's death. For a time they even conquered and ruled Spain. It spread through trade and migration (relocation diffusion) into Southeast Asia, Western Hemisphere, and Sub-Saharan Africa.
Islam is the predominant religion in the Middle East from North Africa to Central Asia. More than half of the world’s Muslims live in four countries outside the Middle East: Indonesia, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and India. Sacred spaces are called Mosques.
Buddhism
Buddhism is a world religion or philosophy that does not believe in worshipping gods but seeks the truth and self-awareness based on the teaching of the Buddha (Siddhartha Gautama) and holding that a state of enlightenment can be attained by suppressing worldly desire (reaching Nirvana).
Nirvana is attained through an Eightfold Path that stresses the rightness of belief, resolve, speech, action, livelihood, effort, thought, and meditation. It began in present-day Nepal (6th-century B.C.E Northern India).

The core belief is Reincarnation (reborn after dying). There are two branches: Theravada which is the oldest (practiced in Southeast Asia and Sri Lanka) and Mahayana (emphasized the search for universal salvation and is found in East Asia).
Contagious diffusion allowed for its spread in India and it attempted to compete with Islam in Northern India. Missionaries allowed for the religion/philosophy to spread throughout Asia. Through syncretism, it has been adopted with Hinduism.
In both Buddhism and Shinto, pagodas are the common architecture. They are typically built to enshrine sacred religious artifacts.
Hinduism
Hinduism originated in the Indus River Valley in Pakistan and through contagious diffusion, it spread into the Indian Subcontinent. Traders spread Hinduism into Southeast Asia and Bali. Through Relocation Diffusion it also spread as Hindus migrated in search of better opportunities.
80% of Hindus are located in India. Hinduism as mentioned previously is polytheistic, believing in hundreds of gods. The principle of reincarnation is the cornerstone of Hinduism, and their doctrine closely mirrors India’s caste system.
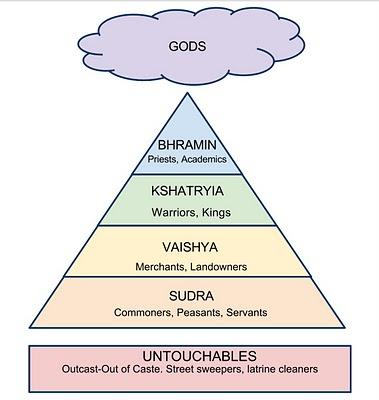
The caste system has been widely adopted into Indian Society. The image on the right depicts the Hindu Caste System in India. In Hinduism, temples are built within the home or individual community. They have a central room to house a spirit, with rooms for rituals, and outer purifying pools.
To Hindus, the Ganges (or Ganga, in Hindi) is the most sacred river in India and that's where many disperse the ashes of the deceased after cremation. It also has a collection of ancient scriptures called Vedas.
Judaism
Judaism is a monotheistic ethnic religion of Jews having its spiritual and ethical principles in the sacred Torah and in the Talmud. It emerged in The Middle East (Mesopotamian cultural hearth) and regards Jerusalem as sacred, similar to Christianity and Islam, and the Western Wall is one of their holy sites.
The Diaspora (Dispersion) of Jews occurred in response to religious persecution. The Jewish state is Israel which Jews regard as their homeland. Christianity and Islam find some of their roots in Judaism, recognizing Abraham as a Patriarch.

