Biology Long Essay Free Response Questions
9 min read•june 18, 2024
Jessica Nadzam
Jessica Nadzam
Overview of the Long Essay (FRQ) Questions
The AP Biology exam used to consist of eight long-form free response questions, but in 2019 it was redesigned to consist of only six free response questions. Two of those questions are in the “long” form, and these consist of 50% of the free response score, or 25% of your total score.
Long story short, those two questions make a biiiiiiiiig impact on your score!
The long essay questions will always be the first two on your exam, so you’ll see them as soon as you open the test booklet. You have to write in blue or black ink (for all things that are good, please do not use a pencil), so have a few of your favorite pens ready. You’ll have lots of pages to write on (if you use all of them, you may have written too much), and you’ll be given a copy of the Formulas and Equations sheet for any calculations you need to do.
Questions are between 8-10 points apiece, and they typically contain content and problems concerning multiple content areas. You could initially respond about protein structure in the first part and then end up describing the evidence of evolution by the end of the question. There’s a lot of points on the table, and CollegeBoard will make you work for them.
There is one guarantee on the long essay portion, and that is that one of these questions will ask you to graph something, but IMHO, this is the easiest part. Graphs are usually just that - graphs! And they’re worth three whole points just for plotting some information from a table - woohoo! I always tell my students to go straight to the graph and complete it, if possible. Just remember that when you complete that graph, you must:
- Scale your graph appropriately
- Label the axes and use proper units (if you don’t list your units, this point won’t count)
- Plot the actual data Pretty simple, right?
Response Grading (from a former AP Reader)
There are almost twenty points in this section, and they make up 25% of your AP Biology score. So, how are those points calculated and scored? CollegeBoard is fantastic at writing rigorous questions, but they’re also very good at training their graders (called AP Readers) how to objectively score the questions. Readers spend a whole day training to grade just ten points worth of questions, and then spend a whole week grading only those questions, eight hours a day.
A well-oiled machine may be an understatement. The bottom of the line is, AP Readers know exactly what they’re looking for when they’re grading. They read a hundred tests a day (minimum), and if you don’t have the answer they’ve been told is the right answer, they tend to move on pretty quickly.
While this seems intimidating, it’s actually good news for you - but only if you pay very close attention to the next section on verbage. You see, the bolded verbs in AP free response questions are just hints as to what AP Readers are looking for in an answer. If you know those verbs backwards and forwards, you will know what type of response AP Readers want. And if you know that, you don’t have to worry about writing something that may be right content-wise, but still missing a point on a technicality.
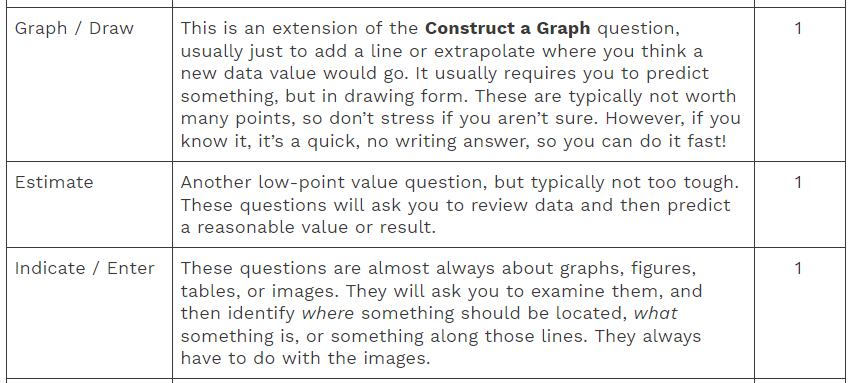
Essential Verbiage
There are a lot of verbs used in AP exams to pose questions for students to ponder and rip their hair out over.
To keep all that hair on your head, we’ve made you a table. It’s pretty easy - if you know exactly what to do when you encounter each bolded verb, you know exactly what to do to answer the question the way the Reader wants to see it. You know how many points it's worth, and therefore can figure out how much time to spend on it.
Side note - keep in mind that if a question asks you do something more than once - maybe to describe two factors or explain three phenomenon, you should multiple that # Points by however many things it expects you to do.





