Browse By Unit
Sana Fatah
Riya Patel
Sana Fatah
Riya Patel
Geographic Data
Geographic data is any data that is associated with a specific location on the Earth's surface. It can include a wide range of information, such as coordinates (latitude and longitude), names of places, addresses, terrain features, land use patterns, population statistics, and many other types of data.
Names of Places
There are many different types of places that have names, including cities, towns, villages, regions, countries, and natural features. Here are a few examples of names of places:
- Cities: Examples of city names include New York, London, Paris, Rome, and Tokyo.
- Towns: Examples of town names include Millville, Maplewood, and Westfield.
- Villages: Examples of village names include Hogsmeade, Twin Peaks, and Bon Temps.
- Regions: Examples of region names include the Southwest, the Midwest, and the Deep South.
- Countries: Examples of country names include the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Australia.
- Natural features: Examples of natural feature names include Mount Everest, the Grand Canyon, and the Amazon River.
Terrain Features
Terrain features are the natural features of the Earth's surface, such as mountains, valleys, rivers, lakes, and oceans. Here are a few examples of terrain features:
- Mountains: Mountains are large landforms that rise significantly above the surrounding land. They can be formed by a variety of geological processes, such as tectonic activity or erosion. Examples of mountains include the Rocky Mountains, the Himalayas, and Mount Everest.
- Valleys: Valleys are low areas of land that are surrounded by higher land, such as mountains or hills. They can be formed by a variety of processes, including erosion and tectonic activity. Examples of valleys include the Grand Canyon, the Shenandoah Valley, and the Rift Valley.
- Rivers: Rivers are natural waterways that flow from higher to lower elevations, and are typically fed by rainwater and melting snow. They can be used for transportation, irrigation, and as a source of drinking water. Examples of rivers include the Amazon, the Nile, and the Mississippi.
- Lakes: Lakes are bodies of standing water that are surrounded by land. They can be formed by a variety of processes, including glacial activity, river erosion, and damming. Examples of lakes include Lake Superior, Lake Baikal, and Lake Victoria.
- Oceans: Oceans are vast bodies of saltwater that cover most of the Earth's surface. They are home to a wide variety of marine life, and are important for transportation, recreation, and as a source of food. Examples of oceans include the Atlantic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, and the Indian Ocean.
Land Use Patterns
Land use patterns refer to the way that land is used or managed within a specific area. Here are a few examples of land use patterns:
- Agricultural: Land that is used for growing crops or raising animals is considered agricultural land. This may include land used for traditional farming, as well as land used for specialty crops such as vineyards or orchards.
- Residential: Land that is used for housing is considered residential land. This may include single-family homes, apartments, and other types of dwellings.
- Commercial: Land that is used for business or commerce is considered commercial land. This may include land used for retail stores, office buildings, and other types of commercial development.
- Industrial: Land that is used for manufacturing or other types of industrial activity is considered industrial land. This may include land used for factories, warehouses, and other types of industrial development.
- Natural: Land that is left in a natural state, or that is used for conservation or recreation purposes, is considered natural land. This may include land used for parks, forests, or wildlife habitats.
Population Statistics
Population statistics are numerical data that describe the characteristics of a population, such as size, age, gender, and other demographic characteristics. Here are a few examples of population statistics:
- Total population: The total population is the number of people living within a specific area, such as a city, state, or country.
- Population density: Population density is a measure of how many people live in a specific area, typically expressed as the number of people per square mile or square kilometer.
- Age structure: The age structure of a population refers to the distribution of people by age group, such as children, working-age adults, and seniors.
- Gender ratio: The gender ratio is the ratio of males to females within a population.
- Birth rate: The birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people in a population in a given year.
- Death rate: The death rate is the number of deaths per 1,000 people in a population in a given year.
- Life expectancy: Life expectancy is the average number of years that a person can expect to live in a given population.
It is important because it provides information about the location and characteristics of features on the Earth's surface. This information is used in a wide range of fields and applications, such as transportation, urban planning, environmental management, natural resource management, and many others.
Geographic data can be used to create maps, which are powerful tools for visualizing and understanding spatial relationships and patterns. It can also be used to analyze and understand the distribution and movement of people, animals, and other phenomena on the Earth's surface.