The three branches of Judaism are Orthodox, Conservative, and Reform. Judaism is distributed throughout parts of the Middle East and North Africa, the United States, Russia, and Europe. Sacred spaces are called Synagogues. Zionism is a movement that mainly seeks indigenous return to Jewish homelands. Being a Zionist does not equal being Pro-Israel, despite the number of people who are Pro-Israel and Zionist.
Interfaith Boundaries
Interfaith Boundaries are between the world's major faiths. Ex: Pakistan was once part of India and established itself as a Muslim state in 1947 while the Indian population is mostly Hindu. India and Pakistan have had conflict emerge over control over the northern territory of Kashmir.
Other examples include the Palestinian conflict (Judaism and Islam), Former Yugoslavia conflict between Christianity and Islam.
Intrafaith boundaries are within a major religion. Ex: Iraq Sunnis and Shiites conflict over control of the political landscape. Another example is the violent conflict between protestant Christians and Roman Catholics in Northern Ireland.
Secularism
Secularism is when religious beliefs and systems are rejected. It is rising in popularity in Europe. Autonomous religions are self-sufficient with little organization. Ex. Islam prefers to unify by faith rather than specific boundaries. Sikhism is a monotheistic universalizing religion with a cultural hearth in the Indian Subcontinent.
Confucianism
Confucianism (in china) developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius Is a system of ethics and family behavior that values public service.
Taoism (sometimes Daoism) is a philosophical, ethical, or religious tradition of Chinese origin, that emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao and it’s important to them to reflect on the mystical and magical aspects of life. In Indonesia, there is a multilayered cultural landscape.
***** SIX MAJOR RELIGIONS TO KNOW: Christianity, Islam, Judaism, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Sikhism *****
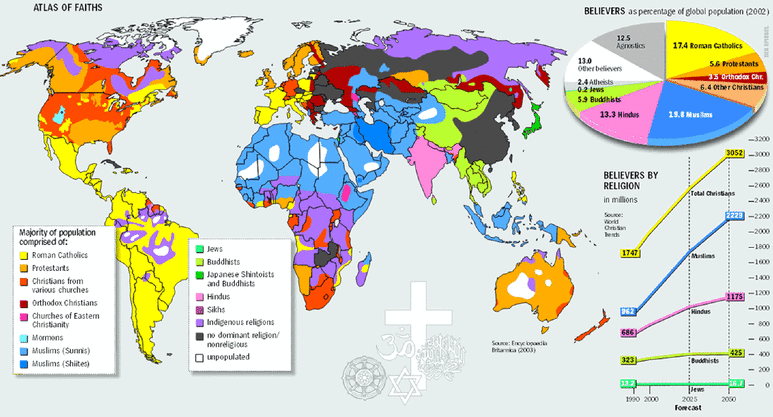
Illustrates modern extents of religions
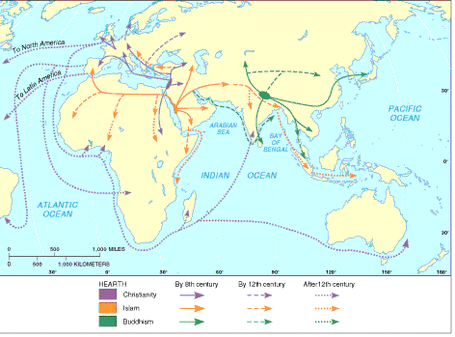
This map depicts the diffusion of the three main universalizing religions within different time periods.
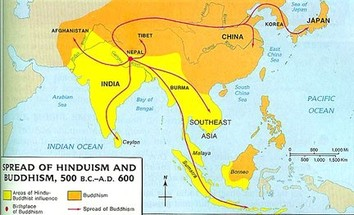
This map depicts the spread of Hinduism and Buddhism.
Ethnicity
An Ethnic group is a population of people that share a common nationality, language, culture, religion, and/or more. Race differs from an ethnic group in that the shared trait is that they originate from a common biological ancestor. Ethnic groups have migrated for centuries and settled to establish a cultural society in a certain area (charter group).
Ethnic enclaves are small areas of cities where minority cultural groups reside and some even separate themselves into ghettos either due to involuntary persecution (ex: Jewish residences in Venice) or voluntary isolation by ethnic commonalities.
Gender Roles
Cultures in less developed regions assign traditional roles based on gender. In less developed regions such as sub-Saharan Africa traditional roles of women are to care for children, cook, clean, and take care of agriculture while men hold superiority in laborious jobs providing economic stability for their families.
In more developed regions, women have more freedom to work and provide for their families' incomes. As society changes and modernizes, gender roles and societal norms change. Women's traditional roles have altered due to industrialization and they are now appreciated, educated, and accomplished in workplaces.
🎥 Watch: AP HUG - Religion and Language
<< Hide Menu
3.7 Diffusion of Religion and Language
10 min read•june 18, 2024
Danna Esther Gelfand
Danna Esther Gelfand
Language
Languages can unify, diffuse, change, divide, and more. A language family is a group of languages originating from an earlier language (protolanguage-reconstructed ancestral language). The Indo-European language family is the largest language family. It includes European, some Asian, and newly adopted American languages.

