Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Skills you’ll gain in this topic:
- Explain how checkpoints regulate cell cycle progression and prevent errors.
- Describe how proteins like cyclins and CDKs control cell division.
- Relate cell cycle regulation to conditions like cancer.
- Analyze the consequences of disrupted cell cycle regulation.
- Predict the impact of cell cycle dysregulation on cell and tissue health.
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Mistakes in duplication can lead to mutations that can lead to cells being abnormal and develop into cancer. Because of this, cell cycle checkpoints are done.
At checkpoints, the progression of the cell cycle is halted until all parts are checked and conditions are correct to continue with duplication. Checkpoints are at the end of G1, at the G2 and M transition, and during metaphase.
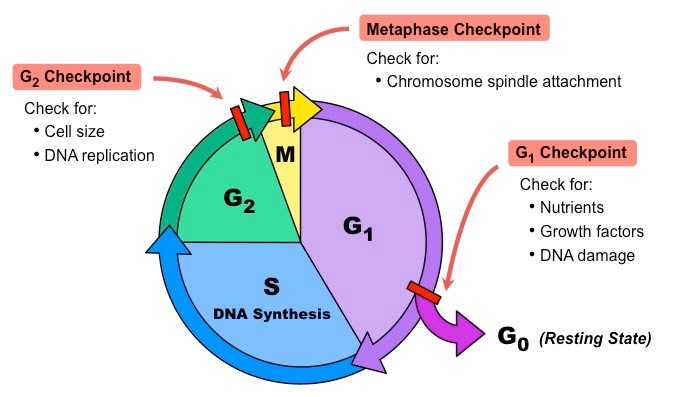
Image courtesy of BioNinja.
At G1, there is a cell growth checkpoint. This check occurs at the end of the G1 growth phase. During this checkpoint, it checks whether the cell is big enough and has the proper proteins and nutrients for the synthesis phase. If the cell is not big enough or not ready to go onto the next phase, they enter the G0 phase as you can see on the diagram. In G0, the cell is in a resting phase until it is ready to move on.
At the G2 checkpoint, there is a DNA synthesis checkpoint during the S phase. Here, there is a check to make sure that the DNA has been replicated correctly. If the DNA is replicated correctly, it moves on to the M (Mitosis) phase.
The final checkpoint is the metaphase checkpoint. This occurs in the (M) Mitosis phase and checks whether metaphase is complete. If it is complete, the cell divides and the process repeats.
Cdk-Cyclin Complex
The entire cell division process is regulated through the Cdk-Cyclin complex.
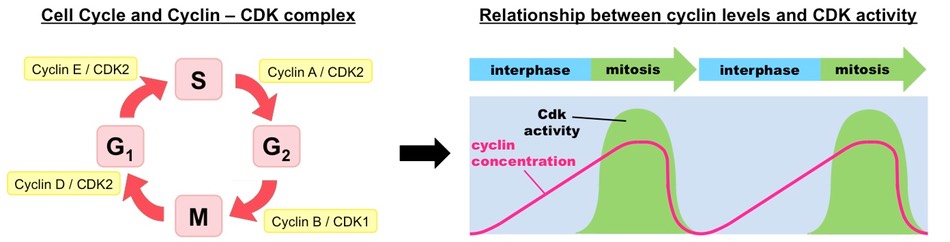
Image Courtesy of BioNinja
Cdk is always within the cytoplasm; it doesn't disappear. The number of cyclin goes up during interphase, and after the amount of cyclin reaches a certain threshold, mitosis is triggered. This leads to the degradation of cyclin, and Cdk is dephosphorylated. The number of cyclin is a great mechanism the cell uses to regulated mitosis activity.
Genes and Proteins
There are genes and proteins that can also regulate mitosis. The best example of a protein is p53. p53 was actually named the molecule of the year (1992) for its contribution to cancer research. p53 is essentially the toolbox of the cell.
Any segment of DNA can be damaged by heat, radiation or chemicals. p53 will notice this damage and stop cell division. It then triggers enzymes that will repair the damaged region. If the DNA is properly repaired, p53 will allow for the DNA replication and cell division to continue. However, if p53 determines that the damage is beyond repair, it will trigger apoptosis, or cell programmed death. When your skin peels off, it's because of apoptosis, so you're actually witnessing p53 at work!
Because p53 is so important, it can cause problems when it is malfunctioning. DNA damage will not be detected by a malfunctioning p53, and it will fail to stop cell division or repair DNA. Instead, the cell will continue to divide with damaged DNA. If this damage accumulates, the cell can turn cancerous.
There are about 6 key genes that also regulate the division process. If there are mutations in these 6 genes, cancer is likely to develop. Keep in mind, these genes don't cause cancer. When turned on and off correctly, cancer does not develop. It's when these genes stay on or off that causes the issue.
- Growth Promoter Genes ON = unlimited growth
- Tumor Suppressor Gene (p53) OFF = ignore checkpoint stop signs
- Apoptosis Genes OFF = cell doesn't go through apoptosis
- Chromosome Maintenance Genes (telomerase) ON = unlimited divisions
- Touch-Sensor Gene OFF = overcome density dependence
Cancerous Cells
However, disruptions in the cell cycle can lead to cancerous cells. Cancerous cells are cells that are unregulated and divide uncontrollably. Cancerous cells have the ability to migrate or metastasize to other regions of the body that they didn’t originate in.
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is programmed cell death. Apoptosis is a normal and controlled process within multicellular organisms. It is very important because it maintains the balance of cells within an organism. Apoptosis happens when the lysosome bursts, causing the cell to burst and die from the acid.
For example, apoptosis can occur during the development of new cells. If these cells are not divided correctly, they could lead to cancer or a virus. Without apoptosis, these harmful cells could continue dividing and multiplying which could cause an adverse effect on the organism. Apoptosis is very important because if damaged or mutated cells do not get the signal to go through apoptosis, cancer can form.