Geographic data is also important because it can help us make informed decisions about how to use and manage the Earth's resources. For example, it can be used to identify areas that are at risk of natural disasters, or to identify areas that are suitable for agriculture or urban development.
When you want to go on a road trip, how do you navigate? Do you have a stack of endless roadmaps? Or do you open up Google Maps on your phone? Most likely, the second option. This makes us wonder, what are all of the geospatial technologies that we have access to?
I bet you have a stack of roadmaps in your car that you use when you go on a road trip. Just kidding. You open up Google Maps on your phone. What are the geospatial technologies we have access to?
- Global Positioning System (GPS): used for navigation, provides your precise location in relation to surrounding areas and your destination
- Remote sensing: satellites orbit Earth and send the data back to Earth
- Geographic Information System (GIS): a computer system that stores information about locations in “layers”
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic data is often collected and organized using geographic information systems (GIS), which are specialized software tools that allow users to map, analyze, and visualize spatial data. GIS can be used for a wide range of applications, including environmental studies, transportation planning, public health, natural resource management, and many other fields.
GIS is particularly important because it allows us to integrate different types of data and to analyze them in the context of their location. This means that we can better understand the relationships between different phenomena and how they are affected by their location and surroundings.
There are many examples of geographic information systems (GIS) being used in a variety of fields and applications. Here are a few examples:
- Urban planning: GIS can be used to create maps and analyze data related to land use, population density, transportation networks, and other factors that are relevant to urban planning. This information can help city planners make informed decisions about how to best use and develop land within a city.
- Environmental management: GIS can be used to map and analyze data related to natural resources, such as water, forests, and wildlife. This information can be used to monitor and manage the health of these resources, and to make decisions about how to best use and conserve them.
- Disaster response: GIS can be used to map and analyze data related to natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods. This information can help emergency responders and government agencies plan and coordinate their efforts to respond to and recover from these events.
- Agriculture: GIS can be used to map and analyze data related to crop production, soil conditions, and other factors that are relevant to agriculture. This information can help farmers optimize their use of resources and make more informed decisions about how to manage their land.
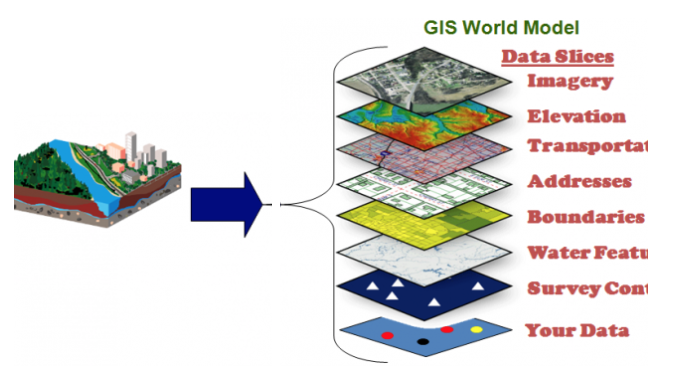
A layer represents a different piece of human or environmental information (such as cities, highways, landforms, fast food restaurants)
🎥 Watch: AP HUG - Maps, Maps, Maps
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system that allows users to determine their precise location, velocity, and time anywhere on the Earth's surface. It works by receiving signals from a network of orbiting satellites and using these signals to calculate the user's position. GPS is widely used in a variety of applications, including transportation, mapping, and location-based services.
GPS data is a type of geographic data that is collected and recorded using GPS technology. It consists of coordinates (latitude and longitude), as well as other types of information such as altitude, speed, and time. GPS data is often used in conjunction with other types of geographic data, such as maps, aerial or satellite imagery, and geospatial databases, to create more comprehensive and accurate representations of the Earth's surface.
GPS data is used in a wide range of applications, including navigation and location-based services, such as map apps and ride-sharing services. It is also used in fields such as surveying, agriculture, and environmental management, to help map and monitor changes in the landscape and natural resources.
In addition to its practical applications, GPS is also important because it has played a significant role in the development of new technologies and industries. For example, the widespread adoption of GPS has led to the development of new location-based services, such as map apps and ride-sharing services, which have transformed the way we move around and interact with our environment.