Language Sub-families
Subfamilies are Divisions within a language family where the commonalities are more definite and the origin is more recent. Indo-European languages have spread through expansion and relocation diffusion. (There are 2.5 to 3.5 billion speakers. There are two theories of the origin of the Indo-European language family:
-
Anatolian dispersion (sedentary farmer) - language diffused through agriculture.
-
Kurgan Hypothesis (Nomadic warrior) - language diffused through conquest. The branches of the Indo-European language family include but are not limited to germanic, Baltic-Slavic, Roman, Celtic, and Indo-Iranian. Languages can diverge (scatter and develop variations)
-
Germanic languages reflect the expansion of peoples out of Northern Europe to the west and south ex: German, English, and Swedish.
-
Romance languages are located in areas that were once controlled by the Roman Empire. Ex: French, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese. Language divergence occurs when a language breaks down into two such as Spanish and Portuguese. Language convergence occurs when two languages form into one such as Malta forming from Maltese and English. The Sino-Tibetan language family is the second largest, originating and diffusing throughout Asian regions and territories.
Common and Mixed Languages
Lingua Francas are adopted common languages due to trade and business, such as English, Spanish, and Chinese. Creole languages (a mixture of two languages that is a native language of a group of people). It is used to describe languages in the Caribbean when slavery and colonization merged cultures. Ex: Haitian Creole.
A pidgin language is a language that develops when two or more different languages meet in one geographic region, usually a result of trading among people who speak different languages such as Swahili which combines some Bantu dialects with Arabic. When it evolves into a primary language of a region, it becomes a creole language.
Dialects
Dialects are variations of speech. Different regions throughout the United States have dialects of the English language. Someone in the southern regions may pronounce English words differently compared to someone in the northern regions of the US due to variations in vocabulary and accent.
An isogloss is a geographic “barrier” that exists between the use of one word over another.
Bilingualism
Bilingualism is the speaking of two or more languages. This proves more beneficial than monolingualism (one official language) in that it establishes cultural diversity, alliances among political figures, improved communication, tourism which is also beneficial economically, syncretism, and a sense of belonging (sense of place) among cultural landscapes of minority language speakers.
It can also have negative consequences of cultural tensions such as discrimination, increased costs for educating multiple languages as opposed to one, and making certain news resources and documents are in multiple languages. Many countries have one sole official language by law that all must speak. Ex: Argentina-Spanish, Brazil-Portuguese, France-French, Germany-German.
The United States does NOT have an official language. Africa has the most languages out of any continent. Many Africans are bilingual.
Referring back to Hierarchical Diffusion, The English language diffused through India under British colonial rule through hierarchical diffusion. The British Raj brought a new administrative system to India and the language of the ruling authority was English therefore those in office had to learn English. English spread from the ruler to the population.
Religions
Common Terms
Universalizing Religion - anyone can be a member of it. Their beliefs attract the universal population. Missionaries were sent throughout the world seeking converts. Diversity in its worshipers from various ethnic backgrounds. They spread through three main ones, Christianity, Buddhism, and Islam.
Ethnic Religion - part of a particular ethnic or political group. In order to practice the religion you must be born into it and/or through marriage. Ex: Judaism, Hinduism. Ethnic religions are found near the hearth(origin) but spread through relocation diffusion. Judaism diffused by the scattering of Jews around the world after the Roman destruction of Jerusalem in 70 AD. Ethnic religions haven’t spread primarily because in some cases, universalizing religions, replace ethnic religions.
Tribal religions are practiced in small, cultural groups. They usually combine the ethnic beliefs of tribes and local areas with animism and/or diffused religions. Ex: Shamanism.
Syncretism is the combination of multiple religious beliefs and ideals.
Animism is the belief that spirits live within objects. Ex: Shinto, the traditional religion of Japan, is highly animistic.
The Branch is a large fundamental division within a religion followed by Denomination which is a division of a branch that unites a number of local congregations in a single legal and administrative body followed by a sect which is a relatively small group that has broken away from an established denomination.
Monotheism and Polytheism are the two classifications of religion.
Monotheistic when they believe in one supreme being or god.
Polytheistic religions believe in more than one supreme deity. Polytheistic religions practiced today include Hinduism and Shintoism.
Pagans are followers of a polytheistic religion in ancient times.
Proselytic religion is a universalizing religion that tries to convert others to practice.
Fundamentalism is the literal/strict interpretation of the fundamental(basic) principles of religion.
Theocracies are governments ruled by religious laws. During the Enlightenment era, the vast majority of theocracies ended in the western hemisphere. Today, it is still practiced in countries such as Iran and Saudi Arabia.
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic universalizing religion spread throughout Europe mostly by Hierarchical and expansion diffusion. Through Relocation Diffusion it was brought to the new world. It is the largest Universalizing religion.
It is founded on the teachings of Jesus, believing that God is a Trinity and Jesus Christ is the Son of God. The three main branches of Christianity are Catholics, Orthodox, and Protestants. Roman Catholics have deep roots in Latin American culture and are present as well in Southwest Europe, Protestants present in Northwest Europe and North America, and Orthodox in Eastern Europe.
Eastern Orthodoxy is the largest single religious faith in Greece, Cyprus, and Russia.
Protestantism
Protestantism is the theological system of any of the churches of western Christendom that separated from the Roman Catholic Church during the Reformation. A Lutheran is a member of one of the Protestant churches that follow the teachings of Martin Luther. A Baptist is a member of a Christian denomination that baptizes believers by immersion and that is usually Calvinistic in doctrine. Mormonism is a term used to describe religious, ideological, and cultural aspects of the various denominations of the Latter Day Saint movement.
Protestant missionaries spread their religious beliefs throughout Sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America. The spread of the British empire diffused Protestantism into South Asia, East Asia, and the Pacific Islands with citizens residing in China, India, and Japan maintaining their strong ethnic beliefs and resisting the spread of Protestantism.
A sacred space in Christianity is a church.
Islam
Islam is based on the teachings of Mohammed, a prophet following Abraham, Moses, and David. It is the second largest universalizing religion. Those who practice Islam are Muslims, which means in Arabic “one who surrenders to God” while Islam translates to “submitting to the will of god”.
The Koran (Quran) is a sacred book. Muslims follow the tenets of their religion strictly.
The five pillars of Islam are a repetition of the Muslim creed, prayer five times daily, observance of the one month of fasting called Ramadan, almsgiving (giving to others as an act of virtue), and lastly a pilgrimage to Mecca before death.

