Browse By Unit
Isabela Padilha
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha
Christine Lin
Economic Effects of European Colonialism
Many European countries established colonies and commercial networks which led to a global exchange of goods of animals🐷, plants🥬, diseases🦠, slaves and cultural practices💭. This is called the Columbian Exchange. The expansion of this exchange expanded West Atlantic European powers and their economic opportunities.
Mercantilism, the economic theory that rejects free trade and promotes government regulations of the economy for the purpose of enhancing state power, came about due to the Columbian Exchange. The introduction of horses🐎 and sugar to the New World and tobacco🚬, chocolate🍫, and potatoes🥔 to the Old World also had economic effects.
European nations saw their economies expand drastically, as their access to different fauna, floras and other types of resources placed them in a place of dominance 👑 in the world. The dynamics of the Columbian exchange also contributed to the expansion of the slave trade, in addition to opening the world market. The purchase of goods and animals from the "New world" was also a symbol of wealth to many European elites that perceived these goods as exotic and a symbol of their power. Europeans were also able to integrate these products into their culture. For example, the introduction of potatoes to Europe, a crop that had been consumed for years before in South America, was revolutionary as they grew easily in any region and access to them helped in period of war and hunger.
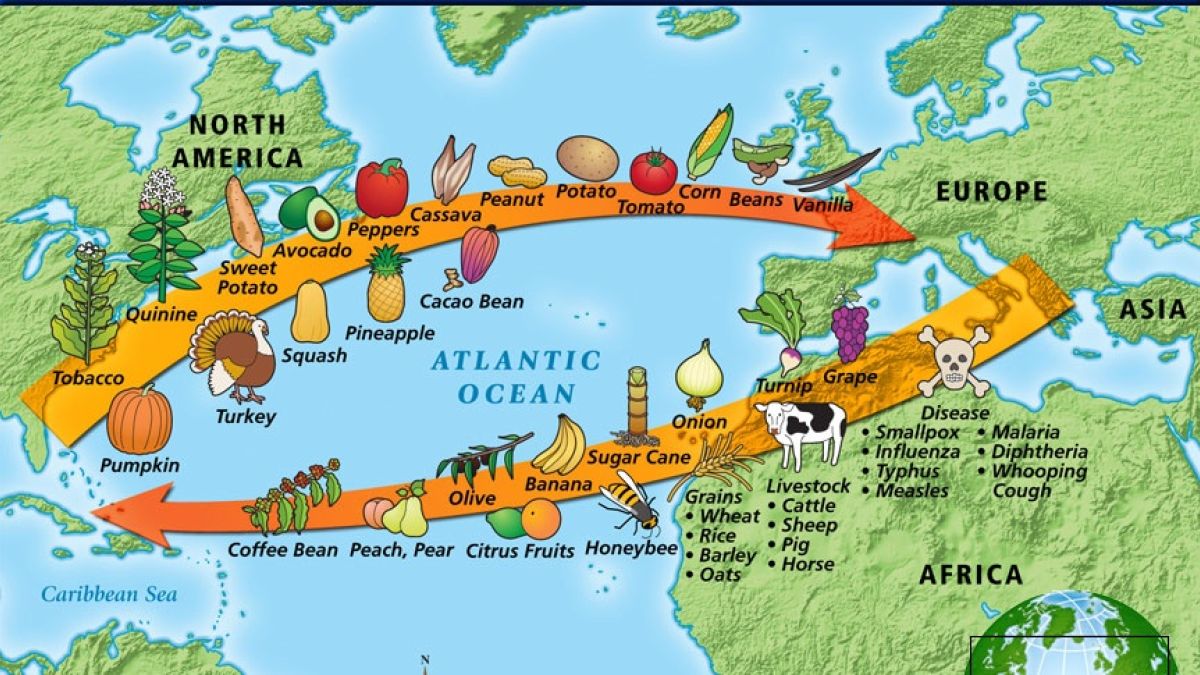
Image Courtesy of The Irish Times
The ports became an important piece of exchange, and major port cities became relevant economically and politically across the world. Some important Atlantic port cities included London, Bristol, Amsterdam and Antwerp.