Here are a few examples of GPS:
- Navigation: GPS is widely used in navigation devices, such as car GPS systems and smartphone apps, to help people find their way from one place to another. GPS can provide turn-by-turn directions, and can also be used to search for nearby points of interest, such as gas stations or restaurants.
- Transportation: GPS is used in a variety of transportation applications, including fleet management, asset tracking, and public transit. For example, GPS can be used to track the location and movement of buses, trucks, or delivery vehicles, and to optimize routes and schedules.
- Agriculture: GPS is used in precision agriculture to help farmers optimize the use of resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides. For example, GPS can be used to create maps of fields and to track the movement of farm equipment, and to apply inputs in precise amounts at specific locations.
- Environmental management: GPS is used to map and monitor natural resources, such as forests, wetlands, and wildlife habitats. It can also be used to track the movement of animals, and to monitor environmental conditions such as air and water quality.
Remote Sensing
Geographic data is also often used in conjunction with remote sensing, which is the use of satellite or aerial imagery to collect data about the Earth's surface. Together, these technologies allow us to better understand the spatial patterns and relationships that exist on the Earth's surface, and to make informed decisions based on this information.
Remote sensing is particularly useful for applications where it is difficult or impractical to collect data on the ground, such as in remote or inaccessible areas, or in situations where it is not safe for humans to go. It can also be used to monitor changes in the Earth's surface over time, by collecting imagery at regular intervals.
Remote sensing is used in a wide range of fields and applications, including environmental monitoring, land use and land cover mapping, natural resource management, and many others. It is a powerful tool that can provide valuable information about the Earth's surface and the processes that are taking place there.
Here are a few examples of how remote sensing is used:
- Monitoring land use and land cover: Remote sensing can be used to map and monitor changes in land use and land cover over time. This information can be used to understand how humans are affecting the landscape, and to make decisions about land management and conservation.
- Mapping and monitoring natural resources: Remote sensing can be used to map and monitor natural resources such as forests, crops, water bodies, and minerals. This information can be used to understand how these resources are being used and managed, and to make decisions about their conservation and use.
- Disaster response: Remote sensing can be used to quickly assess the damage caused by natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods. This information can help emergency responders and government agencies plan and coordinate their efforts to respond to and recover from these events.
- Environmental monitoring: Remote sensing can be used to monitor environmental conditions such as air and water quality, and to track the health of ecosystems over time. This information can be used to understand the impacts of human activities on the environment, and to make informed decisions about how to protect and conserve natural resources.
<< Hide Menu
Sana Fatah
Riya Patel
Sana Fatah
Riya Patel
Geographic Data
Geographic data is any data that is associated with a specific location on the Earth's surface. It can include a wide range of information, such as coordinates (latitude and longitude), names of places, addresses, terrain features, land use patterns, population statistics, and many other types of data.
Names of Places
There are many different types of places that have names, including cities, towns, villages, regions, countries, and natural features. Here are a few examples of names of places:
- Cities: Examples of city names include New York, London, Paris, Rome, and Tokyo.
- Towns: Examples of town names include Millville, Maplewood, and Westfield.
- Villages: Examples of village names include Hogsmeade, Twin Peaks, and Bon Temps.
- Regions: Examples of region names include the Southwest, the Midwest, and the Deep South.
- Countries: Examples of country names include the United States, Canada, Brazil, and Australia.
- Natural features: Examples of natural feature names include Mount Everest, the Grand Canyon, and the Amazon River.
Terrain Features
Terrain features are the natural features of the Earth's surface, such as mountains, valleys, rivers, lakes, and oceans. Here are a few examples of terrain features:
- Mountains: Mountains are large landforms that rise significantly above the surrounding land. They can be formed by a variety of geological processes, such as tectonic activity or erosion. Examples of mountains include the Rocky Mountains, the Himalayas, and Mount Everest.
- Valleys: Valleys are low areas of land that are surrounded by higher land, such as mountains or hills. They can be formed by a variety of processes, including erosion and tectonic activity. Examples of valleys include the Grand Canyon, the Shenandoah Valley, and the Rift Valley.
- Rivers: Rivers are natural waterways that flow from higher to lower elevations, and are typically fed by rainwater and melting snow. They can be used for transportation, irrigation, and as a source of drinking water. Examples of rivers include the Amazon, the Nile, and the Mississippi.