Strategies for 5able Responses
Do you want a 5 on this test? Then here’s what you need to know and be able to do:
- Read. The. Question. Care. Fully. Seriously. You don’t know how many students miss points because they were skimming and missed a critical word. It’s a heartbreaker for Readers, who want to give you that point, but can’t. Also, read the directions carefully. Your papers always say something about how responses on the actual question page will not be scored. Do not write on the question page. You can for brainstorming or outlining as scratch paper, but if your words aren’t written on lined paper or a graph or table, they won’t be scored. So make sure you put your answers in the right place!
- Complete. Sentences. Unless it’s an identify or construct or calculate question, you need a capital letter and a period, or the Reader will not grade that response. Period. Outlines, bulleted lists, and drawings won’t be graded unless specified in the question’s directions.
- Circle your bolded verbs. Find them. Figure out which are worth the most points, the least points, will take the longest, will be the quickest, etc. Then, figure out which ones to answer first.
- When you start the test, you don’t have to go in order. If your mind goes blank on question one, skip it. It’s not going anywhere, you can come back to it. But don’t waste time on it when there are others you can definitely answer later in the booklet.
- Skip around to answer these types of questions first, as they are worth the most points and/or are the quickest to answer: Construct a graph, Design an experiment, Identify, Graph/draw. Most other question types take longer just to read the question and write out the full answer, so these are the quickest and most bang-for-your-buck question types.
- Time yourself. You get 90 minutes, but it goes by fast. Keep a digital watch that does not beep, and refer to it regularly. Plot how long you want to spend on each question so you don’t waste time in one area and lose points on another question you could have easily answered.
- This is not AP English. The graders are not English teachers. They don’t care how pretty your introduction is or how thought-provoking your thesis statement is, so don’t write these. Skip the fluff and go straight to the point. Don’t restate the question or introduce the topic or regurgitate random knowledge - it won’t get you extra points, it’s a waste of time for you, and the Readers get bored sorting through all your thoughts and writing.
- Label your responses. While you still have to write in complete sentences, please label each response with a, b, c, etc. if the essay question has multiple parts. You don’t even have to go in order, but this helps Readers find your answer so they don’t have to sift and guess what you meant.
- COMMIT TO YOUR ANSWER. Readers don’t like wishy-washy papers. Erase the words “might” and “possible” and “I think” from your vocabulary. You could be completely wrong, but if you’re writing about a purple hippopotamus, COMMIT to that purple hippopotamus. Don’t say “I think the purple hippopotamus might possibly maybe do photosynthesis if it feels like it.” That’s wishy washy, and Readers don’t accept that as an actual answer, so they won’t give points for it. Be committed, and loudly proclaim “This purple hippopotamus does photosynthesis!” Ta-da!
- If possible, always give an example. We said earlier not to mind dump and regurgitate, but examples are usually a good way to sweep up an extra point or two if you have budgeted your time wisely and can accurately apply it to the scenario. Examples should be a demonstration of the phenomenon you’re describing.
For exampleif you’re asked to describe the differences between natural and artificial selection, a good example of artificial selection would be to discuss the development of different dog breeds for different traits and features. Now that’s we’ve passed on the knowledge, let’s take it out for a test drive. Below you will find a sample question with tips to apply to maximize your time and points for that Fiveable 5 score!
Sample Question
Soybeans, or Glycine max, are grown and harvested in the American delta. They are a popular crop and are used in a variety of foodstuffs including soy milks, tofu, and other added ingredients. As a high protein bean, they are very popular and fast to grow, with only sixty days from planting to harvest. However, they are very sensitive to their environments, and farmers frequently worry about frost destroying their crops. Also, they do not work alone. Soybeans rely on fungi in their roots (mycorhizzae) to exchange nutrients and fix nitrogen.
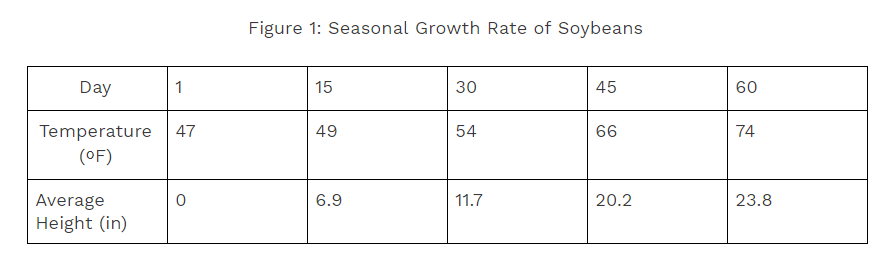
a) Construct a graph of soybean grown between days 1 and 60.
b) Draw and label a line for your prediction if the mycorhizzae were not present in soybean roots. Explain why this would occur.
c) The mycorhizzae in plant roots are responsible for fixing nitrogen that plants need. Identify the type of relationship that occurs between the plants and the mycorhizzae, and make a claim as to why it is beneficial or harmful.
d) Botanists recommend rotating soybean fields every three years or so. Typically, farmers will alternate soybeans and corn in different fields. Describe why this is done and how it benefits the plants and their environments.