The two branches of Islam are Sunni and Shiite. The division between the Sunni and Shia originated in a disagreement over leadership after Muhammad’s death in 632 CE. Sunnis have much more followers than Shiites.
Through expansion diffusion, it spread throughout Southwest Asia and into India after Muhammad's death. For a time they even conquered and ruled Spain. It spread through trade and migration (relocation diffusion) into Southeast Asia, Western Hemisphere, and Sub-Saharan Africa.
Islam is the predominant religion in the Middle East from North Africa to Central Asia. More than half of the world’s Muslims live in four countries outside the Middle East: Indonesia, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and India. Sacred spaces are called Mosques.
Buddhism
Buddhism is a world religion or philosophy that does not believe in worshipping gods but seeks the truth and self-awareness based on the teaching of the Buddha (Siddhartha Gautama) and holding that a state of enlightenment can be attained by suppressing worldly desire (reaching Nirvana).
Nirvana is attained through an Eightfold Path that stresses the rightness of belief, resolve, speech, action, livelihood, effort, thought, and meditation. It began in present-day Nepal (6th-century B.C.E Northern India).

The core belief is Reincarnation (reborn after dying). There are two branches: Theravada which is the oldest (practiced in Southeast Asia and Sri Lanka) and Mahayana (emphasized the search for universal salvation and is found in East Asia).
Contagious diffusion allowed for its spread in India and it attempted to compete with Islam in Northern India. Missionaries allowed for the religion/philosophy to spread throughout Asia. Through syncretism, it has been adopted with Hinduism.
In both Buddhism and Shinto, pagodas are the common architecture. They are typically built to enshrine sacred religious artifacts.
Hinduism
Hinduism originated in the Indus River Valley in Pakistan and through contagious diffusion, it spread into the Indian Subcontinent. Traders spread Hinduism into Southeast Asia and Bali. Through Relocation Diffusion it also spread as Hindus migrated in search of better opportunities.
80% of Hindus are located in India. Hinduism as mentioned previously is polytheistic, believing in hundreds of gods. The principle of reincarnation is the cornerstone of Hinduism, and their doctrine closely mirrors India’s caste system.