- Lakes: Lakes are bodies of standing water that are surrounded by land. They can be formed by a variety of processes, including glacial activity, river erosion, and damming. Examples of lakes include Lake Superior, Lake Baikal, and Lake Victoria.
- Oceans: Oceans are vast bodies of saltwater that cover most of the Earth's surface. They are home to a wide variety of marine life, and are important for transportation, recreation, and as a source of food. Examples of oceans include the Atlantic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean, and the Indian Ocean.
Land Use Patterns
Land use patterns refer to the way that land is used or managed within a specific area. Here are a few examples of land use patterns:
- Agricultural: Land that is used for growing crops or raising animals is considered agricultural land. This may include land used for traditional farming, as well as land used for specialty crops such as vineyards or orchards.
- Residential: Land that is used for housing is considered residential land. This may include single-family homes, apartments, and other types of dwellings.
- Commercial: Land that is used for business or commerce is considered commercial land. This may include land used for retail stores, office buildings, and other types of commercial development.
- Industrial: Land that is used for manufacturing or other types of industrial activity is considered industrial land. This may include land used for factories, warehouses, and other types of industrial development.
- Natural: Land that is left in a natural state, or that is used for conservation or recreation purposes, is considered natural land. This may include land used for parks, forests, or wildlife habitats.
Population Statistics
Population statistics are numerical data that describe the characteristics of a population, such as size, age, gender, and other demographic characteristics. Here are a few examples of population statistics:
- Total population: The total population is the number of people living within a specific area, such as a city, state, or country.
- Population density: Population density is a measure of how many people live in a specific area, typically expressed as the number of people per square mile or square kilometer.
- Age structure: The age structure of a population refers to the distribution of people by age group, such as children, working-age adults, and seniors.
- Gender ratio: The gender ratio is the ratio of males to females within a population.
- Birth rate: The birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people in a population in a given year.
- Death rate: The death rate is the number of deaths per 1,000 people in a population in a given year.
- Life expectancy: Life expectancy is the average number of years that a person can expect to live in a given population.
It is important because it provides information about the location and characteristics of features on the Earth's surface. This information is used in a wide range of fields and applications, such as transportation, urban planning, environmental management, natural resource management, and many others.
Geographic data can be used to create maps, which are powerful tools for visualizing and understanding spatial relationships and patterns. It can also be used to analyze and understand the distribution and movement of people, animals, and other phenomena on the Earth's surface.
Geographic data is also important because it can help us make informed decisions about how to use and manage the Earth's resources. For example, it can be used to identify areas that are at risk of natural disasters, or to identify areas that are suitable for agriculture or urban development.
When you want to go on a road trip, how do you navigate? Do you have a stack of endless roadmaps? Or do you open up Google Maps on your phone? Most likely, the second option. This makes us wonder, what are all of the geospatial technologies that we have access to?
I bet you have a stack of roadmaps in your car that you use when you go on a road trip. Just kidding. You open up Google Maps on your phone. What are the geospatial technologies we have access to?
- Global Positioning System (GPS): used for navigation, provides your precise location in relation to surrounding areas and your destination
- Remote sensing: satellites orbit Earth and send the data back to Earth
- Geographic Information System (GIS): a computer system that stores information about locations in “layers”
Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic data is often collected and organized using geographic information systems (GIS), which are specialized software tools that allow users to map, analyze, and visualize spatial data. GIS can be used for a wide range of applications, including environmental studies, transportation planning, public health, natural resource management, and many other fields.
GIS is particularly important because it allows us to integrate different types of data and to analyze them in the context of their location. This means that we can better understand the relationships between different phenomena and how they are affected by their location and surroundings.
There are many examples of geographic information systems (GIS) being used in a variety of fields and applications. Here are a few examples:
- Urban planning: GIS can be used to create maps and analyze data related to land use, population density, transportation networks, and other factors that are relevant to urban planning. This information can help city planners make informed decisions about how to best use and develop land within a city.
- Environmental management: GIS can be used to map and analyze data related to natural resources, such as water, forests, and wildlife. This information can be used to monitor and manage the health of these resources, and to make decisions about how to best use and conserve them.