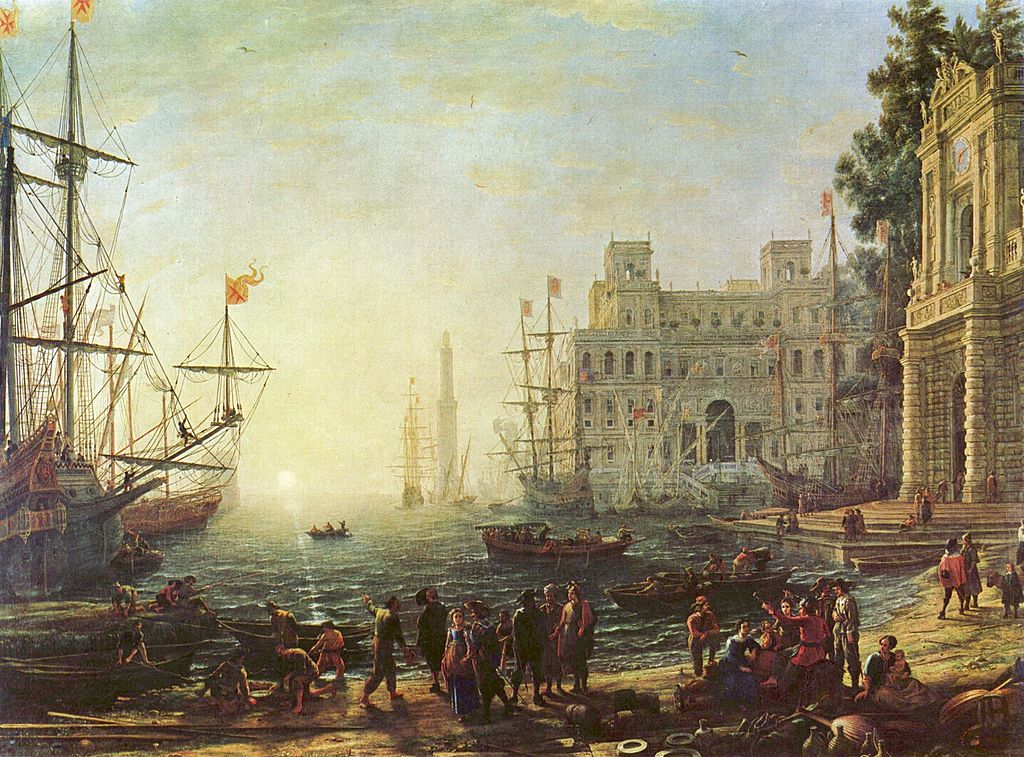
Social and Cultural Effects
European expansions prompted the Columbian Exchange and food, new diseases, and new cultural practices changed the lives of indigenous civilization. The exchange of diseases was one of the most detrimental to the natives in North and South America. Smallpox, mumps, chickenpox and measles were diseases brought over by European explorers and killed millions of natives. Europeans did get a disease from the natives as well: the sexual transmitted disease of syphilis.
Europe's dominating presence caused many destructions on the indigenous civilizations as indigenous groups were forced into labor for the European plantation. There was also a heavy religious push by the Europeans that forced indigenous groups to abandon original practices and traditions.
One more major effect of these diseases killing the Native Americans was their decrease in population which ultimately meant the European's labor source for cash crops was gone. In the longer run, this led to the slave trade which brought large numbers of Africans to the Americas after a hard voyage.
🎥 Watch: AP European History - Exploration
<< Hide Menu
Isabela Padilha
Christine Lin
Isabela Padilha
Christine Lin
Economic Effects of European Colonialism
Many European countries established colonies and commercial networks which led to a global exchange of goods of animals🐷, plants🥬, diseases🦠, slaves and cultural practices💭. This is called the Columbian Exchange. The expansion of this exchange expanded West Atlantic European powers and their economic opportunities.
Mercantilism, the economic theory that rejects free trade and promotes government regulations of the economy for the purpose of enhancing state power, came about due to the Columbian Exchange. The introduction of horses🐎 and sugar to the New World and tobacco🚬, chocolate🍫, and potatoes🥔 to the Old World also had economic effects.