Sample Question Answer Key
Phew. That’s a lot of words, a lot of scientific terminology, and a lot to answer in approximately twenty minutes - the maximum amount of time you should spend on one FRQ. Remember, you don’t have to answer questions in order and you can pick and choose parts to answer each time, but for the sake of this example, I’ll be moving from a-d.
Before we answer, let’s do some quick recon. It’s question one, so we know it’s a long FRQ. It’s got four parts, and six parts are bolded. We tally it up, and we find this question is worth 10 points. But we don’t panic, because we know how to tackle these AP verbs!
Part A is pretty simple, and I recommend doing it first. Draw and label the graph. I’ve linked my example below. Notice that I labeled my axes and made sure to include my units (1), and the scales on my graph are equidistant and accurate (1), and I plotted my points correctly (1). Ding ding ding, that’s three points right there!
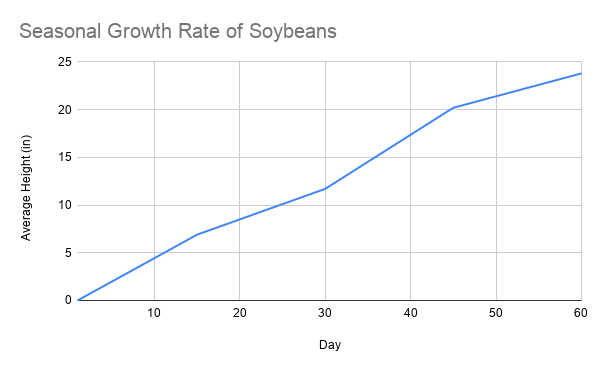
Moving on to Part B, we’re asked to draw a line. Okay, cool, we can do that. But where do we draw the line? Remember, this is only 1 point, so it’s okay to skip it for now if you aren’t sure. Definitely don’t waste your time wracking your brain if it baffles you. But, if you were to draw it, you’d have a flat line on the bottom of the X-axis. Why? Because mycorrhizae are essential for plant growth. Without them, the plant wouldn’t survive.
We’ve got 4 points total and two more parts to go, so there’s going to be a lot expected from these questions. Part C wants you to identify a relationship between a plant and a fungus - that’s Ecology 101 again, and the answer is “mutualism.” Remember, since this is an identify question, we don’t need complete sentences, just the one word answer to get our 1 point. Yay, time saved! For the make a claim portion, explain this relationship. Why is it good or bad? Well, it’s mutualism, which means both parties benefit. For this one, you do need complete sentences, but since it’s just 1 point, one complete sentence defining mutualism should suffice. Finally, we get to the finale - Part D. The Describe question. Students typically love or hate these, because they leave a bit of wiggle room in the answer, but they also take a lot of time. Since this one is worth 2 points, we want to take the time to answer it correctly. Why do farmers rotate their crops? The key part to a describe question is identifying the phenomenon or concept, and then explaining it or illustrating it with an example. So in this case, we want to identify that crops are rotated to keep nutrients from being overused, and then provide substance to that answer by saying what nutrients are needed for, how they rebuild over time, etc.
<< Hide Menu
Biology Long Essay Free Response Questions
9 min read•june 18, 2024
Jessica Nadzam
Jessica Nadzam
Overview of the Long Essay (FRQ) Questions
The AP Biology exam used to consist of eight long-form free response questions, but in 2019 it was redesigned to consist of only six free response questions. Two of those questions are in the “long” form, and these consist of 50% of the free response score, or 25% of your total score.
Long story short, those two questions make a biiiiiiiiig impact on your score!
The long essay questions will always be the first two on your exam, so you’ll see them as soon as you open the test booklet. You have to write in blue or black ink (for all things that are good, please do not use a pencil), so have a few of your favorite pens ready. You’ll have lots of pages to write on (if you use all of them, you may have written too much), and you’ll be given a copy of the Formulas and Equations sheet for any calculations you need to do.
