3.5 Boolean Expressions
2 min read•june 18, 2024
Minna Chow
Milo Chang
Minna Chow
Milo Chang
Boolean Variables
Boolean variables can only represent the values true or false. Relational operators are used with Boolean values to test the relationship between two values.
Here are the relational operators you'll see on the test:
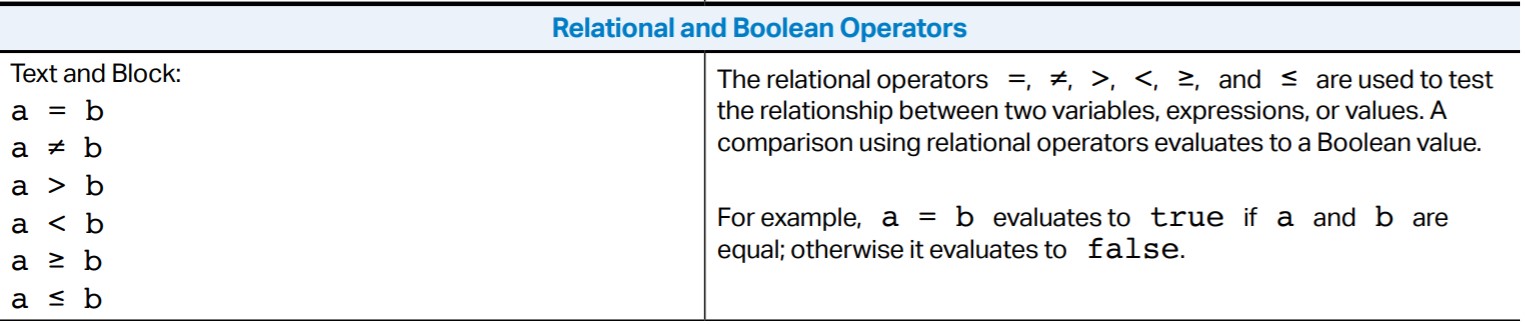
When you compare two values using a relational operator, the computer will return a Boolean value.
Take this Python example below:
y = 5
x = 55
print (x > y)
The computer will print the word "True" because 55 is greater than 5.
Not, And, Or
Boolean values are also used with logical operators known as NOT, AND and OR. These can be used to combine multiple conditions, whereas relational operators can only evaluate one condition.
Logical operators evaluate either Boolean expressions or a single Boolean value.
Not Operator
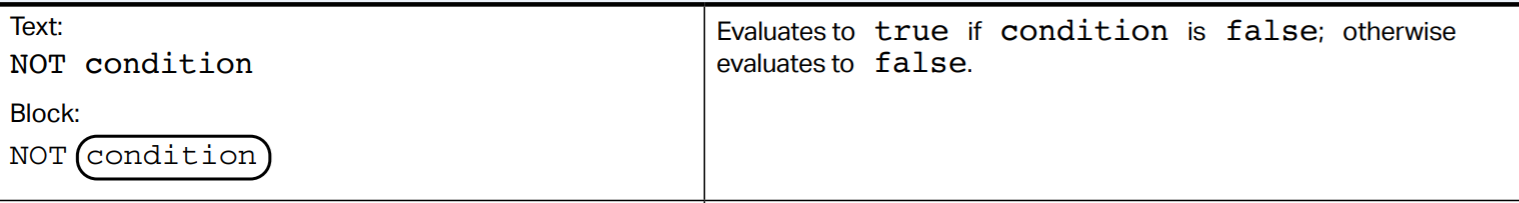
The NOT operator is used to reverse what the condition evaluates to. If a condition is true, the operator will evaluate to false, and vice versa.
y = 5
x = 55
print (not y >= 5)
In this case, the computer will print the word "False". y is equal to 5. This makes the condition *true—*it's the not operator that reverses this so the computer returns false.
Here's the NOT operator in Pseudocode:
And Operator
The AND operator is used to combine two conditions. The operator will only evaluate to true if both conditions are met.
y = 5
x = 55
print (y >= 5 and x <= 44)
The computer will print the word "False" because x is not less than or equal to 44, even though y equals 5.
Here's the AND operator in Pseudocode:

Or Operator
The OR operator also involves two conditions. In this case, the operator will evaluate to true if one condition or the other is met.
y = 5
x = 55
print (y >= 5 or x <= 44)
The computer will print the word "True" because, although the second condition isn't met, the first one is.
Here's the OR operator in Pseudocode:

Image source: College Board CED
<< Hide Menu
3.5 Boolean Expressions
2 min read•june 18, 2024
Minna Chow
Milo Chang
Minna Chow
Milo Chang
Boolean Variables
Boolean variables can only represent the values true or false. Relational operators are used with Boolean values to test the relationship between two values.
Here are the relational operators you'll see on the test:

When you compare two values using a relational operator, the computer will return a Boolean value.
Take this Python example below:
y = 5
x = 55
print (x > y)
The computer will print the word "True" because 55 is greater than 5.
Not, And, Or
Boolean values are also used with logical operators known as NOT, AND and OR. These can be used to combine multiple conditions, whereas relational operators can only evaluate one condition.
Logical operators evaluate either Boolean expressions or a single Boolean value.
Not Operator
The NOT operator is used to reverse what the condition evaluates to. If a condition is true, the operator will evaluate to false, and vice versa.
y = 5
x = 55
print (not y >= 5)
In this case, the computer will print the word "False". y is equal to 5. This makes the condition *true—*it's the not operator that reverses this so the computer returns false.
Here's the NOT operator in Pseudocode:

And Operator
The AND operator is used to combine two conditions. The operator will only evaluate to true if both conditions are met.
y = 5
x = 55
print (y >= 5 and x <= 44)
The computer will print the word "False" because x is not less than or equal to 44, even though y equals 5.
Here's the AND operator in Pseudocode:

Or Operator
The OR operator also involves two conditions. In this case, the operator will evaluate to true if one condition or the other is met.
y = 5
x = 55
print (y >= 5 or x <= 44)
The computer will print the word "True" because, although the second condition isn't met, the first one is.
Here's the OR operator in Pseudocode:

Image source: College Board CED

© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.