European nations saw their economies expand drastically, as their access to different fauna, floras and other types of resources placed them in a place of dominance 👑 in the world. The dynamics of the Columbian exchange also contributed to the expansion of the slave trade, in addition to opening the world market. The purchase of goods and animals from the "New world" was also a symbol of wealth to many European elites that perceived these goods as exotic and a symbol of their power. Europeans were also able to integrate these products into their culture. For example, the introduction of potatoes to Europe, a crop that had been consumed for years before in South America, was revolutionary as they grew easily in any region and access to them helped in period of war and hunger.

Image Courtesy of The Irish Times
The ports became an important piece of exchange, and major port cities became relevant economically and politically across the world. Some important Atlantic port cities included London, Bristol, Amsterdam and Antwerp.
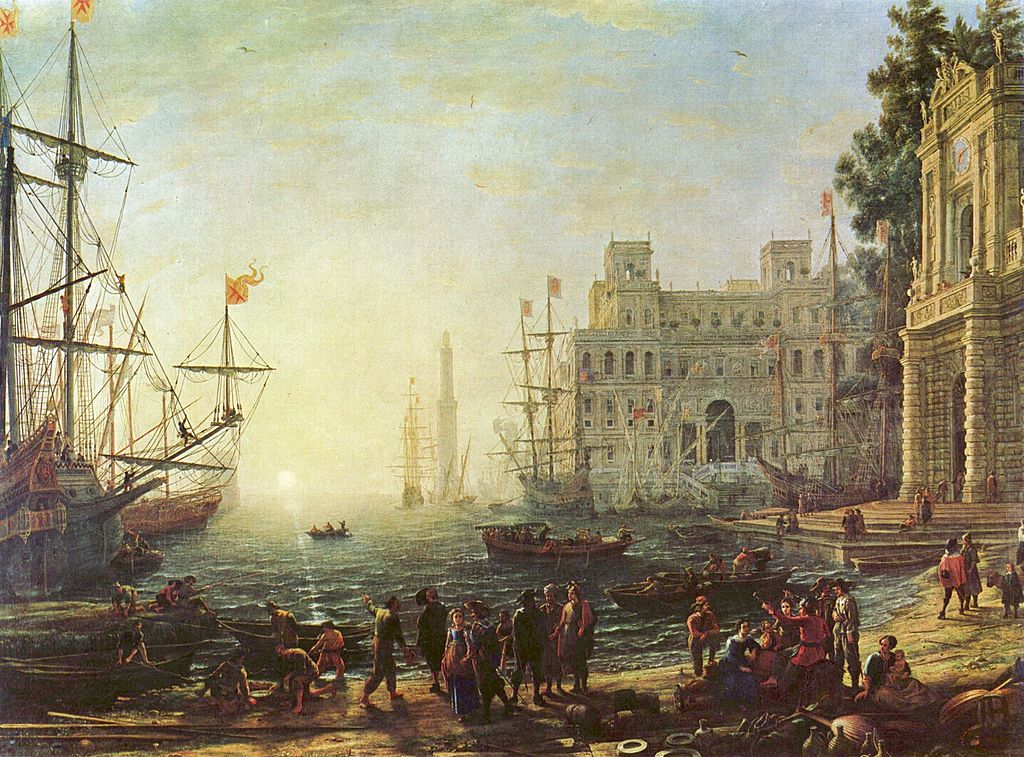
Social and Cultural Effects
European expansions prompted the Columbian Exchange and food, new diseases, and new cultural practices changed the lives of indigenous civilization. The exchange of diseases was one of the most detrimental to the natives in North and South America. Smallpox, mumps, chickenpox and measles were diseases brought over by European explorers and killed millions of natives. Europeans did get a disease from the natives as well: the sexual transmitted disease of syphilis.
Europe's dominating presence caused many destructions on the indigenous civilizations as indigenous groups were forced into labor for the European plantation. There was also a heavy religious push by the Europeans that forced indigenous groups to abandon original practices and traditions.
One more major effect of these diseases killing the Native Americans was their decrease in population which ultimately meant the European's labor source for cash crops was gone. In the longer run, this led to the slave trade which brought large numbers of Africans to the Americas after a hard voyage.
🎥 Watch: AP European History - Exploration

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.