Questions are between 8-10 points apiece, and they typically contain content and problems concerning multiple content areas. You could initially respond about protein structure in the first part and then end up describing the evidence of evolution by the end of the question. There’s a lot of points on the table, and CollegeBoard will make you work for them.
There is one guarantee on the long essay portion, and that is that one of these questions will ask you to graph something, but IMHO, this is the easiest part. Graphs are usually just that - graphs! And they’re worth three whole points just for plotting some information from a table - woohoo! I always tell my students to go straight to the graph and complete it, if possible. Just remember that when you complete that graph, you must:
- Scale your graph appropriately
- Label the axes and use proper units (if you don’t list your units, this point won’t count)
- Plot the actual data Pretty simple, right?
Response Grading (from a former AP Reader)
There are almost twenty points in this section, and they make up 25% of your AP Biology score. So, how are those points calculated and scored? CollegeBoard is fantastic at writing rigorous questions, but they’re also very good at training their graders (called AP Readers) how to objectively score the questions. Readers spend a whole day training to grade just ten points worth of questions, and then spend a whole week grading only those questions, eight hours a day.
A well-oiled machine may be an understatement. The bottom of the line is, AP Readers know exactly what they’re looking for when they’re grading. They read a hundred tests a day (minimum), and if you don’t have the answer they’ve been told is the right answer, they tend to move on pretty quickly.
While this seems intimidating, it’s actually good news for you - but only if you pay very close attention to the next section on verbage. You see, the bolded verbs in AP free response questions are just hints as to what AP Readers are looking for in an answer. If you know those verbs backwards and forwards, you will know what type of response AP Readers want. And if you know that, you don’t have to worry about writing something that may be right content-wise, but still missing a point on a technicality.
Essential Verbiage
There are a lot of verbs used in AP exams to pose questions for students to ponder and rip their hair out over.
To keep all that hair on your head, we’ve made you a table. It’s pretty easy - if you know exactly what to do when you encounter each bolded verb, you know exactly what to do to answer the question the way the Reader wants to see it. You know how many points it's worth, and therefore can figure out how much time to spend on it.
Side note - keep in mind that if a question asks you do something more than once - maybe to describe two factors or explain three phenomenon, you should multiple that # Points by however many things it expects you to do.






Strategies for 5able Responses
Do you want a 5 on this test? Then here’s what you need to know and be able to do:
- Read. The. Question. Care. Fully. Seriously. You don’t know how many students miss points because they were skimming and missed a critical word. It’s a heartbreaker for Readers, who want to give you that point, but can’t. Also, read the directions carefully. Your papers always say something about how responses on the actual question page will not be scored. Do not write on the question page. You can for brainstorming or outlining as scratch paper, but if your words aren’t written on lined paper or a graph or table, they won’t be scored. So make sure you put your answers in the right place!
- Complete. Sentences. Unless it’s an identify or construct or calculate question, you need a capital letter and a period, or the Reader will not grade that response. Period. Outlines, bulleted lists, and drawings won’t be graded unless specified in the question’s directions.
- Circle your bolded verbs. Find them. Figure out which are worth the most points, the least points, will take the longest, will be the quickest, etc. Then, figure out which ones to answer first.
- When you start the test, you don’t have to go in order. If your mind goes blank on question one, skip it. It’s not going anywhere, you can come back to it. But don’t waste time on it when there are others you can definitely answer later in the booklet.
- Skip around to answer these types of questions first, as they are worth the most points and/or are the quickest to answer: Construct a graph, Design an experiment, Identify, Graph/draw. Most other question types take longer just to read the question and write out the full answer, so these are the quickest and most bang-for-your-buck question types.
- Time yourself. You get 90 minutes, but it goes by fast. Keep a digital watch that does not beep, and refer to it regularly. Plot how long you want to spend on each question so you don’t waste time in one area and lose points on another question you could have easily answered.
- This is not AP English. The graders are not English teachers. They don’t care how pretty your introduction is or how thought-provoking your thesis statement is, so don’t write these. Skip the fluff and go straight to the point. Don’t restate the question or introduce the topic or regurgitate random knowledge - it won’t get you extra points, it’s a waste of time for you, and the Readers get bored sorting through all your thoughts and writing.
- Label your responses. While you still have to write in complete sentences, please label each response with a, b, c, etc. if the essay question has multiple parts. You don’t even have to go in order, but this helps Readers find your answer so they don’t have to sift and guess what you meant.
