Browse By Unit
Jillian Holbrook
Jillian Holbrook
New Ideas and Methods
Individualism and a belief in logic among humans inspired intellectuals of the time to read and study Classical writings. 💭 Many found discrepancies and flaws in these ancient Greek and Roman texts and began experimenting with their own observations and tests to prove or disprove the writings.
The Scientific Method
In 1621, a lawyer and philosopher, Francis Bacon, published the scientific method. It was a formal series of steps in which one could form a hypothesis, test the hypothesis, and develop a conclusion based on that test. Then, one could take that conclusion, if insufficient, and retest using different methods or criteria.
Bacon believed in the Empirical Theory- that all knowledge is derived from observation and sense-based information. He also believed that information should be tested through this method, and once tested, conclusions should be made. This style of reasoning is called inductive reasoning- where limited evidence is needed to prove something true, and generalizations are made based on observations.
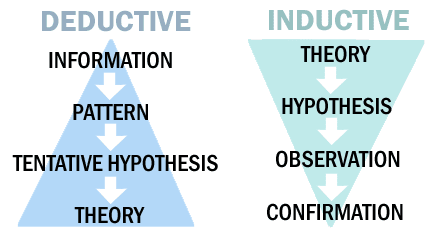
Example: I see a bird outside, and it is white. Therefore, all birds I see are white.
In 1637, mathematician and philosopher Rene Descartes published his method of reasoning, also using the scientific method. However, Descartes believed in deductive reasoning, in which information is collected, patterns are recognized, and then the scientific method is used. Deductive reasoning is more accurate than inductive reasoning.
Example: I study birds of different kinds from different locations and notice many different colors. I note that brightly colored birds tend to hail from tropical areas, white birds mainly live close to oceans, and black-feathered birds remain inland. While not all patterns are true for each bird, it is much more specific than the generalizations proposed by inductive reasoning. 🐦
Anatomy and Medicine
The previously accepted humoral theory of disease proposed that there were four main liquids in the body that required balance: blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile. Common belief saw pain as a result of these fluids being out of balance, contaminated, or not mixed properly.