- Disaster response: GIS can be used to map and analyze data related to natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods. This information can help emergency responders and government agencies plan and coordinate their efforts to respond to and recover from these events.
- Agriculture: GIS can be used to map and analyze data related to crop production, soil conditions, and other factors that are relevant to agriculture. This information can help farmers optimize their use of resources and make more informed decisions about how to manage their land.

A layer represents a different piece of human or environmental information (such as cities, highways, landforms, fast food restaurants)
🎥 Watch: AP HUG - Maps, Maps, Maps
Global Positioning System (GPS)
Global Positioning System (GPS) is a satellite-based navigation system that allows users to determine their precise location, velocity, and time anywhere on the Earth's surface. It works by receiving signals from a network of orbiting satellites and using these signals to calculate the user's position. GPS is widely used in a variety of applications, including transportation, mapping, and location-based services.
GPS data is a type of geographic data that is collected and recorded using GPS technology. It consists of coordinates (latitude and longitude), as well as other types of information such as altitude, speed, and time. GPS data is often used in conjunction with other types of geographic data, such as maps, aerial or satellite imagery, and geospatial databases, to create more comprehensive and accurate representations of the Earth's surface.
GPS data is used in a wide range of applications, including navigation and location-based services, such as map apps and ride-sharing services. It is also used in fields such as surveying, agriculture, and environmental management, to help map and monitor changes in the landscape and natural resources.
In addition to its practical applications, GPS is also important because it has played a significant role in the development of new technologies and industries. For example, the widespread adoption of GPS has led to the development of new location-based services, such as map apps and ride-sharing services, which have transformed the way we move around and interact with our environment.
Here are a few examples of GPS:
- Navigation: GPS is widely used in navigation devices, such as car GPS systems and smartphone apps, to help people find their way from one place to another. GPS can provide turn-by-turn directions, and can also be used to search for nearby points of interest, such as gas stations or restaurants.
- Transportation: GPS is used in a variety of transportation applications, including fleet management, asset tracking, and public transit. For example, GPS can be used to track the location and movement of buses, trucks, or delivery vehicles, and to optimize routes and schedules.
- Agriculture: GPS is used in precision agriculture to help farmers optimize the use of resources such as water, fertilizers, and pesticides. For example, GPS can be used to create maps of fields and to track the movement of farm equipment, and to apply inputs in precise amounts at specific locations.
- Environmental management: GPS is used to map and monitor natural resources, such as forests, wetlands, and wildlife habitats. It can also be used to track the movement of animals, and to monitor environmental conditions such as air and water quality.
Remote Sensing
Geographic data is also often used in conjunction with remote sensing, which is the use of satellite or aerial imagery to collect data about the Earth's surface. Together, these technologies allow us to better understand the spatial patterns and relationships that exist on the Earth's surface, and to make informed decisions based on this information.
Remote sensing is particularly useful for applications where it is difficult or impractical to collect data on the ground, such as in remote or inaccessible areas, or in situations where it is not safe for humans to go. It can also be used to monitor changes in the Earth's surface over time, by collecting imagery at regular intervals.
Remote sensing is used in a wide range of fields and applications, including environmental monitoring, land use and land cover mapping, natural resource management, and many others. It is a powerful tool that can provide valuable information about the Earth's surface and the processes that are taking place there.
Here are a few examples of how remote sensing is used:
- Monitoring land use and land cover: Remote sensing can be used to map and monitor changes in land use and land cover over time. This information can be used to understand how humans are affecting the landscape, and to make decisions about land management and conservation.
- Mapping and monitoring natural resources: Remote sensing can be used to map and monitor natural resources such as forests, crops, water bodies, and minerals. This information can be used to understand how these resources are being used and managed, and to make decisions about their conservation and use.
- Disaster response: Remote sensing can be used to quickly assess the damage caused by natural disasters such as earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods. This information can help emergency responders and government agencies plan and coordinate their efforts to respond to and recover from these events.
- Environmental monitoring: Remote sensing can be used to monitor environmental conditions such as air and water quality, and to track the health of ecosystems over time. This information can be used to understand the impacts of human activities on the environment, and to make informed decisions about how to protect and conserve natural resources.

© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.