- COMMIT TO YOUR ANSWER. Readers don’t like wishy-washy papers. Erase the words “might” and “possible” and “I think” from your vocabulary. You could be completely wrong, but if you’re writing about a purple hippopotamus, COMMIT to that purple hippopotamus. Don’t say “I think the purple hippopotamus might possibly maybe do photosynthesis if it feels like it.” That’s wishy washy, and Readers don’t accept that as an actual answer, so they won’t give points for it. Be committed, and loudly proclaim “This purple hippopotamus does photosynthesis!” Ta-da!
- If possible, always give an example. We said earlier not to mind dump and regurgitate, but examples are usually a good way to sweep up an extra point or two if you have budgeted your time wisely and can accurately apply it to the scenario. Examples should be a demonstration of the phenomenon you’re describing.
For exampleif you’re asked to describe the differences between natural and artificial selection, a good example of artificial selection would be to discuss the development of different dog breeds for different traits and features. Now that’s we’ve passed on the knowledge, let’s take it out for a test drive. Below you will find a sample question with tips to apply to maximize your time and points for that Fiveable 5 score!
Sample Question
Soybeans, or Glycine max, are grown and harvested in the American delta. They are a popular crop and are used in a variety of foodstuffs including soy milks, tofu, and other added ingredients. As a high protein bean, they are very popular and fast to grow, with only sixty days from planting to harvest. However, they are very sensitive to their environments, and farmers frequently worry about frost destroying their crops. Also, they do not work alone. Soybeans rely on fungi in their roots (mycorhizzae) to exchange nutrients and fix nitrogen.

a) Construct a graph of soybean grown between days 1 and 60.
b) Draw and label a line for your prediction if the mycorhizzae were not present in soybean roots. Explain why this would occur.
c) The mycorhizzae in plant roots are responsible for fixing nitrogen that plants need. Identify the type of relationship that occurs between the plants and the mycorhizzae, and make a claim as to why it is beneficial or harmful.
d) Botanists recommend rotating soybean fields every three years or so. Typically, farmers will alternate soybeans and corn in different fields. Describe why this is done and how it benefits the plants and their environments.
Sample Question Answer Key
Phew. That’s a lot of words, a lot of scientific terminology, and a lot to answer in approximately twenty minutes - the maximum amount of time you should spend on one FRQ. Remember, you don’t have to answer questions in order and you can pick and choose parts to answer each time, but for the sake of this example, I’ll be moving from a-d.
Before we answer, let’s do some quick recon. It’s question one, so we know it’s a long FRQ. It’s got four parts, and six parts are bolded. We tally it up, and we find this question is worth 10 points. But we don’t panic, because we know how to tackle these AP verbs!
Part A is pretty simple, and I recommend doing it first. Draw and label the graph. I’ve linked my example below. Notice that I labeled my axes and made sure to include my units (1), and the scales on my graph are equidistant and accurate (1), and I plotted my points correctly (1). Ding ding ding, that’s three points right there!

Moving on to Part B, we’re asked to draw a line. Okay, cool, we can do that. But where do we draw the line? Remember, this is only 1 point, so it’s okay to skip it for now if you aren’t sure. Definitely don’t waste your time wracking your brain if it baffles you. But, if you were to draw it, you’d have a flat line on the bottom of the X-axis. Why? Because mycorrhizae are essential for plant growth. Without them, the plant wouldn’t survive.
We’ve got 4 points total and two more parts to go, so there’s going to be a lot expected from these questions. Part C wants you to identify a relationship between a plant and a fungus - that’s Ecology 101 again, and the answer is “mutualism.” Remember, since this is an identify question, we don’t need complete sentences, just the one word answer to get our 1 point. Yay, time saved! For the make a claim portion, explain this relationship. Why is it good or bad? Well, it’s mutualism, which means both parties benefit. For this one, you do need complete sentences, but since it’s just 1 point, one complete sentence defining mutualism should suffice. Finally, we get to the finale - Part D. The Describe question. Students typically love or hate these, because they leave a bit of wiggle room in the answer, but they also take a lot of time. Since this one is worth 2 points, we want to take the time to answer it correctly. Why do farmers rotate their crops? The key part to a describe question is identifying the phenomenon or concept, and then explaining it or illustrating it with an example. So in this case, we want to identify that crops are rotated to keep nutrients from being overused, and then provide substance to that answer by saying what nutrients are needed for, how they rebuild over time, etc.

© 2025 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.