The caste system has been widely adopted into Indian Society. The image on the right depicts the Hindu Caste System in India. In Hinduism, temples are built within the home or individual community. They have a central room to house a spirit, with rooms for rituals, and outer purifying pools.
To Hindus, the Ganges (or Ganga, in Hindi) is the most sacred river in India and that's where many disperse the ashes of the deceased after cremation. It also has a collection of ancient scriptures called Vedas.
Judaism
Judaism is a monotheistic ethnic religion of Jews having its spiritual and ethical principles in the sacred Torah and in the Talmud. It emerged in The Middle East (Mesopotamian cultural hearth) and regards Jerusalem as sacred, similar to Christianity and Islam, and the Western Wall is one of their holy sites.
The Diaspora (Dispersion) of Jews occurred in response to religious persecution. The Jewish state is Israel which Jews regard as their homeland. Christianity and Islam find some of their roots in Judaism, recognizing Abraham as a Patriarch.

The three branches of Judaism are Orthodox, Conservative, and Reform. Judaism is distributed throughout parts of the Middle East and North Africa, the United States, Russia, and Europe. Sacred spaces are called Synagogues. Zionism is a movement that mainly seeks indigenous return to Jewish homelands. Being a Zionist does not equal being Pro-Israel, despite the number of people who are Pro-Israel and Zionist.
Interfaith Boundaries
Interfaith Boundaries are between the world's major faiths. Ex: Pakistan was once part of India and established itself as a Muslim state in 1947 while the Indian population is mostly Hindu. India and Pakistan have had conflict emerge over control over the northern territory of Kashmir.
Other examples include the Palestinian conflict (Judaism and Islam), Former Yugoslavia conflict between Christianity and Islam.
Intrafaith boundaries are within a major religion. Ex: Iraq Sunnis and Shiites conflict over control of the political landscape. Another example is the violent conflict between protestant Christians and Roman Catholics in Northern Ireland.
Secularism
Secularism is when religious beliefs and systems are rejected. It is rising in popularity in Europe. Autonomous religions are self-sufficient with little organization. Ex. Islam prefers to unify by faith rather than specific boundaries. Sikhism is a monotheistic universalizing religion with a cultural hearth in the Indian Subcontinent.
Confucianism
Confucianism (in china) developed from the teachings of the Chinese philosopher Confucius Is a system of ethics and family behavior that values public service.
Taoism (sometimes Daoism) is a philosophical, ethical, or religious tradition of Chinese origin, that emphasizes living in harmony with the Tao and it’s important to them to reflect on the mystical and magical aspects of life. In Indonesia, there is a multilayered cultural landscape.
***** SIX MAJOR RELIGIONS TO KNOW: Christianity, Islam, Judaism, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Sikhism *****

Illustrates modern extents of religions

This map depicts the diffusion of the three main universalizing religions within different time periods.

This map depicts the spread of Hinduism and Buddhism.

Ethnicity
An Ethnic group is a population of people that share a common nationality, language, culture, religion, and/or more. Race differs from an ethnic group in that the shared trait is that they originate from a common biological ancestor. Ethnic groups have migrated for centuries and settled to establish a cultural society in a certain area (charter group).
Ethnic enclaves are small areas of cities where minority cultural groups reside and some even separate themselves into ghettos either due to involuntary persecution (ex: Jewish residences in Venice) or voluntary isolation by ethnic commonalities.
Gender Roles
Cultures in less developed regions assign traditional roles based on gender. In less developed regions such as sub-Saharan Africa traditional roles of women are to care for children, cook, clean, and take care of agriculture while men hold superiority in laborious jobs providing economic stability for their families.
In more developed regions, women have more freedom to work and provide for their families' incomes. As society changes and modernizes, gender roles and societal norms change. Women's traditional roles have altered due to industrialization and they are now appreciated, educated, and accomplished in workplaces.
🎥 Watch: AP HUG - Religion and Language

© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.