During the Scientific Revolution, scientists began studying the human anatomy, bodily systems, and medicine to better understand how to combat illnesses, which challenged the classical ideas proposed by Galen, a Greek physician.
William Harvey 🫀
The most important discovery of this time regarding human anatomy and medicine was William Harvey’s discovery of blood circulation. Harvey employed extensive observations and experiments, and his work provided a new understanding of the circulatory system as a whole, which was widely accepted and adopted by the medical community. After Harvey disproved the formerly accepted humoral theory and proposed an integrated human body, other scientists began to study the functions of the human body during the development of physiology, which revolutionized how people understood anatomy and disease.
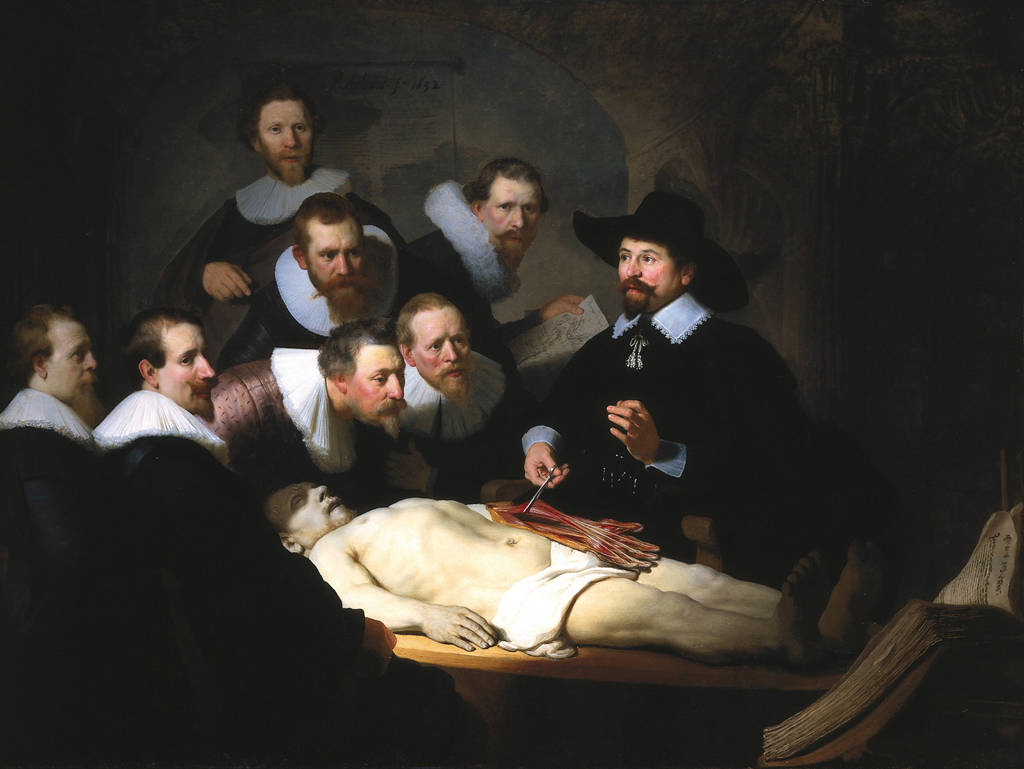
Image Courtesy of Western Civilization II Guides
New Technology and Medical Practices 🔬
The development of the microscope and the discovery of microorganisms also played a significant role in challenging traditional beliefs about the causes of disease. Scientists could now observe small organisms, such as bacteria and viruses. Additionally, the scientific revolution also saw the rise of new medical practices such as surgery and the use of anatomy and physiology in diagnosis and treatment.
Astronomy and Alchemy
Developments in Astronomy 🪐
Nicholas Copernicus developed the Heliocentric Theory in opposition to the Geocentric Theory. Copernicus shared his theory that all planets in our solar system revolve around the sun with other scientists. However, the Catholic Church’s doctrine stated that Ptolemy’s 2nd-century Geocentric Theory, in which all planets revolve around Earth, was the accepted belief, and no one had challenged it with any authenticity before Copernicus.
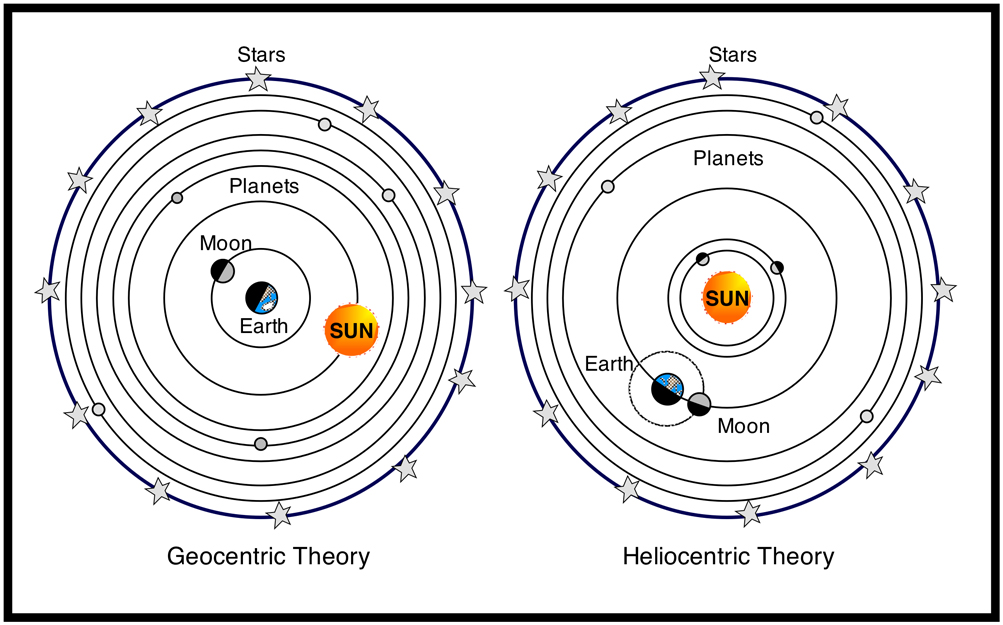
Image Courtesy of Little Thinkers Blog
- The Heliocentric Theory: The most significant contribution to astronomy during the scientific revolution was the development of the heliocentric model of the solar system by Copernicus, which proposed that the sun, not the earth, was at the center of the solar system. This challenged the traditional geocentric model, which placed the earth at the center of the universe.