Image courtesy of Giphy.
<< Hide Menu
Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Haseung Jun
Annika Tekumulla
Skills you’ll gain in this topic:
- Explain how checkpoints regulate cell cycle progression and prevent errors.
- Describe how proteins like cyclins and CDKs control cell division.
- Relate cell cycle regulation to conditions like cancer.
- Analyze the consequences of disrupted cell cycle regulation.
- Predict the impact of cell cycle dysregulation on cell and tissue health.
Cell Cycle Checkpoints
Mistakes in duplication can lead to mutations that can lead to cells being abnormal and develop into cancer. Because of this, cell cycle checkpoints are done.
At checkpoints, the progression of the cell cycle is halted until all parts are checked and conditions are correct to continue with duplication. Checkpoints are at the end of G1, at the G2 and M transition, and during metaphase.

Image courtesy of BioNinja.
At G1, there is a cell growth checkpoint. This check occurs at the end of the G1 growth phase. During this checkpoint, it checks whether the cell is big enough and has the proper proteins and nutrients for the synthesis phase. If the cell is not big enough or not ready to go onto the next phase, they enter the G0 phase as you can see on the diagram. In G0, the cell is in a resting phase until it is ready to move on.
At the G2 checkpoint, there is a DNA synthesis checkpoint during the S phase. Here, there is a check to make sure that the DNA has been replicated correctly. If the DNA is replicated correctly, it moves on to the M (Mitosis) phase.
The final checkpoint is the metaphase checkpoint. This occurs in the (M) Mitosis phase and checks whether metaphase is complete. If it is complete, the cell divides and the process repeats.
Cdk-Cyclin Complex
The entire cell division process is regulated through the Cdk-Cyclin complex.

Image Courtesy of BioNinja
Cdk is always within the cytoplasm; it doesn't disappear. The number of cyclin goes up during interphase, and after the amount of cyclin reaches a certain threshold, mitosis is triggered. This leads to the degradation of cyclin, and Cdk is dephosphorylated. The number of cyclin is a great mechanism the cell uses to regulated mitosis activity.
Genes and Proteins
There are genes and proteins that can also regulate mitosis. The best example of a protein is p53. p53 was actually named the molecule of the year (1992) for its contribution to cancer research. p53 is essentially the toolbox of the cell.
Any segment of DNA can be damaged by heat, radiation or chemicals. p53 will notice this damage and stop cell division. It then triggers enzymes that will repair the damaged region. If the DNA is properly repaired, p53 will allow for the DNA replication and cell division to continue. However, if p53 determines that the damage is beyond repair, it will trigger apoptosis, or cell programmed death. When your skin peels off, it's because of apoptosis, so you're actually witnessing p53 at work!
Because p53 is so important, it can cause problems when it is malfunctioning. DNA damage will not be detected by a malfunctioning p53, and it will fail to stop cell division or repair DNA. Instead, the cell will continue to divide with damaged DNA. If this damage accumulates, the cell can turn cancerous.
There are about 6 key genes that also regulate the division process. If there are mutations in these 6 genes, cancer is likely to develop. Keep in mind, these genes don't cause cancer. When turned on and off correctly, cancer does not develop. It's when these genes stay on or off that causes the issue.
- Growth Promoter Genes ON = unlimited growth
- Tumor Suppressor Gene (p53) OFF = ignore checkpoint stop signs
- Apoptosis Genes OFF = cell doesn't go through apoptosis
- Chromosome Maintenance Genes (telomerase) ON = unlimited divisions
- Touch-Sensor Gene OFF = overcome density dependence
Cancerous Cells
However, disruptions in the cell cycle can lead to cancerous cells. Cancerous cells are cells that are unregulated and divide uncontrollably. Cancerous cells have the ability to migrate or metastasize to other regions of the body that they didn’t originate in.
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is programmed cell death. Apoptosis is a normal and controlled process within multicellular organisms. It is very important because it maintains the balance of cells within an organism. Apoptosis happens when the lysosome bursts, causing the cell to burst and die from the acid.
For example, apoptosis can occur during the development of new cells. If these cells are not divided correctly, they could lead to cancer or a virus. Without apoptosis, these harmful cells could continue dividing and multiplying which could cause an adverse effect on the organism. Apoptosis is very important because if damaged or mutated cells do not get the signal to go through apoptosis, cancer can form.

Image courtesy of Giphy.

© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.