- Kepler's laws of planetary motion: Johannes Kepler formulated three laws of planetary motion, which accurately described the motion of planets around the sun. This was a major advancement in astronomy, as it helped explain the observed motion of planets.
- Galileo's telescope: Galileo Galilei's development and use of the telescope to observe the night sky led to several important discoveries, including the observation of mountains on the moon, the phases of Venus, and the presence of four large moons orbiting Jupiter. By tracking planetary motion, Galileo found that Earth did move within the solar system, supporting Copernicus' proposals of heliocentricism.
- Discovery of new astronomical objects: The scientific revolution saw the discovery of new astronomical objects, such as comets, nebulae, and galaxies, which expanded the understanding of the universe.
- Improved astronomical instruments: The invention of more advanced astronomical instruments, such as the sextant and the quadrant, improved the accuracy of astronomical measurements and allowed for more detailed observations of the sky.
- The introduction of mathematical methods: Introduction of mathematical methods to the field of astronomy improved the accuracy of astronomical predictions. Isaac Newton, through the use of mathematics, developed the Three Laws of Motion, which proved that Earth revolves around the sun. While none of these ideas were accepted by the Catholic Church at the time, they later became widely accepted by society. Galileo was silenced by the Inquisition of the Church and placed on house arrest after a trial in which he was forced to retract his original statements supporting the Heliocentric Theory. Copernicus never even published his own works. They were actually published on his behalf after his death due to his fear of persecution and excommunication from the Catholic Church.
Thus, alchemy and astrology saw the influence of science in creating predictable and reliable knowledge of the universe. However, the Church continued to emphasize that the cosmos was governed by spiritual forces.
🎥 Watch: AP Euro - Scientific Revolution
<< Hide Menu
Jillian Holbrook
Jillian Holbrook
New Ideas and Methods
Individualism and a belief in logic among humans inspired intellectuals of the time to read and study Classical writings. 💭 Many found discrepancies and flaws in these ancient Greek and Roman texts and began experimenting with their own observations and tests to prove or disprove the writings.
The Scientific Method
In 1621, a lawyer and philosopher, Francis Bacon, published the scientific method. It was a formal series of steps in which one could form a hypothesis, test the hypothesis, and develop a conclusion based on that test. Then, one could take that conclusion, if insufficient, and retest using different methods or criteria.
Bacon believed in the Empirical Theory- that all knowledge is derived from observation and sense-based information. He also believed that information should be tested through this method, and once tested, conclusions should be made. This style of reasoning is called inductive reasoning- where limited evidence is needed to prove something true, and generalizations are made based on observations.

Example: I see a bird outside, and it is white. Therefore, all birds I see are white.
In 1637, mathematician and philosopher Rene Descartes published his method of reasoning, also using the scientific method. However, Descartes believed in deductive reasoning, in which information is collected, patterns are recognized, and then the scientific method is used. Deductive reasoning is more accurate than inductive reasoning.
Example: I study birds of different kinds from different locations and notice many different colors. I note that brightly colored birds tend to hail from tropical areas, white birds mainly live close to oceans, and black-feathered birds remain inland. While not all patterns are true for each bird, it is much more specific than the generalizations proposed by inductive reasoning. 🐦
Anatomy and Medicine
The previously accepted humoral theory of disease proposed that there were four main liquids in the body that required balance: blood, phlegm, yellow bile, and black bile. Common belief saw pain as a result of these fluids being out of balance, contaminated, or not mixed properly.
During the Scientific Revolution, scientists began studying the human anatomy, bodily systems, and medicine to better understand how to combat illnesses, which challenged the classical ideas proposed by Galen, a Greek physician.
William Harvey 🫀
The most important discovery of this time regarding human anatomy and medicine was William Harvey’s discovery of blood circulation. Harvey employed extensive observations and experiments, and his work provided a new understanding of the circulatory system as a whole, which was widely accepted and adopted by the medical community. After Harvey disproved the formerly accepted humoral theory and proposed an integrated human body, other scientists began to study the functions of the human body during the development of physiology, which revolutionized how people understood anatomy and disease.

Image Courtesy of Western Civilization II Guides
New Technology and Medical Practices 🔬
The development of the microscope and the discovery of microorganisms also played a significant role in challenging traditional beliefs about the causes of disease. Scientists could now observe small organisms, such as bacteria and viruses. Additionally, the scientific revolution also saw the rise of new medical practices such as surgery and the use of anatomy and physiology in diagnosis and treatment.
Astronomy and Alchemy
Developments in Astronomy 🪐
Nicholas Copernicus developed the Heliocentric Theory in opposition to the Geocentric Theory. Copernicus shared his theory that all planets in our solar system revolve around the sun with other scientists. However, the Catholic Church’s doctrine stated that Ptolemy’s 2nd-century Geocentric Theory, in which all planets revolve around Earth, was the accepted belief, and no one had challenged it with any authenticity before Copernicus.

Image Courtesy of Little Thinkers Blog
- The Heliocentric Theory: The most significant contribution to astronomy during the scientific revolution was the development of the heliocentric model of the solar system by Copernicus, which proposed that the sun, not the earth, was at the center of the solar system. This challenged the traditional geocentric model, which placed the earth at the center of the universe.
- Kepler's laws of planetary motion: Johannes Kepler formulated three laws of planetary motion, which accurately described the motion of planets around the sun. This was a major advancement in astronomy, as it helped explain the observed motion of planets.
- Galileo's telescope: Galileo Galilei's development and use of the telescope to observe the night sky led to several important discoveries, including the observation of mountains on the moon, the phases of Venus, and the presence of four large moons orbiting Jupiter. By tracking planetary motion, Galileo found that Earth did move within the solar system, supporting Copernicus' proposals of heliocentricism.
- Discovery of new astronomical objects: The scientific revolution saw the discovery of new astronomical objects, such as comets, nebulae, and galaxies, which expanded the understanding of the universe.
- Improved astronomical instruments: The invention of more advanced astronomical instruments, such as the sextant and the quadrant, improved the accuracy of astronomical measurements and allowed for more detailed observations of the sky.
- The introduction of mathematical methods: Introduction of mathematical methods to the field of astronomy improved the accuracy of astronomical predictions. Isaac Newton, through the use of mathematics, developed the Three Laws of Motion, which proved that Earth revolves around the sun. While none of these ideas were accepted by the Catholic Church at the time, they later became widely accepted by society. Galileo was silenced by the Inquisition of the Church and placed on house arrest after a trial in which he was forced to retract his original statements supporting the Heliocentric Theory. Copernicus never even published his own works. They were actually published on his behalf after his death due to his fear of persecution and excommunication from the Catholic Church.
Thus, alchemy and astrology saw the influence of science in creating predictable and reliable knowledge of the universe. However, the Church continued to emphasize that the cosmos was governed by spiritual forces.
🎥 Watch: AP Euro - Scientific Revolution

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.